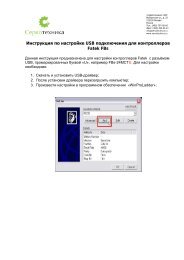
- Page 6 and 7:
Conventional Ladder DiagramPLC Ladd
- Page 8 and 9:
Input processing (Reading thestatus
- Page 10 and 11:
We must energize the coil of relay
- Page 12 and 13:
Network: Network is a circuit repre
- Page 15 and 16:
1.5 The De-Composition of a Network
- Page 18 and 19:
• When a single element or a seri
- Page 20 and 21:
MEMO
- Page 22 and 23:
2.2 Digital and Register Allocation
- Page 24 and 25: Relay No. Function Description3. Pu
- Page 26 and 27: Relay No. Function DescriptionM1965
- Page 28 and 29: 2.4 Special Registers DetailsRegist
- Page 30 and 31: Register No. Function DescriptionR4
- Page 32 and 33: Register No. Function DescriptionR4
- Page 34 and 35: Register No. Function DescriptionR4
- Page 36 and 37: Register No. Function DescriptionR4
- Page 38 and 39: Register No. Function DescriptionD4
- Page 40 and 41: Instruction Operand Symbol Function
- Page 42 and 43: FUNNo.NameOperandDerivativeInstruct
- Page 44 and 45: FUNNo.NameOperandDerivativeinstruct
- Page 46 and 47: • Ramp Function InstructionsFUNNo
- Page 48 and 49: MEMO
- Page 50 and 51: ※For the relays marked with a ‘
- Page 52 and 53: FUN7 is the UDCTR function. While r
- Page 54 and 55: X0X1Node ANode BIncerseInversediffe
- Page 56 and 57: All input controls of the function
- Page 58 and 59: • The names and functions of the
- Page 60 and 61: 5.1.4 Functions Output (FO)The “F
- Page 62 and 63: Indirect addressing program example
- Page 64 and 65: 5.3.2 The Coding of Numeric Numbers
- Page 66 and 67: (2). 0.5 = (-1) 0 * 2 ( 01111110 )
- Page 68 and 69: While all FBs-PLC numerical operati
- Page 70 and 71: Basic Function InstructionT TIMER T
- Page 72 and 73: Basic Function InstructionT TIMER T
- Page 76 and 77: Basic Function InstructionSET D PSy
- Page 78 and 79: Basic Function InstructionRST D PSy
- Page 80 and 81: Basic Function InstructionFUN 0MCSy
- Page 82 and 83: Basic Function InstructionFUN 1MCES
- Page 84 and 85: Basic Function InstructionFUN 2SKPS
- Page 86 and 87: Basic Function InstructionFUN 4DIFU
- Page 88 and 89: Basic Function InstructionFUN 6 D P
- Page 90 and 91: Basic Function InstructionFUN 7 DUD
- Page 92 and 93: Basic Function InstructionFUN 9 D P
- Page 94 and 95: Basic Function InstructionFUN 11 D
- Page 96 and 97: Basic Function InstructionFUN 13 D
- Page 98 and 99: Basic Function InstructionFUN 14 D
- Page 100 and 101: Basic Function InstructionFUN 15 D
- Page 102 and 103: Basic Function InstructionFUN 17 D
- Page 104 and 105: Basic Function InstructionFUN 19 D
- Page 106 and 107: Basic Function InstructionFUN 21 D
- Page 108 and 109: Advanced Function InstructionFUN22
- Page 110 and 111: Advanced Function InstructionFUN 24
- Page 112 and 113: Advanced Function InstructionFUN 26
- Page 114 and 115: Advanced Function InstructionFUN 28
- Page 116 and 117: Advanced Function InstructionFUN 30
- Page 118 and 119: Advanced Function InstructionFUN32A
- Page 120 and 121: Advanced Function InstructionFUN 36
- Page 122 and 123: Advanced Function InstructionFUN 40
- Page 124 and 125:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 42
- Page 126 and 127:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 44
- Page 128 and 129:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 46
- Page 130 and 131:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 48
- Page 132 and 133:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN50
- Page 134 and 135:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 52
- Page 136 and 137:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 54
- Page 138 and 139:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN55
- Page 140 and 141:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN56
- Page 142 and 143:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 58
- Page 144 and 145:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 59
- Page 146 and 147:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 59
- Page 148 and 149:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 61
- Page 150 and 151:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 63
- Page 152 and 153:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 64
- Page 154 and 155:
Advanced Function InstructionEND PR
- Page 156 and 157:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 66
- Page 158 and 159:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 68
- Page 160 and 161:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 70
- Page 162 and 163:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 74
- Page 164 and 165:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 76
- Page 166 and 167:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 78
- Page 168 and 169:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 79
- Page 170 and 171:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 81
- Page 172 and 173:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 82
- Page 174 and 175:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 84
- Page 176 and 177:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 86
- Page 178 and 179:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 86
- Page 180 and 181:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN89/
- Page 182 and 183:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 90
- Page 184 and 185:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 92
- Page 186 and 187:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 94
- Page 188 and 189:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 95
- Page 190 and 191:
Advanced Function InstructionTable
- Page 192 and 193:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN101
- Page 194 and 195:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN103
- Page 196 and 197:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN105
- Page 198 and 199:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN107
- Page 200 and 201:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN109
- Page 202 and 203:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN110
- Page 204 and 205:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN111
- Page 206 and 207:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN112
- Page 208 and 209:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN114
- Page 210 and 211:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN120
- Page 212 and 213:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN122
- Page 214 and 215:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN124
- Page 216 and 217:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN126
- Page 218 and 219:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN128
- Page 220 and 221:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN130
- Page 222 and 223:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 13
- Page 224 and 225:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN141
- Page 226 and 227:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN143
- Page 228 and 229:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN146
- Page 230 and 231:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 15
- Page 232 and 233:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN160
- Page 234 and 235:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN201
- Page 236 and 237:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 20
- Page 238 and 239:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 20
- Page 240 and 241:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 20
- Page 242 and 243:
Advance Function InstructionFUN 208
- Page 244 and 245:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 21
- Page 246 and 247:
Advanced Function InstructionFUN 21
- Page 248 and 249:
MEMO
- Page 250 and 251:
8.2 Basic Formation of Step Ladder
- Page 252 and 253:
. Single CycleM1924X0• When step
- Page 254 and 255:
●STP Sxxx : S20≦Sxxx≦S999(Dis
- Page 256 and 257:
【Description】: 1. When ON, the
- Page 258 and 259:
●STPEND :(Displayed in WinProladd
- Page 260 and 261:
Example 1WinProladderFP-07M1924STP
- Page 262 and 263:
Example 3WinProladderFP-07M1924STP
- Page 264 and 265:
WinProladderFP-07M1924STP S0X1X2X0S
- Page 266 and 267:
WinProladderM1924TO S0X1STP S0SET Y
- Page 268 and 269:
●Pedestrian Crossing Lights Contr
- Page 270 and 271:
8.6 Syntax Check Error Codes for St
- Page 272 and 273:
1.1 Profile112798716外 徑 4ψ×4
- Page 274 and 275:
〝H〞 indicates hexadecimal↓
- Page 276 and 277:
1.5.2 FUN function description• F
- Page 278 and 279:
【Example】Assume definition as R
- Page 280 and 281:
• Locations and application of th
- Page 282 and 283:
1.7.2 The Information formats of me


![[Instruction] Contents](https://img.yumpu.com/51325878/74/500x640/instruction-contents.jpg)