Literacy Trends in Pakistan - UNESCO Islamabad
Literacy Trends in Pakistan - UNESCO Islamabad Literacy Trends in Pakistan - UNESCO Islamabad
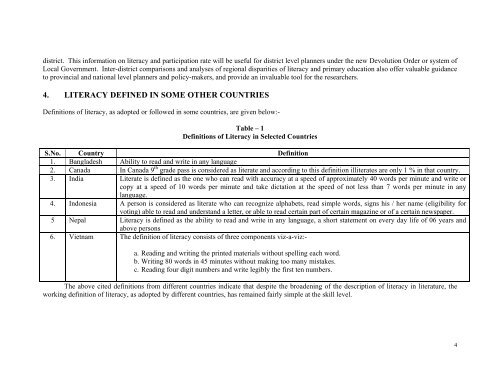
district. This information on literacy and participation rate will be useful for district level planners under the new Devolution Order or system ofLocal Government. Inter-district comparisons and analyses of regional disparities of literacy and primary education also offer valuable guidanceto provincial and national level planners and policy-makers, and provide an invaluable tool for the researchers.4. LITERACY DEFINED IN SOME OTHER COUNTRIESDefinitions of literacy, as adopted or followed in some countries, are given below:-Table – 1Definitions of Literacy in Selected CountriesS.No. Country Definition1. Bangladesh Ability to read and write in any language2. Canada In Canada 9 th grade pass is considered as literate and according to this definition illiterates are only 1 % in that country.3. India Literate is defined as the one who can read with accuracy at a speed of approximately 40 words per minute and write orcopy at a speed of 10 words per minute and take dictation at the speed of not less than 7 words per minute in anylanguage.4. Indonesia A person is considered as literate who can recognize alphabets, read simple words, signs his / her name (eligibility forvoting) able to read and understand a letter, or able to read certain part of certain magazine or of a certain newspaper.5 Nepal Literacy is defined as the ability to read and write in any language, a short statement on every day life of 06 years andabove persons6. Vietnam The definition of literacy consists of three components viz-a-viz:-a. Reading and writing the printed materials without spelling each word.b. Writing 80 words in 45 minutes without making too many mistakes.c. Reading four digit numbers and write legibly the first ten numbers.The above cited definitions from different countries indicate that despite the broadening of the description of literacy in literature, theworking definition of literacy, as adopted by different countries, has remained fairly simple at the skill level.4
5. INTERNATIONAL CONTEXT OF DEFINITIONSThe definition of literacy is context specific. The parameters of literacy may vary from one geographical region to another, and from one era toanother. It can be as simple as just recognition of the alphabets, or signing of one’s own name, or may be broader in order to include handling ofequipment by studying manuals. Literacy has multiple meanings ranging from simple ability to read and write, to interpreting and implementingideas, knowledge and skills that a person may require to possess for effective participation in daily life.Some definitions of literacy focus on perception and decoding. For example, Spache (1964) described literacy as “a series of word perceptionsi.e. reading only”. Kaestle (1985), described literacy as “the ability to decode and comprehend language at a rudimentary level, that is the abilityto look at written words corresponding to ordinary oral discourse, to say them, and to understand them”. These two definitions emphasize theaspect of having the skills to read the printed symbols and to map those symbols into the understanding of oral language. This definition isconsistent with the teaching of reading through an emphasis on sound-symbol correspondence, and helping readers make connections to theiroral vocabulary and comprehension abilities. But this definition lacks the important component of writing.It is observed that initially, the definition of literacy was confined to the acquisition of the basic skills of the 3 R’s (reading, writing andarithmetic). Over a period of time, basic literacy was upgraded to functional literacy, expanding further into knowing to do things by usinginsight. This transformation of literacy is, infact, associated with its importance for the society as a whole, and to enable a person to effectivelyparticipate in the lifeThough defining literacy is complex, yet it is important to deliberate upon it, since the definition has far-reaching implications. Some expertshave emphasized cognitive processes in describing literacy, some more generally and others more specifically. For example, Goodman (1976)suggested that “reading is a psycholinguistic guessing game”. Venezky (1991) states that it is “a cognitive skill”. Calfee and Nelson-Barber(1991) describe it as “the capacity to employ language as a tool for oral communication”. These definitions are consistent with teaching readingand writing as a cognitive process that involve the processing of information through such strategies as activating background knowledge,encouraging readers to make predictions, or writers to organize their ideas into categories.Literacy, Politics and Democracy“Although literacy may not be the great panacea that leads to happiness and wealth, it could lead to a change in theway power is distributed in society”.(UNESCO, 1991, A Literate World, International Bureau of Education, Geneva)“Survival in relation to political institutions is once again dependent on literacy. In many countries the right to vote isdenied to the illiterate. Responsible voting is not easy without literacy. Literacy makes democracy possible andhistorical responses to the tribal drum less likely”.(H.S. Bhola, UNESCO, 1990)5
- Page 2 and 3: ContributorsDescription and Analysi
- Page 4 and 5: Literacy Trends in PakistanUNESCO O
- Page 6 and 7: Part I - An Analysis of Literacy Tr
- Page 8 and 9: Part II Statistical Tables (Based o
- Page 10 and 11: an education that includes learning
- Page 14 and 15: In the present day context, when pa
- Page 16 and 17: 7. FUNCTIONAL LITERACYThe definitio
- Page 18 and 19: Middle Level (Level II)A) TARGET GR
- Page 20 and 21: Table - 3Comparison of Pakistan wit
- Page 22 and 23: Previous attempts made for the enha
- Page 24 and 25: 11. CURRENT LITERACY SITUATION IN P
- Page 26 and 27: Graph No. 1Growth of Literacy Rate
- Page 28 and 29: Table 7 below indicates the highest
- Page 30 and 31: Table 8Literacy Growth Rate Trends
- Page 32 and 33: District has progressed from a very
- Page 34 and 35: Table 11Districts in Various Litera
- Page 36 and 37: 13.2 Public Expenditure on Primary
- Page 38 and 39: lowest female literacy rate in Paki
- Page 40 and 41: All this suggests that a considerab
- Page 42 and 43: Graph No.4LITERACY RATE DIRECTLY EF
- Page 44 and 45: 16. LITERACY AND NATIONAL PLAN OF A
- Page 46 and 47: 17.1 Why has it been established?Th
- Page 48 and 49: Table 16 - Focus Areas and Key Stra
- Page 50 and 51: 17.5 Resource MobilizationThe Liter
- Page 52 and 53: PART - IIStatistical Tables(Based o
- Page 57: Table IILiteracy Rates (10 Years &
district. This <strong>in</strong>formation on literacy and participation rate will be useful for district level planners under the new Devolution Order or system ofLocal Government. Inter-district comparisons and analyses of regional disparities of literacy and primary education also offer valuable guidanceto prov<strong>in</strong>cial and national level planners and policy-makers, and provide an <strong>in</strong>valuable tool for the researchers.4. LITERACY DEFINED IN SOME OTHER COUNTRIESDef<strong>in</strong>itions of literacy, as adopted or followed <strong>in</strong> some countries, are given below:-Table – 1Def<strong>in</strong>itions of <strong>Literacy</strong> <strong>in</strong> Selected CountriesS.No. Country Def<strong>in</strong>ition1. Bangladesh Ability to read and write <strong>in</strong> any language2. Canada In Canada 9 th grade pass is considered as literate and accord<strong>in</strong>g to this def<strong>in</strong>ition illiterates are only 1 % <strong>in</strong> that country.3. India Literate is def<strong>in</strong>ed as the one who can read with accuracy at a speed of approximately 40 words per m<strong>in</strong>ute and write orcopy at a speed of 10 words per m<strong>in</strong>ute and take dictation at the speed of not less than 7 words per m<strong>in</strong>ute <strong>in</strong> anylanguage.4. Indonesia A person is considered as literate who can recognize alphabets, read simple words, signs his / her name (eligibility forvot<strong>in</strong>g) able to read and understand a letter, or able to read certa<strong>in</strong> part of certa<strong>in</strong> magaz<strong>in</strong>e or of a certa<strong>in</strong> newspaper.5 Nepal <strong>Literacy</strong> is def<strong>in</strong>ed as the ability to read and write <strong>in</strong> any language, a short statement on every day life of 06 years andabove persons6. Vietnam The def<strong>in</strong>ition of literacy consists of three components viz-a-viz:-a. Read<strong>in</strong>g and writ<strong>in</strong>g the pr<strong>in</strong>ted materials without spell<strong>in</strong>g each word.b. Writ<strong>in</strong>g 80 words <strong>in</strong> 45 m<strong>in</strong>utes without mak<strong>in</strong>g too many mistakes.c. Read<strong>in</strong>g four digit numbers and write legibly the first ten numbers.The above cited def<strong>in</strong>itions from different countries <strong>in</strong>dicate that despite the broaden<strong>in</strong>g of the description of literacy <strong>in</strong> literature, thework<strong>in</strong>g def<strong>in</strong>ition of literacy, as adopted by different countries, has rema<strong>in</strong>ed fairly simple at the skill level.4