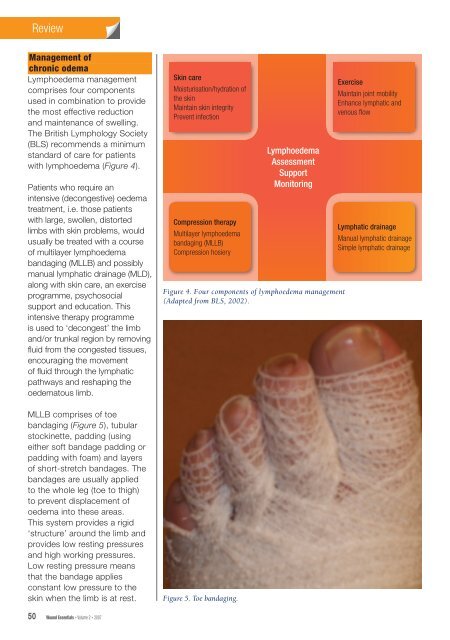
ReviewManagement of<strong>chronic</strong> odemaLymph<strong>oedema</strong> <strong>management</strong>comprises four componentsused <strong>in</strong> comb<strong>in</strong>ation to providethe most effective reductionand ma<strong>in</strong>tenance of swell<strong>in</strong>g.The British Lymphology Society(BLS) recommends a m<strong>in</strong>imumstandard of care for <strong>patients</strong><strong>with</strong> lymph<strong>oedema</strong> (Figure 4).Patients who require an<strong>in</strong>tensive (decongestive) <strong>oedema</strong>treatment, i.e. those <strong>patients</strong><strong>with</strong> large, swollen, distortedlimbs <strong>with</strong> sk<strong>in</strong> problems, wouldusually be treated <strong>with</strong> a courseof multilayer lymph<strong>oedema</strong>bandag<strong>in</strong>g (MLLB) and possiblymanual lymphatic dra<strong>in</strong>age (MLD),along <strong>with</strong> sk<strong>in</strong> care, an exerciseprogramme, psychosocialsupport and education. This<strong>in</strong>tensive therapy programmeis used to ‘decongest’ the limband/or trunkal region by remov<strong>in</strong>gfl uid from the congested tissues,encourag<strong>in</strong>g the movementof fl uid through the lymphaticpathways and reshap<strong>in</strong>g the<strong>oedema</strong>tous limb.MLLB comprises of toebandag<strong>in</strong>g (Figure 5), tubularstock<strong>in</strong>ette, padd<strong>in</strong>g (us<strong>in</strong>geither soft bandage padd<strong>in</strong>g orpadd<strong>in</strong>g <strong>with</strong> foam) and layersof short-stretch bandages. Thebandages are usually appliedto the whole <strong>leg</strong> (toe to thigh)to prevent displacement of<strong>oedema</strong> <strong>in</strong>to these areas.This system provides a rigid‘structure’ around the limb andprovides low rest<strong>in</strong>g pressuresand high work<strong>in</strong>g pressures.Low rest<strong>in</strong>g pressure meansthat the bandage appliesconstant low pressure to thesk<strong>in</strong> when the limb is at rest.Sk<strong>in</strong> careMoisturisation/hydration ofthe sk<strong>in</strong>Ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> sk<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>tegrityPrevent <strong>in</strong>fectionCompression therapyMultilayer lymph<strong>oedema</strong>bandag<strong>in</strong>g (MLLB)Compression hosieryLymph<strong>oedema</strong>AssessmentSupportMonitor<strong>in</strong>gFigure 4. Four components of lymph<strong>oedema</strong> <strong>management</strong>(Adapted from BLS, 2002).Figure 5. Toe bandag<strong>in</strong>g.ExerciseMa<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> jo<strong>in</strong>t mobilityEnhance lymphatic andvenous fl owLymphatic dra<strong>in</strong>ageManual lymphatic dra<strong>in</strong>ageSimple lymphatic dra<strong>in</strong>age50 Wound Essentials • Volume 2 • 2007
ReviewFigure 6. Positive Stemmer’s sign.When the muscles contract andexpand (e.g. dur<strong>in</strong>g exercise)they press aga<strong>in</strong>st the bandageand the pressure <strong>in</strong> the limbtemporarily <strong>in</strong>creases. This<strong>in</strong>creased ‘work<strong>in</strong>g’ pressurestimulates lymphatic pump<strong>in</strong>gand reabsorption of lymph(Moffatt, 2000).Management of <strong>leg</strong> <strong>ulcer</strong>sA graduated, susta<strong>in</strong>edcompression therapy istraditionally used <strong>in</strong> the<strong>management</strong> of <strong>leg</strong> <strong>ulcer</strong>s, <strong>with</strong>a wound dress<strong>in</strong>g selected asappropriate for the specificwound. A layered bandag<strong>in</strong>gsystem is used and is said tobe more effective than s<strong>in</strong>glelayer systems (Fletcher et al,1997). These systems are onlyapplied below the knee anddo not <strong>in</strong>clude the toes. Thebandages are left <strong>in</strong> situ forup to one week. The choiceof dress<strong>in</strong>g and bandag<strong>in</strong>gsystem will depend upon thepatient’s condition, assessmentand patient choice (Dowsett,2005).Management of <strong>leg</strong> <strong>ulcer</strong>sand <strong>chronic</strong> <strong>oedema</strong>: whichbandag<strong>in</strong>g system?Patients <strong>with</strong> <strong>chronic</strong> <strong>oedema</strong>and <strong>ulcer</strong>ation require a differentapproach to treatment thanthose <strong>with</strong> venous <strong>ulcer</strong>ationalone. The specific issuesassociated <strong>with</strong> manag<strong>in</strong>g thepatient <strong>with</strong> lymph<strong>oedema</strong>tous<strong>ulcer</strong>ation <strong>in</strong>clude:8Limb shape distortion8Care of sk<strong>in</strong> creases and folds8Swell<strong>in</strong>g of the toesand forefoot.These issues require a modifiedapproach to the usual venous<strong>leg</strong> <strong>ulcer</strong> bandag<strong>in</strong>g regimens(Moffatt et al, 2005).Patients <strong>with</strong> limb distortionand sk<strong>in</strong> folds or creases willrequire a more specialisedapproach to their careand, if available, work<strong>in</strong>g<strong>in</strong> conjunction <strong>with</strong> alymph<strong>oedema</strong> specialist serviceis useful. The use of padd<strong>in</strong>gor foams is needed to correctthe limb shape, pad out thesk<strong>in</strong> creases and even out thebandage shape to ensure thelimb reta<strong>in</strong>s a cyl<strong>in</strong>drical shape<strong>in</strong> order to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> the correctcompression gradient(Todd, 2000).In many cases where traditionalvenous <strong>leg</strong> <strong>ulcer</strong> bandag<strong>in</strong>g isused for <strong>patients</strong> <strong>with</strong> <strong>chronic</strong><strong>oedema</strong>, <strong>oedema</strong> of the toesand forefoot develops. Oedemaof the toes occurs when thebandages cause pressure onthe dorsum of the foot, push<strong>in</strong>gfluid down <strong>in</strong>to the toes. Wherevenous <strong>leg</strong> <strong>ulcer</strong> bandages havenot been applied far enoughdown the foot, dorsal swell<strong>in</strong>gmay occur. If the lymphatics<strong>in</strong> this area become stagnant,secondary sk<strong>in</strong> changes maytake place (Tiwari, 2003), suchas a positive Stemmer’s sign(Figure 6), thickened sk<strong>in</strong>, orpapillomatosis.It has been suggested thattraditional venous <strong>ulcer</strong>bandag<strong>in</strong>g systems used for<strong>patients</strong> <strong>with</strong> <strong>chronic</strong> <strong>oedema</strong>may result <strong>in</strong> persistent <strong>oedema</strong>of the toes, knees and thighs,exacerbat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>ulcer</strong>ation andprevent<strong>in</strong>g heal<strong>in</strong>g (Williams,2003). ‘Slippage’ of thebandage due to a reduction <strong>in</strong>swell<strong>in</strong>g, particularly <strong>in</strong> the earlydays of treatment can lead to atourniquet effect and can causefurther distortion <strong>in</strong> the shapeof the limb. Hence, MLLB maybe more appropriate for thispatient group.Components of sk<strong>in</strong> careSk<strong>in</strong> careCare of the sk<strong>in</strong> is a majorconcern when manag<strong>in</strong>g<strong>patients</strong> <strong>with</strong> <strong>ulcer</strong>ation52 Wound Essentials • Volume 2 • 2007