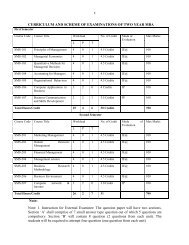
Paper Code: BPL-105PHARMACOLOGY- I (Anatomy, Physiology <strong>and</strong> HealthEducation)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: In this subject emphasis is given to anatomy of different organs of humanbody. The students are familiarized with basic structures, location of different organs whichplay a role in the normal function of human body <strong>and</strong> applied aspects of developmental, gross<strong>and</strong> microscopic anatomy without burdening the students with unnecessary details of basicanatomy. Students are taught the general principles of functions of human body withemphasis on practical applications <strong>and</strong> basic physiological consideration of different systemsof human body. Functional study of different organs <strong>and</strong> their inter-relationship <strong>and</strong> basichistological study of human cells <strong>and</strong> different organs is another important objective.UNIT IIntroduction• Scope of anatomy, physiology <strong>and</strong> basic Terminology used in these subjects.• Introduction to human body & organization of human body.• Functional & structural characteristics of cell, cell components <strong>and</strong> theirfunction.• Detailed structure of cell membrane & physiology of transport process.• Structural & functional characteristics of elementary tissues of human body:epithelial, connective, muscular <strong>and</strong> nervous tissue, <strong>and</strong> their sub-types.Osseous system: Structure, composition & functions of skeleton. Classification ofjoints, types of movements at joints, disorders of joints.Skeletal muscles: Their gross anatomy & physiology of muscle contraction,physiological properties of skeletal muscles <strong>and</strong> their disorders.Haemopoetic system: Composition & function of blood <strong>and</strong> its elements, theirdisorders, blood groups, <strong>and</strong> their significance, mechanism of coagulation, disordersof platelets <strong>and</strong> coagulation.Lymph <strong>and</strong> lymphatic system: Composition, formulation <strong>and</strong> circulation of lymph,disorders of lymph <strong>and</strong> lymphatic system, basic physiology <strong>and</strong> functions of spleen.Respiratory system: Anatomy of respiratory organs, functions of respirationmechanism <strong>and</strong> regulation of respiration, respiratory volumes <strong>and</strong> vital capacity.UNIT II Cardiovascular system: Basic anatomy of heart, physiology of heart, blood vessels <strong>and</strong>circulation. Basic underst<strong>and</strong>ing of cardiac cycle, heart sounds <strong>and</strong> electrocardiogram.Blood pressure <strong>and</strong> its regulation, Brief outline of cardiovascular disorders likehypertension, hypotension, arteriosclerosis, angina, myocardial infraction, congestiveheart failure <strong>and</strong> cardiac arrhythmias. Digestive system: Gross anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract, function of its differentparts including those of liver, pancreas <strong>and</strong> gallbladder, various gastrointestinalsecretions <strong>and</strong> their role in the absorption <strong>and</strong> digestion of food.24
Autonomic nervous system: Physiology <strong>and</strong> functions of the autonomic nervoussystem. Mechanism of neurohumoral transmission in the autonomic nervous system. Central nervous system: Functions of different parts of brain <strong>and</strong> spinal chord.Neurohumoral transmission in the central nervous system, reflux action,electroencephalogram, specialized functions of the brain, cranial nerves <strong>and</strong> theirfunctions.UNIT III Endocrine system: basic anatomy <strong>and</strong> physiology of pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid,adrenals, pancreas, testes <strong>and</strong> ovary, their hormones <strong>and</strong> functions. Urinary system: various parts, structures <strong>and</strong> functions of the kidney <strong>and</strong> urinary tract.Physiology of the urine formation <strong>and</strong> acid base balance. Disease of urinary system. Reproductive system: Male <strong>and</strong> female reproductive systems <strong>and</strong> their hormones,physiology of menstruation, coitus <strong>and</strong> fertilization. Sex differentiation, spermatogenesis<strong>and</strong> oogenesis. Pregnancy its maintenance <strong>and</strong> parturition. Sense organs: Basic anatomy <strong>and</strong> physiology of the eye (vision), ear (hearing), tastebuds, smell <strong>and</strong> skin (superficial receptors).UNIT IV: Health Education:Classification of food requirements, balance diet, nutritional deficiency disorders,their treatment <strong>and</strong> prevention, specification of drinking water.Demography <strong>and</strong> family planning: Demography cycle, family planning, <strong>and</strong> variouscontraceptive methods. Medical Termination of pregnancy.Communicable Diseases: Brief out line of communicable diseases, their causativeagents, modes of transmission <strong>and</strong> prevention (chicken pox, influenza, diphtheria,cough, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, hepatitis, cholera, typhoid, food poisoning,helminthiasis, malaria, filariasis, rabies, trachoma, tetanus, leprosy, syphilis,gonorrhea <strong>and</strong> AIDS).First aid: emergency treatment of shock, snakebites, burns, poisoning, fractures <strong>and</strong>resuscitation methods.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.25
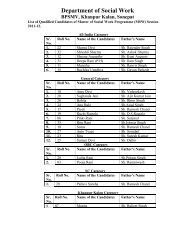
- Page 1 and 2: BPS Mahila Vishwavidyalaya, Khanpur
- Page 3 and 4: 7.2 The examination in each semeste
- Page 5 and 6: 9.4 Adhoc Grace:If there is any dis
- Page 7 and 8: 10. Promotion:11. Division:WhereCi
- Page 9 and 10: 16. General Guidelines:16.1 Where t
- Page 11 and 12: Drug chargesPre-packagingCentral st
- Page 13: Note: Instruction for Examiner:The
- Page 17 and 18: Paper Code: BPL-107 REMEDIAL BIOLOG
- Page 19 and 20: Suggested Readings (Latest Editions
- Page 21 and 22: Paper Code: BPP-113Pharmaceutical C
- Page 23 and 24: Paper Code: BPP-117REMEDIAL BIOLOGY
- Page 25 and 26: products i.e. PVP, Dextran, absorba
- Page 27 and 28: Suggested Readings (Latest Editions
- Page 29 and 30: Note: Instruction for Examiner:The
- Page 31 and 32: Note: Instruction for Examiner:The
- Page 33 and 34: Paper Code: BPP-112 Pharmaceutical
- Page 35 and 36: Paper Code: BPP-116 Pharmaceutical
- Page 37 and 38: measurement, large-scale equipment
- Page 39 and 40: UNIT IVComplexometric Titrations: C
- Page 41 and 42: Pyridine-piperidine: tobacco, areca
- Page 43 and 44: Note: Instruction for Examiner:The
- Page 45 and 46: nuclear hazards, Solid waste manage
- Page 47 and 48: NOTE:Types of listeningStrategies f
- Page 49 and 50: Paper Code: BPP-213 Pharmaceutical
- Page 51 and 52: Paper Code: BPL-202Pharmaceutical C
- Page 53 and 54: Paper Code: BPL-204Pharmaceutical C
- Page 55 and 56: Paper Code: BPL-206Pharmaceutics-V
- Page 57 and 58: Paper Code: BPL-208Computer Science
- Page 59 and 60: Paper Code: BPL-210Pharmaceutical M
- Page 61 and 62: Paper Code: BPP-212Pharmaceutical C
- Page 63 and 64: Paper Code: BPP-216Pharmaceutics-V
- Page 65 and 66:
Paper Code: BPL-301 Pharmaceutical
- Page 67 and 68:
Paper Code: BPL-303 Pharmaceutics-V
- Page 69 and 70:
Paper Code: BPL-305Pharmaceutics-VI
- Page 71 and 72:
Paper Code: BPL-307Pharmacology-II
- Page 73 and 74:
Paper Code: ENG-301Communication Sk
- Page 75 and 76:
Paper Code: FFA-100Communicative Fr
- Page 77 and 78:
Paper Code: LAW- 001Legal LiteracyL
- Page 79 and 80:
Paper Code: BPP-309Pharmaceutical C
- Page 81 and 82:
Paper Code: BPP-313Pharmaceutics-VI
- Page 83 and 84:
Propanthaline bromide, Benzhexol, O
- Page 85 and 86:
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The
- Page 87 and 88:
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions
- Page 89 and 90:
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The
- Page 91 and 92:
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions
- Page 93 and 94:
Paper Code: BPP-314Pharmaceutics-VI
- Page 95 and 96:
Paper Code: BPP-318Pharmacology-III
- Page 97 and 98:
Nifedipine, Procainamide, Verapamil
- Page 99 and 100:
Packaging of Pharmaceutical Product
- Page 101 and 102:
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The
- Page 103 and 104:
UNIT IVAnti-epileptics drugs.Anti-P
- Page 105 and 106:
Types of closures used for the ster
- Page 107 and 108:
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions
- Page 109 and 110:
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions
- Page 111 and 112:
Paper Code: BPP-417Pharmaceutics -X
- Page 113 and 114:
Paper Code: BPP-421Pharmacology-IV
- Page 115 and 116:
Paper Code: BPL-402Pharmaceutical C
- Page 117 and 118:
Paper Code: BPL-404Pharmaceutical C
- Page 119 and 120:
Paper Code: BPL-406Pharmaceutics -X
- Page 121 and 122:
Paper Code: BPL-408Pharmacology-V (
- Page 123 and 124:
Paper Code: BPL-410Pharmacology-VI
- Page 125 and 126:
Paper Code: BPP-412Pharmaceutical C
- Page 127 and 128:
Paper Code: BPP-416Pharmaceutics -X