You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
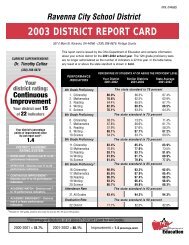
FIGURE <strong>26</strong>.7 Phylogenetic Tree of ReptilesThe diversific<strong>at</strong>ion of ancient reptiles eventually led to the evolution of modern animals.lizards, snakes,mammals turtles and tu<strong>at</strong>aras crocodiliansbirdsMillions ofyears agoCenozoicCretaceousichthyosaursplesiosaurspterosaursdinosaurs50100150Jurassic200TriassicPermianpelycosaurs250300Carboniferousanapsidsdiapsids350synapsidsreptilesAnalyze Are there any diapsid mammals? Explain your answer using the diagram.Dinosaurs were the second gre<strong>at</strong> radi<strong>at</strong>ion of the amniote family. Theyappeared 230 million years ago and were the dominant land vertebr<strong>at</strong>es forthe next 150 million years. Many kinds of dinosaurs evolved during th<strong>at</strong> time.Herbivorous species included huge sauropods, tanklike cer<strong>at</strong>opsians, andduck-billed dinosaurs. They were hunted by carnivorous theropod dinosaurs,which eventually gave rise to birds. All of the nonavian, or walking, dinosaurswent extinct 65 million years ago.Pterosaurs were the first vertebr<strong>at</strong>es to evolve powered flight. Their wingsconsisted of skin supported by an extremely elong<strong>at</strong>ed fourth finger. Theearliest species, from the end of the Triassic, were small animals with longtails. L<strong>at</strong>er species, such as Pteranodon lost their tails and grew as large as smallairplanes. Recent fossils show th<strong>at</strong> pterosaurs may have been covered withhair, suggesting th<strong>at</strong> they were endothermic. They went extinct <strong>at</strong> the endof the Cretaceous along with the dinosaurs.Apply How did the discovery of temporal skull holes help scientists determinephylogeny of amniotes?ConnectingCONCEPTSPhylogeny Recall from Chapter17 th<strong>at</strong> a phylogeny is a type ofevolutionary tree th<strong>at</strong> illustr<strong>at</strong>eshow different species are rel<strong>at</strong>edto each other. The rel<strong>at</strong>ionshipsbetween modern animals andancient reptiles help scientistsunderstand evolution.Chapter <strong>26</strong>: A <strong>Closer</strong> <strong>Look</strong> <strong>at</strong> <strong>Amniotes</strong> 795