Ordinance and Syllabus - Bhagat Phool Singh Mahila ...
Ordinance and Syllabus - Bhagat Phool Singh Mahila ...
Ordinance and Syllabus - Bhagat Phool Singh Mahila ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
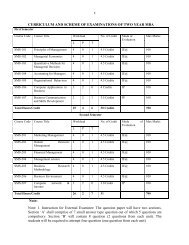
Paper Code: BPL-209Environmental Studies (Environmental Studies)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 004 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Paper Objectives is to become familiar with the Natural Resources,Ecosystems, Biodiversity <strong>and</strong> its Conservation, Environmental Pollution, EnvironmentProtection Act etc.UNIT IUNIT IIThe Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studies: Definition, scope <strong>and</strong>importance. Need for public awarenessNatural Resources: Renewable <strong>and</strong> non- renewable resources. Natural resources <strong>and</strong>associated problems, (a) Forest resources: Use <strong>and</strong> over-exploitation, deforestation,case studies. Timber extraction, mining, dams <strong>and</strong> their effects on forests <strong>and</strong> tribalpeople. (b) Water resources: Use <strong>and</strong> over-utilization of surface <strong>and</strong> ground water,floods, drought, conflicts over water, dams benefits <strong>and</strong> problems. (c) Mineralresources: Use <strong>and</strong> over-exploitation, environmental effects of extracting <strong>and</strong> usingmineral resources, case studies. (d) Food resources: World food problems, changescaused by agriculture <strong>and</strong> over-grazing, effects of modern agriculture, fertilizerpesticideproblems, water logging, salinity, case studies. (e) Energy resources:Growing energy needs, renewable <strong>and</strong> non- renewable energy sources, use ofalternate energy sources, case studies. (f) L<strong>and</strong> resources: L<strong>and</strong> as a resource, l<strong>and</strong>degradation man induced l<strong>and</strong> slides, soil erosion <strong>and</strong> desertification. Role of anindividual in conservation of natural resources. Equitable use of resources foesustainable life styles.Ecosystems: Concept of an ecosystem. Structure <strong>and</strong> function of an ecosystem.Producers, consumers <strong>and</strong> decomposers. Energy flow in the ecosystem. Ecologicalsuccession. Food chains, food webs <strong>and</strong> ecological pyramids. Introduction, types,characteristic features, structure <strong>and</strong> function of the following ecosystem: Forestecosystem, Grassl<strong>and</strong> ecosystem, Desert ecosystem, Aquatic ecosystem (ponds,streams, lakes, rivers, oceans, estuaries)Biodiversity <strong>and</strong> its Conservation: Introduction-Definition: genetic, species <strong>and</strong>ecosystem diversity. Biogeographically classification of India. Value of biodiversity:consumptive use, productive use, social, ethical, aesthetic <strong>and</strong> option values.Biodiversity at global, national <strong>and</strong> local levels. India as a mega-diversity nation. Hotspotsof biodiversity. Threats to biodiversity: habitat loss, poaching of wildlife, manwildlifeconflicts. Endangered <strong>and</strong> endemic species of India. Conservation ofbiodiversity: In-situ <strong>and</strong> Ex-situ conservation of biodiversity.UNIT IIIEnvironmental Pollution: Definition. Causes, effects <strong>and</strong> measures of Air pollution,Water pollution, Soil pollution, Marine pollution, Noise pollution, Thermal pollution,54