Engine Maintenance and Modification Bradley Artigue
FIAT 124 Spider Engine Maintenance + Modification - Artigue.com
FIAT 124 Spider Engine Maintenance + Modification - Artigue.com
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
FIAT 124 Spider<br />
<strong>Engine</strong> <strong>Maintenance</strong> + <strong>Modification</strong><br />
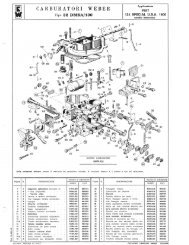
6. The Cylinder Head<br />
If you open your hood <strong>and</strong> look at the center of the engine you’ll see four spark plugs.<br />
The aluminum thing that your spark plugs are screwed into is the cylinder head. The<br />
cylinder head on a FIAT 124 Spider is of the semi-hemispherical, dual overhead cam<br />
(DOHC) type. It is called semi-hemispherical because the operation occurs along a 180<br />
degree arc. The two camshafts sit on either side of the spark plugs <strong>and</strong> rotate in time<br />
with the engine main crankshaft to draw in, burn, <strong>and</strong> expel fuel. A cylinder head has<br />
three major components:<br />
Camshafts are metal poles with lobes on them. The lobes press against valves<br />
that open <strong>and</strong> close, allowing gases into <strong>and</strong> out of the engine. Lobes are<br />
engineered into a specific pattern, resulting in the camshaft being the<br />
mechanical brain governing the Otto cycle.<br />
Valves cover ports between the intake <strong>and</strong> exhaust manifolds <strong>and</strong> the<br />
combustion chamber. Valves are held closed by a high tension double-spring<br />
assembly. The spring is held down by retainers installed in a donut-shaped cap.<br />
The entire assembly is capped off by a bucket. The camshaft strikes a shim on<br />
the top of the bucket, opening the valve. The shim is adjustable to maintain<br />
proper valve clearance.<br />
Spark plugs descend into the combustion chamber <strong>and</strong> create a spark that<br />
ignites the air/fuel mixture.<br />
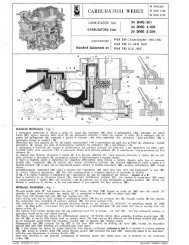
We start this section with the intake of fuel from the fuel system <strong>and</strong> finish with the<br />
expulsion of spent fuel into the exhaust system. Assume your engine is just starting the<br />
intake cycle – the camshaft has depressed the intake valve, drawing air <strong>and</strong> fuel into the<br />
combustion chamber (figure 41.1). As the camshaft rotates the valve closes. The piston<br />
is pushed upwards, compressing the mixture (figure 41.2). Ignition occurs (figure 41.3),<br />
exploding the mixture <strong>and</strong> forcing the piston down. Finally, the camshaft opens the<br />
exhaust valve <strong>and</strong> the piston is drawn up, expelling the burned mixture (figure 41.4).<br />
59