Organic Chemistry
Chirality
Chirality
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
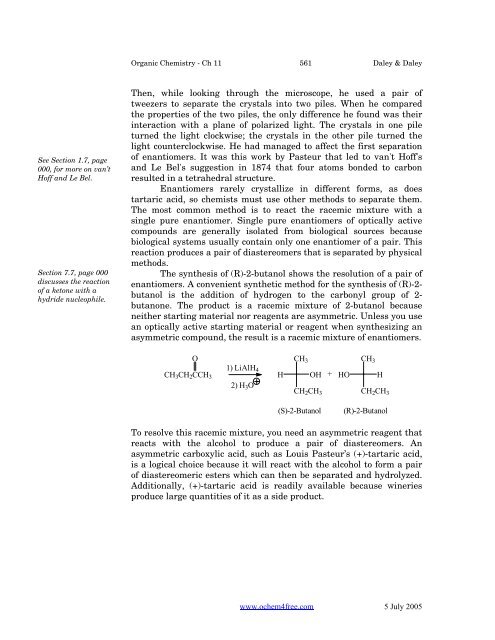
<strong>Organic</strong> <strong>Chemistry</strong> - Ch 11 561 Daley & DaleySee Section 1.7, page000, for more on van’tHoff and Le Bel.Section 7.7, page 000discusses the reactionof a ketone with ahydride nucleophile.Then, while looking through the microscope, he used a pair oftweezers to separate the crystals into two piles. When he comparedthe properties of the two piles, the only difference he found was theirinteraction with a plane of polarized light. The crystals in one pileturned the light clockwise; the crystals in the other pile turned thelight counterclockwise. He had managed to affect the first separationof enantiomers. It was this work by Pasteur that led to van't Hoff'sand Le Bel's suggestion in 1874 that four atoms bonded to carbonresulted in a tetrahedral structure.Enantiomers rarely crystallize in different forms, as doestartaric acid, so chemists must use other methods to separate them.The most common method is to react the racemic mixture with asingle pure enantiomer. Single pure enantiomers of optically activecompounds are generally isolated from biological sources becausebiological systems usually contain only one enantiomer of a pair. Thisreaction produces a pair of diastereomers that is separated by physicalmethods.The synthesis of (R)-2-butanol shows the resolution of a pair ofenantiomers. A convenient synthetic method for the synthesis of (R)-2-butanol is the addition of hydrogen to the carbonyl group of 2-butanone. The product is a racemic mixture of 2-butanol becauseneither starting material nor reagents are asymmetric. Unless you usean optically active starting material or reagent when synthesizing anasymmetric compound, the result is a racemic mixture of enantiomers.OCH 3 CH 2 CCH 3CH 31) LiAlH 4H OH2) H 3 OCH 2 CH 3+HOCH 3HCH 2 CH 3(S)-2-Butanol(R)-2-ButanolTo resolve this racemic mixture, you need an asymmetric reagent thatreacts with the alcohol to produce a pair of diastereomers. Anasymmetric carboxylic acid, such as Louis Pasteur’s (+)-tartaric acid,is a logical choice because it will react with the alcohol to form a pairof diastereomeric esters which can then be separated and hydrolyzed.Additionally, (+)-tartaric acid is readily available because wineriesproduce large quantities of it as a side product.www.ochem4free.com 5 July 2005