08a The Skeletal System.pdf - Haspi.org
08a The Skeletal System.pdf - Haspi.org
08a The Skeletal System.pdf - Haspi.org
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
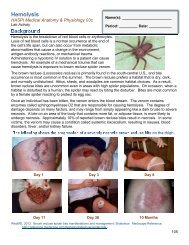
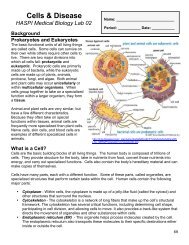
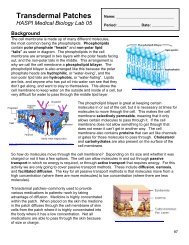
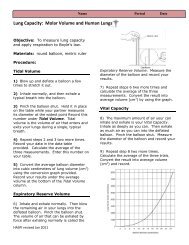
they become osteocytes. Osteocytes function tomaintain the bone matrix and calcium homeostasis.<strong>The</strong>y are unable to move from their assigned location orspace, which is called the lacunae. Osteoclasts are largecells that are capable of reabsorbing bone minerals,and therefore remodeling bone structure.Osteoclasts also remove minerals to thebloodstream for a variety of bodily functions, suchas muscle contraction.<strong>The</strong> bone matrix can be arranged into twoclassifications of bone; compact and trabecular bone.Compact bone, also known as dense or corticalbone, is extremely hard and compact with very littlespace. Bone mineral in compact bone is arrangedinto tight circles called osteons, with nerves and bloodvessels passing through the center. Compact boneaccounts for 80% of the total bone mass.Trabecular bone, also known as spongy or cancellous bone, is porous and more like a network thatallows nerves, blood vessels, and bone marrow to easily fill trabecular bone. Stress on trabecularbone causes it to create new and stronger networks, making it extremely adaptable. Althoughtrabecular bone only accounts for 20% of the total bone mass, it has a much greater surface areathan compact bone.Bone Types<strong>The</strong>re are five main types of bone based on their shape. <strong>The</strong>se include long bones, short bones,irregular bones, sesamoid bones, and flat bones. <strong>The</strong> following table provides examples of thesebone types.Bone TypeLongBonesShortBonesDescription and ExamplesBones which are longer than they are wide andmade up primarily of compact bone. Examplesinclude arm bones, leg bones, and phalanges.Cube-shaped with a thin layer of compact bone.Examples include wrist and ankle bones.http://antranik.<strong>org</strong>/wp-content/uploads/2011/09/microscopic-structure-ofcompact-bone.pngSesamoidBonesFlatBonesIrregularBonesBones embedded in tendons. Examplesinclude the patella and pisiform.Thin and curved with parallel layers of compactbone. Examples include the sternum andbones of the skull.Bones that do not fit in any of the othercategories. Examples include the vertebra andbones of the sinus.252http://dc219.4shared.com/doc/QD-VsUDC/preview004.pngSaladin, K. 2012. <strong>The</strong> <strong>Skeletal</strong> <strong>System</strong>. Anatomy and Physiology: <strong>The</strong> Unity of Form and Function. New York,McGraw-Hill Publishing.