Glossary and scoring for BVAS 2003. GENERAL ... - Rare Disease
Glossary and scoring for BVAS 2003. GENERAL ... - Rare Disease
Glossary and scoring for BVAS 2003. GENERAL ... - Rare Disease
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
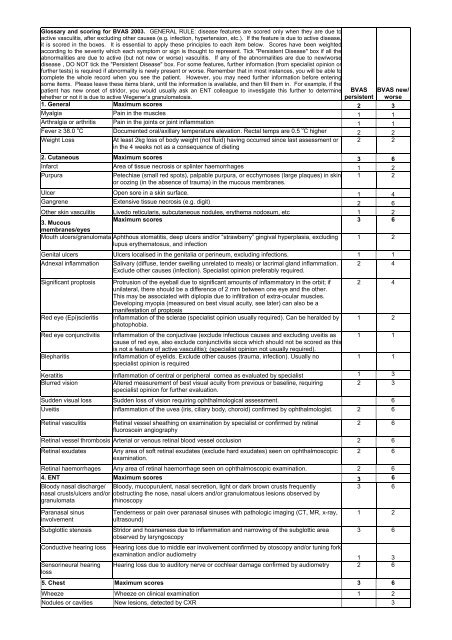
<strong>Glossary</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>scoring</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>BVAS</strong> <strong>2003.</strong> <strong>GENERAL</strong> RULE: disease features are scored only when they are due toactive vasculitis, after excluding other causes (e.g. infection, hypertension, etc.). If the feature is due to active disease,it is scored in the boxes. It is essential to apply these principles to each item below. Scores have been weightedaccording to the severity which each symptom or sign is thought to represent. Tick "Persistent <strong>Disease</strong>" box if all theabnormalities are due to active (but not new or worse) vasculitis. If any of the abnormalities are due to new/worsedisease , DO NOT tick the "Persistent <strong>Disease</strong>" box. For some features, further in<strong>for</strong>mation (from specialist opinion orfurther tests) is required if abnormality is newly present or worse. Remember that in most instances, you will be able tocomplete the whole record when you see the patient. However, you may need further in<strong>for</strong>mation be<strong>for</strong>e enteringsome items. Please leave these items blank, until the in<strong>for</strong>mation is available, <strong>and</strong> then fill them in. For example, if thepatient has new onset of stridor, you would usually ask an ENT colleague to investigate this further to determinewhether or not it is due to active Wegener’s granulomatosis.<strong>BVAS</strong>persistent<strong>BVAS</strong> new/worse1. General Maximum scores 2 3Myalgia Pain in the muscles 1 1Arthralgia or arthritis Pain in the joints or joint inflammation 1 1Fever ≥ 38.0 0 C Documented oral/axillary temperature elevation. Rectal temps are 0.5 0 C higher 2 2Weight LossAt least 2kg loss of body weight (not fluid) having occurred since last assessment or 2 2in the 4 weeks not as a consequence of dieting2. Cutaneous Maximum scores 3 6Infarct Area of tissue necrosis or splinter haemorrhages 1 2PurpuraPetechiae (small red spots), palpable purpura, or ecchymoses (large plaques) in skin 1 2or oozing (in the absence of trauma) in the mucous membranes.Ulcer Open sore in a skin surface. 1 4Gangrene Extensive tissue necrosis (e.g. digit) 2 6Other skin vasculitis Livedo reticularis, subcutaneous nodules, erythema nodosum, etc 1 23. MucousMaximum scores 3 6membranes/eyesMouth ulcers/granulomata Aphthous stomatitis, deep ulcers <strong>and</strong>/or “strawberry” gingival hyperplasia, excludinglupus erythematosus, <strong>and</strong> infection1 2Genital ulcers Ulcers localised in the genitalia or perineum, excluding infections. 1 1Adnexal inflammationSignificant proptosisRed eye (Epi)scleritisRed eye conjunctivitisBlepharitisSalivary (diffuse, tender swelling unrelated to meals) or lacrimal gl<strong>and</strong> inflammation.Exclude other causes (infection). Specialist opinion preferably required.Protrusion of the eyeball due to significant amounts of inflammatory in the orbit; ifunilateral, there should be a difference of 2 mm between one eye <strong>and</strong> the other.This may be associated with diplopia due to infiltration of extra-ocular muscles.Developing myopia (measured on best visual acuity, see later) can also be amanifestation of proptosisInflammation of the sclerae (specialist opinion usually required). Can be heralded byphotophobia.Inflammation of the conjuctivae (exclude infectious causes <strong>and</strong> excluding uveitis ascause of red eye, also exclude conjunctivitis sicca which should not be scored as thisis not a feature of active vasculitis); (specialist opinion not usually required).Inflammation of eyelids. Exclude other causes (trauma, infection). Usually nospecialist opinion is required2 42 41 21 11 1Keratitis Inflammation of central or peripheral cornea as evaluated by specialist 1 3Blurred visionAltered measurement of best visual acuity from previous or baseline, requiring2 3specialist opinion <strong>for</strong> further evaluation.Sudden visual loss Sudden loss of vision requiring ophthalmological assessment. 6Uveitis Inflammation of the uvea (iris, ciliary body, choroid) confirmed by ophthalmologist. 2 6Retinal vasculitisRetinal vessel sheathing on examination by specialist or confirmed by retinalfluoroscein angiography2 6Retinal vessel thrombosis Arterial or venous retinal blood vessel occlusion 2 6Retinal exudatesAny area of soft retinal exudates (exclude hard exudates) seen on ophthalmoscopicexamination.2 6Retinal haemorrhages Any area of retinal haemorrhage seen on ophthalmoscopic examination. 2 64. ENT Maximum scores 3 6Bloody nasal discharge/ Bloody, mucopurulent, nasal secretion, light or dark brown crusts frequentlynasal crusts/ulcers <strong>and</strong>/or obstructing the nose, nasal ulcers <strong>and</strong>/or granulomatous lesions observed bygranulomatarhinoscopyParanasal sinusinvolvementSubglottic stenosisConductive hearing lossSensorineural hearinglossTenderness or pain over paranasal sinuses with pathologic imaging (CT, MR, x-ray,ultrasound)Stridor <strong>and</strong> hoarseness due to inflammation <strong>and</strong> narrowing of the subglottic areaobserved by laryngoscopy3 61 23 6Hearing loss due to middle ear involvement confirmed by otoscopy <strong>and</strong>/or tuning <strong>for</strong>kexamination <strong>and</strong>/or audiometry1 3Hearing loss due to auditory nerve or cochlear damage confirmed by audiometry 2 65. Chest Maximum scores 3 6Wheeze Wheeze on clinical examination 1 2Nodules or cavities New lesions, detected by CXR 3
Pleural effusion/pleurisyPleural pain <strong>and</strong>/or friction rub on clinical assessment or new onset of radiologicallyconfirmed pleural effusion. Other causes (e.g. infection, malignancy) should beexcluded<strong>BVAS</strong> <strong>BVAS</strong> new/persistent worse2 4Infiltrate Detected by CXR or CT scan. Other causes (infection) should be excluded 2 4EndobronchialinvolvementMassivehaemoptysis/alveolarhaemorrhageEndobronchial pseudotumor or ulcerative lesions. Other causes such as infection ormalignancy should be excluded. NB: smooth stenotic lesions to be included in VDI;subglottic lesions to be recorded in the ENT section.Major pulmonary bleeding, with shifting pulmonary infiltrates; other causes ofbleeding should be excluded if possible2 44 6Respiratory failure Dyspnoea which is sufficiently severe as to require artificial ventilation 4 66. Cardiovascular Maximum scores 3 6Loss of pulsesLoss of pulses in any vessel detected clinically; this may include loss of pulses1 4leading to threatened loss of limbValvular heart diseaseSignificant valve abnormalities in the aortic mitral or pulmonary valves detectedclinically or echocardiographically.2 4Pericarditis Pericardial pain &/or friction rub on clinical assessment. 1 3Ischaemic cardiac pain Typical clinical history of cardiac pain leading to myocardial infarction or angina. 2 4Consider the possibility of more common causes (eg atherosclerosis)CardiomyopathySignificant impairment of cardiac function due to poor ventricular wall motionconfirmed on echocardiography3 6Congestive cardiac failure Heart failure by history or clinical examination 3 67. Abdominal Maximum scores 4 9PeritonismAcute abdominal pain with peritonism/peritonitis due to per<strong>for</strong>ation/infarction of smallbowel, appendix or gallbladder etc., or acute pancreatitis confirmed byradiology/surgery/elevated amylase3 9Bloody diarrhoea Of recent onset; inflammatory bowel disease <strong>and</strong> infectious causes excluded. 3 9Ischaemic abdominal pain Severe abdominal pain with typical features of ischaemia confirmed by imaging or atsurgery, with typical appearances of aneursyms or abnormal vasculaturecharacteristic of vasculitis.2 68. Renal Maximum scores 6 12Hypertension Diastolic BP>95, accelerated or not, with or without retinal changes. 1 4Proteinuria >1+ on urinalysis; >0.2g/24 hours Infection should be excluded. 2 410 or more RBC per hpf ( high power field ), excluding urinary infection <strong>and</strong> urinaryHaematurialithiasis (stone) 3 6Creatinine 125-249 Serum creatinine values 125-249 µmol/l at first assessment only. 2 4Creatinine 250-499 Serum creatinine values 250-499 µmol/l at first assessment only. 3 6Creatinine ≥ 500 Serum creatinine values 500 µmol/l or greater at first assessment only. 4 8Rise in creatinine > 30% Significant deterioration in renal function attributable to active vasculitis. 6or creatinine clearance fall> 25%9. Nervous system Maximum scores 6 9Headache New, unaccustomed & persistent headache 1 1MeningitisOrganic confusionSeizures (nothypertensive)Severe headache with neck stiffness ascribed to inflammatory meningitis afterexcluding infection/bleedingImpaired orientation, memory or other intellectual function in the absence ofmetabolic, psychiatric, pharmacological or toxic causes.Paroxysmal electrical discharges in the brain & producing characteristic physicalchanges including tonic & clonic movements & certain behavioural changes.1 31 33 9StrokeCord lesionCranial nerve palsySensory peripheralneuropathyCerebrovascular accident resulting in focal neurological signs such as paresis,weakness, etc. A stroke due to other causes (eg atherosclerosis) should beconsidered & appropriate neurological advice is recommendedTransverse myelitis with lower extremity weakness or sensory loss (usually with adetectable sensory level) with loss of sphincter control (rectal & urinary bladder).Facial nerve palsy, recurrent nerve palsy, oculomotor nerve palsy etc. excludingsensorineural hearing loss <strong>and</strong> ophthalmic symptoms due to inflammationSensory neuropathy resulting in glove &/or stocking distribution of sensory loss.Other causes should be excluded (e.g. idiopathic, metabolic, vitamin deficiencies,infectious, toxic, hereditary).3 93 93 63 6Motor mononeuritismultiplexSimultaneous neuritis of many peripheral nerves, only scored if motor involvement.Other causes should be excluded (diabetes, sarcoidosis, carcinoma, amyloidosis).10. OTHER Other feature of active vasculitis-please describe3 9