- Page 1:
U.S. Department of Justice
- Page 5 and 6:
4. UNITED STATES ATTORNEY’S OFFIC
- Page 7 and 8:
V. CONCLUSION .....................
- Page 9 and 10:
amount of information, including: (
- Page 12 and 13:
assisting state, local, tribal and
- Page 14 and 15:
goals that can provide some measura
- Page 16 and 17:
State and federal investigators and
- Page 18 and 19:
a. Available indicators suggest chi
- Page 20 and 21:
These two applications (Fairplay, R
- Page 22 and 23:
The Figure below shows the number o
- Page 24 and 25:
For FY 2008, ICAC Task Forces repor
- Page 26 and 27:
Some researchers suggest that viewi
- Page 28 and 29:
interests in children and their des
- Page 31 and 32:
could later bediscovered by lawenfo
- Page 33 and 34:
domains are commercial purveyors of
- Page 35 and 36:
• The offender communicates with
- Page 37 and 38:
1. Online enticement complaints are
- Page 39 and 40:
elationship. After the child has ga
- Page 41 and 42:
Influenced and Corrupt Organization
- Page 43 and 44:
D. Child Sex TourismChild sex touri
- Page 45 and 46:
Exploitation of Children Today (PRO
- Page 47 and 48:
A task force model often is employe
- Page 49 and 50:
The United States Attorney’s offi
- Page 51 and 52:
FBI and CEOS, in conjunction with N
- Page 53 and 54:
The effects of child sex tourism re
- Page 55 and 56:
352 investigations and 162 charged
- Page 57 and 58:
• CEOS worked closely with NDIC i
- Page 59 and 60:
• Alameda County, CA, Children's
- Page 61 and 62:
• Additional data have been submi
- Page 63 and 64:
postsentence persons and civilly co
- Page 65 and 66:
B. A Review of the Internet Crimes
- Page 67 and 68:
• Providing training and technica
- Page 69 and 70:
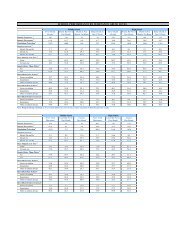
Table 1 : ICAC Task Force Agencies
- Page 71 and 72:
State Task Force Agency Number of T
- Page 73 and 74:
State Agency FY 2009 FY 2009 FY 200
- Page 75 and 76:
State Agency FY2008#AZCACACACACACOC
- Page 77 and 78:
Number of Criminal Referrals to Uni
- Page 79 and 80:
d. Number of local prosecutions and
- Page 81 and 82:
State Agency FY 2008# of Cases Refe
- Page 83 and 84:
State Agency FY 2008 Jan.-June 2009
- Page 85 and 86:
8. Number and type of ICAC Task For
- Page 87 and 88:
ICAC Undercover Chat 4 Regional 9.2
- Page 89 and 90:
has developed highly successful ini
- Page 91 and 92:
field offices, both domestic and fo
- Page 93 and 94:
2. Department of Defense’s Effort
- Page 95 and 96:
of a mail circular. Since the progr
- Page 97 and 98:
• The Street Outreach Program fun
- Page 99 and 100:
the Defense Computer Forensic Labor
- Page 101 and 102:
• Distributes photographs and des
- Page 103 and 104:
iii. Enough Is EnoughEnough Is Enou
- Page 105 and 106:
1. Overarching Efforts to Coordinat
- Page 107 and 108:
combine resources and expertise on
- Page 109 and 110:
United States has submitted annual
- Page 111 and 112:
CEOS has worked with foreign law en
- Page 113 and 114:
. Department of Homeland Security
- Page 115 and 116:
Finally, G/TIP has worked extensive
- Page 117 and 118:
F. Review of Internet Safety Progra
- Page 119 and 120:
the accessibility, cost, and effect
- Page 121 and 122:
activity by predators searching for
- Page 123 and 124:
3. Federal Trade Commission and Dep
- Page 125 and 126:
Funder: • U.S. Department of Agri
- Page 127 and 128:
Delivery: • Online games; printab
- Page 129 and 130:
TABLE 1: FEDERALLY FUNDED INTERNET
- Page 131 and 132:
Program/Product NameandContactInfor
- Page 133 and 134:
TABLE 2: SAMPLE OF PRIVATE NONPROFI
- Page 135 and 136:
Program/Product NameProducerFor Kid
- Page 137 and 138:
TABLE 1: PARTICIPANT EVALUATIONS OF
- Page 139 and 140:
FY 2011. The primary forensics resp
- Page 141 and 142: The DEU is the principal group resp
- Page 143 and 144: CD/DVDs. The CFS has the capability
- Page 145 and 146: First, the Department will continue
- Page 147 and 148: and the Innocence Lost task forces,
- Page 149 and 150: deconflict cases, and share informa
- Page 151 and 152: with the ICACs to help increase the
- Page 153 and 154: from Landslide’s business premise
- Page 155 and 156: victimized children worldwide, incl
- Page 157 and 158: association, was arrested after the
- Page 159 and 160: is transnational in scope; cooperat
- Page 161 and 162: Over the course of their communicat
- Page 163 and 164: An ICE investigation resulted in th
- Page 165 and 166: U.S. v. RichardsonICE PRESS RELEASE
- Page 167 and 168: APPENDIX C THREAT ASSESSMENT: ACADE
- Page 169 and 170: Selected Quotes from Appendix C of
- Page 171 and 172: * * * “Sheldon and Howitt (2007)
- Page 173 and 174: McCarthy, J. and Gaunt, N. (2004).
- Page 175 and 176: high-profile jobs. Some seemed isol
- Page 177 and 178: Trends 2008, http://www.iwf.org.uk/
- Page 179 and 180: Source: National Center for Missing
- Page 181 and 182: Federal Bureau of Investigation (FB
- Page 183 and 184: scientific survey process, but rath
- Page 185 and 186: • 42 percent of respondents repor
- Page 187 and 188: The Effect of the Lack of Internet
- Page 189 and 190: • 44 percent of respondents repor
- Page 191: • 24 percent of respondents repor
- Page 195 and 196: • 37 percent of respondents repor
- Page 197 and 198: • 8 percent of respondents report
- Page 199 and 200: SEX TOURISMNature and ExtentAmong N
- Page 201 and 202: • 50 percent of respondents repor
- Page 203 and 204: Average Federal and State Sentences
- Page 205 and 206: SOURCESNumerous federal, state, and
- Page 207 and 208: Federal Bureau of Investigation (FB
- Page 209 and 210: Southern Texas Utah VermontVirginia
- Page 211 and 212: APPENDIX EDEPARTMENT-FUNDED RESEARC
- Page 213 and 214: victimization. The project has four
- Page 215 and 216: APPENDIX FSYNTHESIS OF MAJOR STUDIE
- Page 217 and 218: 17 that among the participants who
- Page 219 and 220: authors, extrapolating survey data,
- Page 221 and 222: officials can gain greater awarenes
- Page 223 and 224: Moessner, Chris. “Cyberbullying.
- Page 225 and 226: The authors of this chapter in a bo
- Page 227 and 228: Wells, Melissa, David Finkelhor, Ja
- Page 229 and 230: The article reports the results of
- Page 231 and 232: system ۛincluding perspectives of
- Page 233 and 234: etween 42 and 44 percent of pornogr
- Page 235 and 236: Reporting the demographic, psycholo
- Page 237 and 238: predator with a victim took place i
- Page 239 and 240: 1 Tinker v. Des Moines Independent
- Page 241 and 242: conducted between September 1999 an
- Page 243 and 244:
with each grade level, with the per
- Page 245 and 246:
Understanding Online Child Pornogra
- Page 247 and 248:
focusing on violent (including sexu
- Page 249 and 250:
their offending than did Internet o
- Page 251 and 252:
trafficking, rape and sexual assaul
- Page 253 and 254:
States Postal Inspection Service, 8
- Page 255 and 256:
Getting to Grips with Sexual Groomi
- Page 257 and 258:
Child Seduction and Self-Representa
- Page 259 and 260:
Annotated Bibliography: Child Explo
- Page 261 and 262:
Abstract The author discusses teach
- Page 263 and 264:
implications for nursing practice i
- Page 265 and 266:
providers assisting child victims,
- Page 267 and 268:
Problematic Internet Experiences: P
- Page 269 and 270:
Online Requests for Sexual Pictures
- Page 271 and 272:
Sheldon Kennedy and a Canadian Trag
- Page 273 and 274:
people involved in prostitution and
- Page 275 and 276:
debates about child labour, exploit
- Page 277 and 278:
Abstract The article presents the v
- Page 279 and 280:
dealing with sexual offenses agains