chitosan and plga microspheres as drug delivery ... - UniCA Eprints
chitosan and plga microspheres as drug delivery ... - UniCA Eprints
chitosan and plga microspheres as drug delivery ... - UniCA Eprints
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
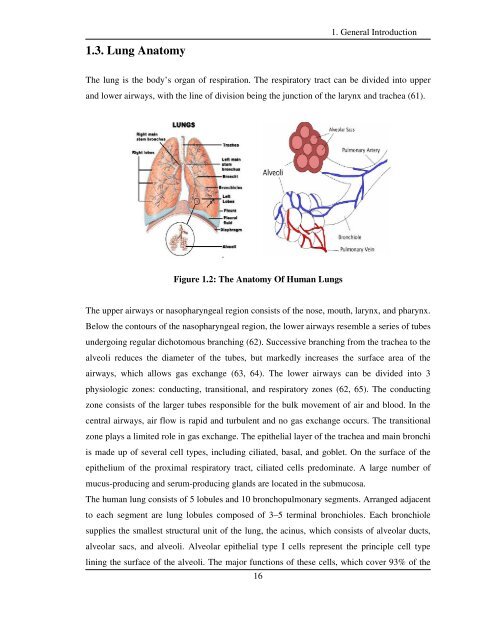
1.3. Lung Anatomy1. General IntroductionThe lung is the body’s organ of respiration. The respiratory tract can be divided into upper<strong>and</strong> lower airways, with the line of division being the junction of the larynx <strong>and</strong> trachea (61).Figure 1.2: The Anatomy Of Human LungsThe upper airways or n<strong>as</strong>opharyngeal region consists of the nose, mouth, larynx, <strong>and</strong> pharynx.Below the contours of the n<strong>as</strong>opharyngeal region, the lower airways resemble a series of tubesundergoing regular dichotomous branching (62). Successive branching from the trachea to thealveoli reduces the diameter of the tubes, but markedly incre<strong>as</strong>es the surface area of theairways, which allows g<strong>as</strong> exchange (63, 64). The lower airways can be divided into 3physiologic zones: conducting, transitional, <strong>and</strong> respiratory zones (62, 65). The conductingzone consists of the larger tubes responsible for the bulk movement of air <strong>and</strong> blood. In thecentral airways, air flow is rapid <strong>and</strong> turbulent <strong>and</strong> no g<strong>as</strong> exchange occurs. The transitionalzone plays a limited role in g<strong>as</strong> exchange. The epithelial layer of the trachea <strong>and</strong> main bronchiis made up of several cell types, including ciliated, b<strong>as</strong>al, <strong>and</strong> goblet. On the surface of theepithelium of the proximal respiratory tract, ciliated cells predominate. A large number ofmucus-producing <strong>and</strong> serum-producing gl<strong>and</strong>s are located in the submucosa.The human lung consists of 5 lobules <strong>and</strong> 10 bronchopulmonary segments. Arranged adjacentto each segment are lung lobules composed of 3–5 terminal bronchioles. Each bronchiolesupplies the smallest structural unit of the lung, the acinus, which consists of alveolar ducts,alveolar sacs, <strong>and</strong> alveoli. Alveolar epithelial type I cells represent the principle cell typelining the surface of the alveoli. The major functions of these cells, which cover 93% of the16