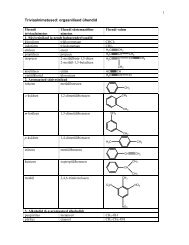
pKa values and gas-phase acidities of superacid molecul
pKa values and gas-phase acidities of superacid molecul
pKa values and gas-phase acidities of superacid molecul
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Important aspects for <strong>superacid</strong>s<br />
• Brønsted acidity<br />
• As strong as possible<br />
• "Clean" protonation desirable<br />
• Lewis acidity is usually not desirable<br />
• Stability under <strong>superacid</strong>ic conditions<br />
• Weak coordinating properties <strong>of</strong> the<br />
anions<br />
23<br />
Design <strong>of</strong> <strong>superacid</strong>ic <strong>molecul</strong>es<br />
• "Acid-based" approach:<br />
• Pick a parent acid<br />
• Introduce substituents<br />
• electronegative, strong electron<br />
acceptors, highly polarizable<br />
CN CN<br />
O O<br />
H<br />
NC P CN<br />
NC<br />
O CN ΔΔG acid =<br />
47 kcal/mol<br />
ΔG acid = 303 256 kcal/mol<br />
(DFT B3LYP/6-311+G**)<br />
O CF 3<br />
S O<br />
ON<br />
F 3 C<br />
S<br />
OH<br />
ON<br />
S O<br />
ΔΔG acid =<br />
O CF 3 40 kcal/mol<br />
ΔG acid = 299.5 260 kcal/mol<br />
(DFT B3LYP/6-311+G**)<br />
Leito et al J. Mol. Stru.<br />
Theochem, 2007, 815, 43<br />
Koppel, Yagupolskii et al<br />
to be submitted<br />
24<br />
12