Assistive Reproductive Technologies: A Literature Review and ...
Assistive Reproductive Technologies: A Literature Review and ...
Assistive Reproductive Technologies: A Literature Review and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
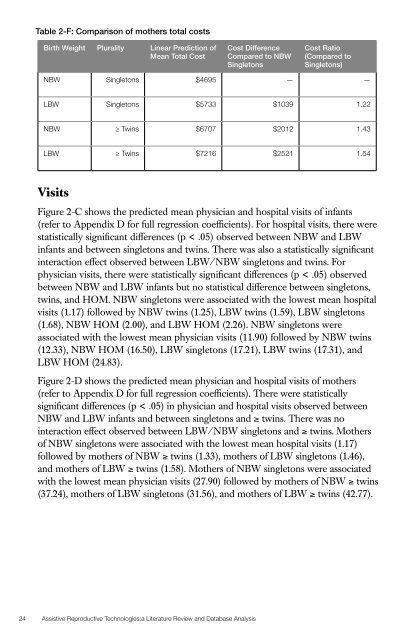
Table 2-F: Comparison of mothers total costsBirth Weight Plurality Linear Prediction ofMean Total CostCost DifferenceCompared to NBWSingletonsCost Ratio(Compared toSingletons)NBW Singletons $4695 — —LBW Singletons $5733 $1039 1.22NBW ≥ Twins $6707 $2012 1.43LBW ≥ Twins $7216 $2521 1.54VisitsFigure 2-C shows the predicted mean physician <strong>and</strong> hospital visits of infants(refer to Appendix D for full regression coefficients). For hospital visits, there werestatistically significant differences (p < .05) observed between NBW <strong>and</strong> LBWinfants <strong>and</strong> between singletons <strong>and</strong> twins. There was also a statistically significantinteraction effect observed between LBW/NBW singletons <strong>and</strong> twins. Forphysician visits, there were statistically significant differences (p < .05) observedbetween NBW <strong>and</strong> LBW infants but no statistical difference between singletons,twins, <strong>and</strong> HOM. NBW singletons were associated with the lowest mean hospitalvisits (1.17) followed by NBW twins (1.25), LBW twins (1.59), LBW singletons(1.68), NBW HOM (2.00), <strong>and</strong> LBW HOM (2.26). NBW singletons wereassociated with the lowest mean physician visits (11.90) followed by NBW twins(12.33), NBW HOM (16.50), LBW singletons (17.21), LBW twins (17.31), <strong>and</strong>LBW HOM (24.83).Figure 2-D shows the predicted mean physician <strong>and</strong> hospital visits of mothers(refer to Appendix D for full regression coefficients). There were statisticallysignificant differences (p < .05) in physician <strong>and</strong> hospital visits observed betweenNBW <strong>and</strong> LBW infants <strong>and</strong> between singletons <strong>and</strong> ≥ twins. There was nointeraction effect observed between LBW/NBW singletons <strong>and</strong> ≥ twins. Mothersof NBW singletons were associated with the lowest mean hospital visits (1.17)followed by mothers of NBW ≥ twins (1.33), mothers of LBW singletons (1.46),<strong>and</strong> mothers of LBW ≥ twins (1.58). Mothers of NBW singletons were associatedwith the lowest mean physician visits (27.90) followed by mothers of NBW ≥ twins(37.24), mothers of LBW singletons (31.56), <strong>and</strong> mothers of LBW ≥ twins (42.77).24 <strong>Assistive</strong> <strong>Reproductive</strong> <strong>Technologies</strong>:a <strong>Literature</strong> <strong>Review</strong> <strong>and</strong> Database Analysis