Session K.pdf - Clarkson University
Session K.pdf - Clarkson University
Session K.pdf - Clarkson University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
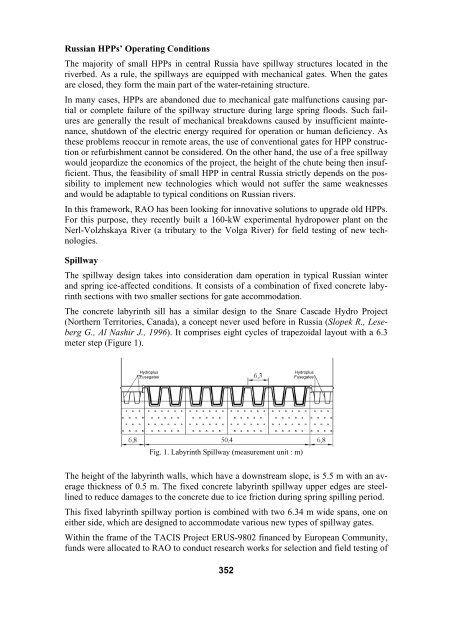
Russian HPPs’ Operating ConditionsThe majority of small HPPs in central Russia have spillway structures located in theriverbed. As a rule, the spillways are equipped with mechanical gates. When the gatesare closed, they form the main part of the water-retaining structure.In many cases, HPPs are abandoned due to mechanical gate malfunctions causing partialor complete failure of the spillway structure during large spring floods. Such failuresare generally the result of mechanical breakdowns caused by insufficient maintenance,shutdown of the electric energy required for operation or human deficiency. Asthese problems reoccur in remote areas, the use of conventional gates for HPP constructionor refurbishment cannot be considered. On the other hand, the use of a free spillwaywould jeopardize the economics of the project, the height of the chute being then insufficient.Thus, the feasibility of small HPP in central Russia strictly depends on the possibilityto implement new technologies which would not suffer the same weaknessesand would be adaptable to typical conditions on Russian rivers.In this framework, RAO has been looking for innovative solutions to upgrade old HPPs.For this purpose, they recently built a 160-kW experimental hydropower plant on theNerl-Volzhskaya River (a tributary to the Volga River) for field testing of new technologies.SpillwayThe spillway design takes into consideration dam operation in typical Russian winterand spring ice-affected conditions. It consists of a combination of fixed concrete labyrinthsections with two smaller sections for gate accommodation.The concrete labyrinth sill has a similar design to the Snare Cascade Hydro Project(Northern Territories, Canada), a concept never used before in Russia (Slopek R., LesebergG., Al Nashir J., 1996). It comprises eight cycles of trapezoidal layout with a 6.3meter step (Figure 1).HydroplusFusegatesHydroplusFusegatesFig. 1. Labyrinth Spillway (measurement unit : m)The height of the labyrinth walls, which have a downstream slope, is 5.5 m with an averagethickness of 0.5 m. The fixed concrete labyrinth spillway upper edges are steellinedto reduce damages to the concrete due to ice friction during spring spilling period.This fixed labyrinth spillway portion is combined with two 6.34 m wide spans, one oneither side, which are designed to accommodate various new types of spillway gates.Within the frame of the TACIS Project ERUS-9802 financed by European Community,funds were allocated to RAO to conduct research works for selection and field testing of352