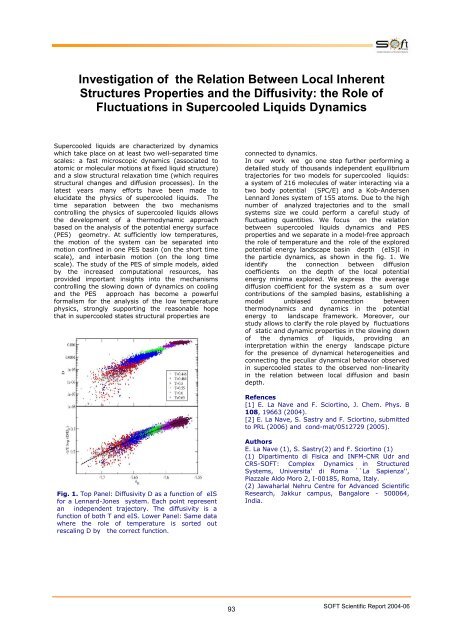
Investigation of the Relation Between Local InherentStructures Properties and the Diffusivity: the Role ofFluctuations in Supercooled Liquids DynamicsSupercooled liquids are characterized by dynamicswhich take place on at least two well-separated timescales: a fast microscopic dynamics (associated toatomic or molecular motions at fixed liquid structure)and a slow structural relaxation time (which requiresstructural changes and <strong>di</strong>ffusion processes). In thelatest years many efforts have been made toelucidate the physics of supercooled liquids. Thetime separation between the two mechanismscontrolling the physics of supercooled liquids allowsthe development of a thermodynamic approachbased on the analysis of the potential energy surface(PES) geometry. At sufficiently low temperatures,the motion of the system can be separated intomotion confined in one PES basin (on the short timescale), and interbasin motion (on the long timescale). The study of the PES of simple models, aidedby the increased computational resources, hasprovided important insights into the mechanismscontrolling the slowing down of dynamics on coolingand the PES approach has become a powerfulformalism for the analysis of the low temperaturephysics, strongly supporting the reasonable hopethat in supercooled states structural properties areconnected to dynamics.In our work we go one step further performing adetailed study of thousands independent equilibriumtrajectories for two models for supercooled liquids:a system of 216 molecules of water interacting via atwo body potential (SPC/E) and a Kob-AndersenLennard Jones system of 155 atoms. Due to the highnumber of analyzed trajectories and to the smallsystems size we could perform a careful study offluctuating quantities. We focus on the relationbetween supercooled liquids dynamics and PESproperties and we separate in a model-free approachthe role of temperature and the role of the exploredpotential energy landscape basin depth (eIS)I inthe particle dynamics, as shown in the fig. 1. Weidentify the connection between <strong>di</strong>ffusioncoefficients on the depth of the local potentialenergy minima explored. We express the average<strong>di</strong>ffusion coefficient for the system as a sum overcontributions of the sampled basins, establishing amodel unbiased connection betweenthermodynamics and dynamics in the potentialenergy to landscape framework. Moreover, ourstudy allows to clarify the role played by fluctuationsof static and dynamic properties in the slowing downof the dynamics of liquids, provi<strong>di</strong>ng aninterpretation within the energy landscape picturefor the presence of dynamical heterogeneities andconnecting the peculiar dynamical behavior observe<strong>di</strong>n supercooled states to the observed non-linearityin the relation between local <strong>di</strong>ffusion and basindepth.Refences[1] E. La Nave and F. Sciortino, J. Chem. Phys. B108, 19663 (2004).[2] E. La Nave, S. Sastry and F. Sciortino, submittedto PRL (2006) and cond-mat/0512729 (2005).Fig. 1. Top Panel: Diffusivity D as a function of eISfor a Lennard-Jones system. Each point representan independent trajectory. The <strong>di</strong>ffusivity is afunction of both T and eIS. Lower Panel: Same datawhere the role of temperature is sorted outrescaling D by the correct function.AuthorsE. La Nave (1), S. Sastry(2) and F. Sciortino (1)(1) <strong>Dipartimento</strong> <strong>di</strong> <strong>Fisica</strong> and INFM-CNR Udr andCRS-SOFT: Complex Dynamics in StructuredSystems, Universita' <strong>di</strong> Roma ``La <strong>Sapienza</strong>'',Piazzale Aldo Moro 2, I-00185, Roma, Italy.(2) Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced ScientificResearch, Jakkur campus, Bangalore - 500064,In<strong>di</strong>a.93SOFT Scientific <strong>Report</strong> 2004-06
Scientific <strong>Report</strong> – Self Assembly, Clustering, Structural arrestCoil-Globule Transition of DNA Molecules Induced byCationic SurfactantsCompaction of DNA induced by cationic surfactantshave attracted in the recent years a large amount ofinterest due to its importance both in technologicaland biome<strong>di</strong>cal applications, particularly for thepotential use of these systems as vehicles for genedelivery and gene transfection. One of limitingfactors for gene therapy is the DNA transport, since,under normal physiological con<strong>di</strong>tion, DNA is a highlycharged polyion that is repelled by the similarlynegative cell membrane.In the complexation between DNA and cationicspecies, the effective negative charge of DNA islowered, allowing the complex to approach thecharged cell membrane. In ad<strong>di</strong>tion, it has beenshown that cationic surfactants collapse in<strong>di</strong>vidualDNA molecules and lead to small particles allowingan efficient internalization of these complexes intothe cells. In relation to this, the DNA inchromosomes was found to be in a highly condensedstate in comparison with the free DNA in thesolution.A wide variety of physical methods have beenapplied to the study of DNA-surfactant interactionsand recently these interactions have been alsostu<strong>di</strong>ed at the single-molecule level, with the use ofa fluorescent microscopy technique [1,2].It has been found that isolated DNA chains undergoa <strong>di</strong>screte coil-globule transition by the ad<strong>di</strong>tion ofcationic surfactants, with a region where coil andglobule form coexist for interme<strong>di</strong>ate concentrationof amphiphile. The molecular mechanism lea<strong>di</strong>ng tothis conformational change has been described asfollows. Cationic surfactants interact with DNA by acombination of initial electrostatic interactionfollowed by a cooperative bin<strong>di</strong>ng of surfactantligands to the same DNA molecule, driven byhydrophobic forces. The coexistence of DNAmolecules with <strong>di</strong>fferent conformation has only beenobserved, to our knowledge, by fluorescencemicroscopy.Recently, we used dynamic light scattering [3] and<strong>di</strong>electric spectroscopy [4] to investigate thecompaction of DNA induced by two simple modelamphiphiles, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide(CTAB), a single chain cationic surfactant, anddodecyl<strong>di</strong>methylamine oxide (DDAO), which cancoexist in either non ionic or cationic form,depen<strong>di</strong>ng on pH. The behaviour of thehydrodynamic ra<strong>di</strong>us and the size <strong>di</strong>stribution of theDNA-surfactant complexes have been stu<strong>di</strong>ed<strong>di</strong>rectly by dynamic light scattering, evidencing abimodal <strong>di</strong>stribution with the simultaneous presenceof coil and compact globule state, whose relativeconcentration changes with the surfactantconcentration (see Fig.1)This clearly shows that coil and globule form coexistin the surfactant solution at a concentration intervalin which the cooperative continuous transition isobserved in the macroscopic ensemble of DNAchains. It is the first time, to our knowledge, that thecoil-globule coexistence is observed in bulk, in a<strong>di</strong>rect way. The overall phenomenology observed forCTAB and DDAO surfactants is quite similar,although, in the latter one, the pH-induced degree ofprotonation is small. This fin<strong>di</strong>ng clearly in<strong>di</strong>cates theimportant role of the hydrophobic interactions in theformation of DNA-surfactant complex.References[1] S.M. Mel'nikov, V.G. Sergeyev, K. Yoshikava, J.Am. Chem. Soc., 117, 2401, (1995).[2] Y.S. Mel'nikova, B. Lindman, Langmuir , 16,5871, (2000).[3] S.Marchetti, G. Onori, C. Cametti, Journal ofPhysical Chemistry B., 109, 3676, (2005).[4] A. Bonincontro. S. Marchetti, G. Onori, A. Rosati,Chem. Phys., 312, 55, (2005).Fig. 1: Average hydrodynamic <strong>di</strong>ameter 2R H of DNA-CTAB complexes as a function of the surfactant toDNA-phosphate molar charge ratio X. The insetshows the size <strong>di</strong>stribution at two <strong>di</strong>fferent values ofX, before and close to the neutralization con<strong>di</strong>tion,X=0.55, where there is a bimodal <strong>di</strong>stribution andX=1.22, where only a monomodal <strong>di</strong>stributionappears.AuthorsG. Onori (a), S. Marchetti (a), C. Cametti (b)(a) <strong>Dipartimento</strong> <strong>di</strong> <strong>Fisica</strong>, Università <strong>di</strong> Perugia andCEMIN and INFM-CRS SOFT, Unità <strong>di</strong> Roma 1.(b) <strong>Dipartimento</strong> <strong>di</strong> <strong>Fisica</strong>, Università <strong>di</strong> Roma « La<strong>Sapienza</strong> », Piazzale A. Moro 5, I-00185- Roma(Italy) and INFM- CRS SOFT, Unità <strong>di</strong> RomaSOFT Scientific <strong>Report</strong> 2004-0694
- Page 4 and 5:
Istituto Nazionale per la Fisica de
- Page 6 and 7:
ContentsIntroduction 7Scientific Mi
- Page 8 and 9:
IntroductionSOFT is a CRS (Centro d
- Page 10 and 11:
Scientific MissionThe scientific wo
- Page 13 and 14:
Missioncolloids and soft colloidal
- Page 15 and 16:
PersonnelManagement, Personnel and
- Page 17 and 18:
FacilitiesSOFT Scientific Report 20
- Page 19 and 20:
FacilitiesX-ray Diffraction Laborat
- Page 21 and 22:
FacilitiesThin Film Laboratory - Ud
- Page 23 and 24:
FacilitiesBrillouin Light Scatterin
- Page 25 and 26:
Facilitieslaserf 2BSf 1FOBSSoftware
- Page 27 and 28:
FacilitiesStatic Light Scattering L
- Page 29 and 30:
FacilitiesSpectroscopy Laboratory -
- Page 31 and 32:
LSFSOFT Scientific Report 2004-0630
- Page 33 and 34:
LSFFig. 1 - BRISP layoutBackground
- Page 35 and 36:
LSFBRISP first spectraLeft panel: e
- Page 37 and 38:
LSFNeutron guideMonochromator cryst
- Page 39 and 40:
LSFAXES: Advanced X-ray Emission Sp
- Page 41 and 42:
LSFID16: Inelastic X-ray Scattering
- Page 43 and 44: LSFExperiments at LSFYear 2004Elett
- Page 45 and 46: LSFYear 2005Elettra - IUVS• High
- Page 47 and 48: LSFYear 2006Elettra - IUVS• Study
- Page 49 and 50: Scientific ReportsScientific Report
- Page 51 and 52: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 53 and 54: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 55 and 56: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 57 and 58: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 59 and 60: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 61 and 62: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 63 and 64: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 65 and 66: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 67 and 68: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 69 and 70: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 71 and 72: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 73 and 74: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 75 and 76: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 77 and 78: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 79 and 80: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 81 and 82: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 83 and 84: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 85 and 86: Scientific Report - Non Equilibrium
- Page 87 and 88: Scientific Report - Self Assembly,
- Page 89 and 90: Scientific Report - Self Assembly,
- Page 91 and 92: Scientific Report - Self Assembly,
- Page 93: Scientific Report - Self Assembly,
- Page 97 and 98: Scientific Report - Self Assembly,
- Page 99 and 100: Scientific Report - Self Assembly,
- Page 101 and 102: Scientific Report - Elastic and ine
- Page 103 and 104: Scientific Report - Elastic and ine
- Page 105 and 106: Scientific Report - Elastic and ine
- Page 107 and 108: Scientific Report - Elastic and ine
- Page 109 and 110: Projects and CollaborationsSOFT Sci
- Page 111 and 112: Projects and CollaborationsPAIS 200
- Page 113 and 114: Projects and CollaborationsCollabor
- Page 115 and 116: DisseminationSOFT Scientific Report
- Page 117 and 118: DisseminationWe also point out the
- Page 119 and 120: DisseminationF. A. Gorelli, V. M. G
- Page 121 and 122: DisseminationL. Angelani, G. Foffi,
- Page 123 and 124: DisseminationC. Casieri, F. De Luca
- Page 125 and 126: DisseminationM. Finazzi, M. Portalu
- Page 127 and 128: DisseminationS. Magazu, F. Migliard
- Page 129 and 130: DisseminationB. Rossi, G. Viliani,
- Page 131 and 132: DisseminationE. Zaccarelli, C. Maye
- Page 133 and 134: DisseminationV. Bortolotti, M. Cama
- Page 135 and 136: DisseminationC. De Michele, A. Scal
- Page 137 and 138: DisseminationJ. Gutierrez, F. J. Be
- Page 139 and 140: DisseminationA. Monaco, A. I. Chuma
- Page 141 and 142: DisseminationM. Reale, M. A. De Lut
- Page 143 and 144: DisseminationF. Bordi, C. Cametti,
- Page 145 and 146:
DisseminationSOFT Scientific Report
- Page 147 and 148:
DisseminationXII Liquid and Amorpho
- Page 149 and 150:
DisseminationConference on "new pro
- Page 151 and 152:
DisseminationX International worksh
- Page 153 and 154:
DisseminationXAFS13, 13 th Internat
- Page 155 and 156:
DisseminationOrganization of School
- Page 157 and 158:
DisseminationSoft Annual WorkshopsE
- Page 159 and 160:
DisseminationSoft WebSiteThe Web Si
- Page 161 and 162:
DisseminationContactsINFM-CNR Resar