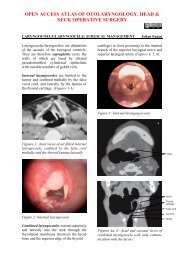
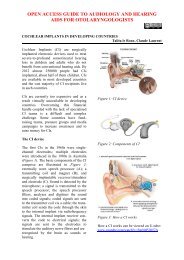
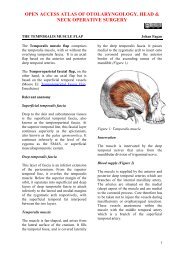
Hammer and gouge mastoidectomy for acute mastoiditis - Vula ...
Hammer and gouge mastoidectomy for acute mastoiditis - Vula ...
Hammer and gouge mastoidectomy for acute mastoiditis - Vula ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
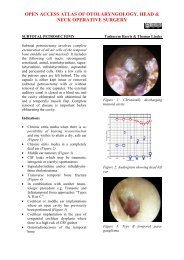
the lateral sinus. This region ismeticulously curetted (Figure 15).Figure 13: Vertical trenchSeventh Step: Exploration of PosteroinferiorRegionThe posteroinferior region, which is alsocalled the region of the mastoid vein, isopened with the <strong>gouge</strong>. The instrument isheld in the same position as describedpreviously but is slanted obliquely frombehind <strong>for</strong>ward <strong>and</strong> gently <strong>for</strong>ced in withlight taps of the mallet. The procedureprogresses backward toward the posteriorportion of the mastoid from below up.(Figure 14)Figure 14: Opening posteroinferior regionOpening this posteroinferior regionexposes the inner table of the skull whichat this level <strong>for</strong>ms the bony outer shell ofFigure 15: Completed posteroinferiordissectionIf the bony disease is very extensive, thesoft tissues may have to be sectioned by ahorizontal incision perpendicular to theretroauricular incision, <strong>for</strong>ming a “T”, <strong>and</strong>additional posterior exposure of themastoid bone done.Eighth Step: Exploration of PosterosuperiorRegion <strong>and</strong> Lateral Sinus /Sinodural Angle (Figure 16)Trephination is continued from below up<strong>and</strong> behind <strong>for</strong>ward, burrowingprogressively into the mastoid <strong>and</strong> to jointhe superficial antral region. The taps onthe <strong>gouge</strong> are per<strong>for</strong>med cautiously. Theyare made on a tangent to permit the gradualremoval of the cortex over the lateral sinusor even to uncover the venous wall, if thisshould be necessary. The rongeur isdangerous when h<strong>and</strong>led blindly <strong>and</strong> maypenetrate dura <strong>and</strong> injure the brain. The<strong>gouge</strong> is much more manageable; its actionmore easily controlled. The posterior limitof trephination is determined by the statusof the bone. The process continues untilnormal resistant bone, which does notbleed, is encountered. If haemorrhageoccurs from the mastoid vein, this may be7