Detailed Syllabus- Outline, End Term Exam Guidelines, Structure, etc.
Detailed Syllabus- Outline, End Term Exam Guidelines, Structure, etc. Detailed Syllabus- Outline, End Term Exam Guidelines, Structure, etc.
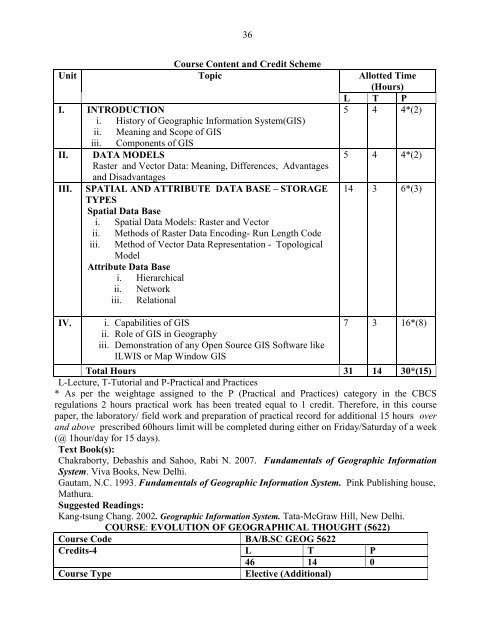
36Course Content and Credit SchemeUnit Topic Allotted Time(Hours)L T PI. INTRODUCTION5 4 4*(2)i. History of Geographic Information System(GIS)ii. Meaning and Scope of GISiii. Components of GISII. DATA MODELS5 4 4*(2)Raster and Vector Data: Meaning, Differences, Advantagesand DisadvantagesIII. SPATIAL AND ATTRIBUTE DATA BASE – STORAGETYPESSpatial Data Base14 3 6*(3)i. Spatial Data Models: Raster and Vectorii.iii.Methods of Raster Data Encoding- Run Length CodeMethod of Vector Data Representation - TopologicalModelAttribute Data Basei. Hierarchicalii. Networkiii. RelationalIV. i. Capabilities of GIS7 3 16*(8)ii. Role of GIS in Geographyiii. Demonstration of any Open Source GIS Software likeILWIS or Map Window GISTotal Hours 31 14 30*(15)L-Lecture, T-Tutorial and P-Practical and Practices* As per the weightage assigned to the P (Practical and Practices) category in the CBCSregulations 2 hours practical work has been treated equal to 1 credit. Therefore, in this coursepaper, the laboratory/ field work and preparation of practical record for additional 15 hours overand above prescribed 60hours limit will be completed during either on Friday/Saturday of a week(@ 1hour/day for 15 days).Text Book(s):Chakraborty, Debashis and Sahoo, Rabi N. 2007. Fundamentals of Geographic InformationSystem. Viva Books, New Delhi.Gautam, N.C. 1993. Fundamentals of Geographic Information System. Pink Publishing house,Mathura.Suggested Readings:Kang-tsung Chang. 2002. Geographic Information System. Tata-McGraw Hill, New Delhi.COURSE: EVOLUTION OF GEOGRAPHICAL THOUGHT (5622)Course Code BA/B.SC GEOG 5622Credits-4 L T P46 14 0Course TypeElective (Additional)
37Lectures to be Delivered 60Course Objective: The purpose of this paper is to teach the students the philosophy of thesubject of Geography, how it has evolved through time and the contributions of various scholarsin its evolution.Continuous Comprehensive Assessment (CCA) and End Semester Examination System: Sameas Prescribed in Course Paper 0203Course Content and Credit SchemeUnit Topic Allotted Time(Hours)L T PI. PREHISTORY OF GEOGRAPHICAL IDEAS15 4 0Brief contributions by:i. Greeksii. Romansiii. Arabsiv. Ancient Indiansv. Impact of Exploration and DiscoveriesII. MODERN SCHOOLS OF GEOGRAPHICAL 15 4 0THOUGHTSi. Americans : W.M. Davis, Richard Hortshorne, andEllen Churchill Sempleii. British: Halford J. Mackinder and Dudley Stampiii. German: Alexander Von Humboldt, Carl Ritter andFredrick Ratzeliv. France: Vidal de la Blache and Jean BrunesIII. DUALISM AND DICHOTOMIES IN GEOGRAPHY 8 3 0i. Physical Versus Humanii. Systematic Versus RegionalIV.TRENDS IN GEOGRAPHYi. Quantitative Revolutionii. Behaviouralism and Feminism8 3 0Total Hours 46 14 0L-Lecture, T-Tutorial and P-Practical and PracticesText Book(s):Husain, M. 2009. Evolution of Geographical Thought. Rawat Publication, JaipurSuggested Readings:Peet, R. 1998. Modern Geographical Thought. Blackwell Publisher, OxfordHartshorne, Richard. 2012. The Nature of Geography: Critical Survey of Current Thought inthe Light of the Past (Reprinted). The Association Lancaster, UK.
- Page 1: Approved in Under Graduate Board of
- Page 5 and 6: 5Compulsory and General Interest /
- Page 7 and 8: 7Semester Course Code Course Name C
- Page 9 and 10: 9OUTLINE OF SYLLABI AND COURSES OF
- Page 11 and 12: 11a. Plane Table: Open & Traverse M
- Page 13 and 14: 1315 hours over and above prescribe
- Page 15 and 16: 15Continuous Comprehensive Assessme
- Page 17 and 18: 17I. BASIC CONCEPTS9 4 0I. Brief In
- Page 19 and 20: 19understanding about the origin of
- Page 21 and 22: 21III.ii. River Water Pollution and
- Page 23 and 24: 23Course Objective: This course int
- Page 25 and 26: 25Singh, Gopal . 2012. Map Work and
- Page 27 and 28: 27A 10 Complete Objective Type 10(0
- Page 29 and 30: 29L-Lecture, T-Tutorial and P-Pract
- Page 31 and 32: 31Text Book(s):Chandna, R.C. 1986.
- Page 33 and 34: 33Continuous Comprehensive Assessme
- Page 35: 35I. HISTORIC BACKGROUNDi. Meaningi
- Page 39 and 40: 39i. Population Growth, Distributio
- Page 41: 41i. Cardinal Directionsii. Primary
36Course Content and Credit SchemeUnit Topic Allotted Time(Hours)L T PI. INTRODUCTION5 4 4*(2)i. History of Geographic Information System(GIS)ii. Meaning and Scope of GISiii. Components of GISII. DATA MODELS5 4 4*(2)Raster and Vector Data: Meaning, Differences, Advantagesand DisadvantagesIII. SPATIAL AND ATTRIBUTE DATA BASE – STORAGETYPESSpatial Data Base14 3 6*(3)i. Spatial Data Models: Raster and Vectorii.iii.Methods of Raster Data Encoding- Run Length CodeMethod of Vector Data Representation - TopologicalModelAttribute Data Basei. Hierarchicalii. Networkiii. RelationalIV. i. Capabilities of GIS7 3 16*(8)ii. Role of GIS in Geographyiii. Demonstration of any Open Source GIS Software likeILWIS or Map Window GISTotal Hours 31 14 30*(15)L-Lecture, T-Tutorial and P-Practical and Practices* As per the weightage assigned to the P (Practical and Practices) category in the CBCSregulations 2 hours practical work has been treated equal to 1 credit. Therefore, in this coursepaper, the laboratory/ field work and preparation of practical record for additional 15 hours overand above prescribed 60hours limit will be completed during either on Friday/Saturday of a week(@ 1hour/day for 15 days).Text Book(s):Chakraborty, Debashis and Sahoo, Rabi N. 2007. Fundamentals of Geographic InformationSystem. Viva Books, New Delhi.Gautam, N.C. 1993. Fundamentals of Geographic Information System. Pink Publishing house,Mathura.Suggested Readings:Kang-tsung Chang. 2002. Geographic Information System. Tata-McGraw Hill, New Delhi.COURSE: EVOLUTION OF GEOGRAPHICAL THOUGHT (5622)Course Code BA/B.SC GEOG 5622Credits-4 L T P46 14 0Course TypeElective (Additional)