Ordinance and Syllabus - Bhagat Phool Singh Mahila ...
Ordinance and Syllabus - Bhagat Phool Singh Mahila ...
Ordinance and Syllabus - Bhagat Phool Singh Mahila ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
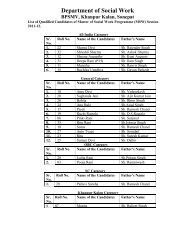
BPS <strong>Mahila</strong> Vishwavidyalaya, Khanpur Kalan (Sonepat)1.Definitions:School of Pharmaceutical Education & ResearchORDINANCEBachelor of Pharmacy(w.e.f. session 2012-13)1.1 Programme st<strong>and</strong>s for Bachelor of Pharmacy (B. Pharm.).1.2 Credit is the weightage assigned to a paper in terms of contacthours.1.3 Grade st<strong>and</strong>s for a letter grade assigned to a student on the basis of evaluationof a paper on the 10 point scale.1.4 Grade Point st<strong>and</strong>s for the numerical equivalent of the letter grade.2. Duration:3. Admissions:The normal duration of Bachelor of Pharmacy programme offered by School ofPharmaceutical Education & Research for a student admitted in I semester isfour years, comprising of eight semesters <strong>and</strong> the maximum duration tocomplete the programme is six years.The normal duration of Bachelor of Pharmacy programme for a studentadmitted in III semester (Lateral Entry) is three years, comprising of sixsemesters <strong>and</strong> the maximum duration to complete the programme is fiveyears.3.1 Eligibility3.1.1 For B Pharmacy I Semester: A female c<strong>and</strong>idate should be pass in10+2 examination from recognized Board/University with Physics &Chemistry as compulsory subjects <strong>and</strong> along with anyone of the followingsubjects:a) Mathematicsb) Biologyc) Bio-Technologyd) Computer ScienceObtained at least 45% marks (40% in case of c<strong>and</strong>idate belonging to reservedcategories) marks in above subjects taken together. Eligibility Criteria may bechanged time to time as per regulatory bodies/ the decisions of the Universityauthorities.3.1.2 For B Pharmacy III Semester: Lateral Entry to the Third Semester B.Pharmacy shall be open to the female c<strong>and</strong>idate who has qualified Diploma inPharmacy paper, from any institute approved by Pharmacy Council of India,11
3.2 ProcedureNew Delhi, obtaining at least 50% marks in aggregate of all semesters /Yearsin D. Pharmacy (45% in case of c<strong>and</strong>idate belonging to reserved categories)Eligibility Criteria may be changed time to time as per regulatory bodies/ thedecisions of the University authorities.3.1.3 No female c<strong>and</strong>idate who is in employment (full-time, part-time, orhonorary service) shall be eligible to take admission in Bachelor of Pharmacyprogramme without taking leave from her office/ institution etc. from the dateof admission to the termination of the examination/ including other essentialrequirements. She has to submit an affidavit in this regard. If found inviolation of this rule her admission shall st<strong>and</strong> cancelled.For B Pharmacy I & III Semester: Admissions will be made on the basis ofmerit/ entrance/ any other criteria decided by the University time to time.4. Fee:The programme fee shall be paid by the c<strong>and</strong>idate as prescribed by theUniversity from time to time.5. Teaching Methodology:6. Credit Weightage:7. Examination:The methods of teaching shall include classroom instructions, assignments,practical, seminars, workshops, skill in computer, etc. The medium ofinstruction shall be English.Each paper has a certain number of credits which reflect its weightage. Creditsof a paper are evaluated as under:6.1 Lecture: One credit per lecture per week per semester will generally beadopted.6.2 Tutorial: Half credit per tutorial hour per week per semester will beadopted.6.3 Practical: Half credit per hour per week per semester will be assigned.6.4 Independent Study / Seminar / Project: Weightage equivalent to theorypaper will be assigned.7.1 At the end of the each semester, there shall be an examination where eachc<strong>and</strong>idate shall be examined in the paper studied by them in that semester.Each semester examination shall be designated as first semester examination,second semester examination, third semester examination <strong>and</strong> so on.12
7.2 The examination in each semester will be held according to the syllabiapproved by the Board of Studies. The panel of Examiners shall be appointedfor each paper <strong>and</strong> shall be recommended by the Under Graduate Board ofStudies (UG BOS).7.3 The examination shall consist of theory papers <strong>and</strong> practical examination.Theory papers are to be set by the internal/ external paper setters appointed bythe Vice Chancellor from a panel of examiners submitted by the Chairpersonof the B. Pharmacy Department dully approved by the BOS of the concerneddepartment.7.4 Practical examination shall be conducted jointly by the external &internal examiners. If an external examiner is not able to join, alternateexaminer (including those of the same University Department) may beappointed by the Chairperson of the B. Pharmacy Department with theintimation to the Controller of Examination in the following preferential order:(i) From outside (ii) From BPSMV, Khanpur Kalan7.5 The examination for all odd semesters will normally be held in December/January <strong>and</strong> for all even semesters in May/ June on such dates as provided bythe University. The concerned teacher/ paper coordinator should ensure that100% syllabus is covered in each subject before the semester examination.7.6 Every paper is coordinated by a member of the teaching staff of thedepartment which is offering the paper in a given semester. This facultymember is called the paper coordinator. He/ She has the full responsibility ofconducting the paper, coordinating the work of the other members of thefaculty involved in the paper, holding the midterm class tests (sessionals) &other components prescribed for internal evaluation . For any difficulty, thestudent is expected to approach the paper coordinator for advice &clarification. All the responsibilities from teaching to the submission ofawards will be of the paper coordinator.7.7 Every student has to appear in the two midterm class tests (sessionals) &other components prescribed for internal evaluation. The marks obtained inthe internal evaluation are to be submitted to the examination branch dulysigned by the Chairperson of the B. Pharmacy Department before the close ofsemester examination.7.8 If a c<strong>and</strong>idate, after attending the classes for the paper of studies in the B.Pharmacy Department either not appeared or having appeared in any semesterexamination has failed in one or more papers for that examination, she canappear for such papers in supplementary examinations without attending afresh paper of studies for that semester, such a c<strong>and</strong>idate may, in themeantime, prosecute her studies for the next semesters.7.9 Two midterm class tests will be conducted as per time table prescribed bythe Chairperson of the B. Pharmacy Department. Examination of othercomponents may be conducted by teacher concerned.13
8. Reappear / Supplementary Examination:Supplementary Examinations For:S.No. Semester Schedule1I Along with regular students of I semester.2II Along with regular students of II semester.3III Along with regular students of III semester.4IV Along with regular students of IV semester.5V Along with regular students of V semester.6VI Along with regular students of VI semester.7VII In all subsequent examinations.8VIII In all subsequent examinations.9. Evaluation <strong>and</strong> Grading:9.1 The assessment will be 50% internal <strong>and</strong> 50% external9.2 The student will have to qualify internal <strong>and</strong> external examinationsseparately.9.3 The weightage for internal evaluation shall be assigned by coveringfollowing areas broadly:For Theory Papers:ComponentWeightage9.3.1 Two midterm class tests (Sessionals) =60%9.3.2 Assignments/Quiz’s/On the Spot testSeminars/Presentations/Group DiscussionsCase Studies/Minor Projects/Industry Interface =30%9.3.3 General Performance(Active classroom participation, Attendance etc.) =10%For Laboratory/ Practical Papers:ComponentWeightage9.3.4 Day to Day assessment = 60%9.3.5 Viva-Voce & Laboratory Record =30%9.3.6 General Performance(Active Laboratory participation, Attendance etc.) =10 %14
9.4 Adhoc Grace:If there is any discrepancy/ out of syllabus /printing error / untowardincident during the examination, the matter be referred to a St<strong>and</strong>ingcommittee of:(i)(ii)(iii)Controller of Examinations.HOD of the Pharmacy Department.One faculty member concerning the subject.The Committee may recommend re-conduct the paper or uniform grace marksto all but that should not exceed 10% marks of that particular paper.9.5 Moderation of Marks:(a)Internal Examinations: If there are more than one teacher associated inany internal assessment, one of the member be made coordinator by theconcerned HOD <strong>and</strong> he along with the others can moderate the marks tomaintain uniformity so that no student get undue advantage or disadvantage.(b)External Examinations: If there is unusual variation (very high or verylow) in the awards, the COE may refer the matter to a Moderation Committeeconsisting of(i)(ii)(iii)Controller of Examinations.HOD of the Pharmacy Department.One faculty member concerning the subject.As per recommendation of the committee the result may be revised.9.6 In case, the c<strong>and</strong>idate is fail or has failed in the internal examination, theinternal examiner may conduct the re-examination as <strong>and</strong> when feelsuitable with prior approval of the Head of the Department.9.7 Grading:The academic performance of a student shall be graded on a scale asprescribed by the Examination Branch of the University. The departmentconcerned shall only prescribe the pass grade.9.7.1 After finalization of the marks, the same shall be displayed on thedepartment notice board for duration of two days for information of students.Students, who have a specific grievance against the marks awarded to her,may discuss the same with the concerned Paper Coordinator who afterconsideration of the grievance of all the students shall finalize the marks to beawarded for the paper.9.7.2 Before submission of the finalized award list in a prescribed formation tothe concerned administrative office, the individual Paper coordinator shalldiscuss the marks distribution of his/her Faculty of Study. However, the finaldiscussion with regard to marks will rest with the Paper Coordinator.15
9.7.3 On receipt of the award list for all papers offered by a given Faculty ofStudy the concerned administrative office shall put up the consolidated resultsfor that Faculty for discussion <strong>and</strong> approval from the Department StaffCouncil (All Faculty Members).9.7.4 The academic performance of a student shall be graded on ascale prescribed by the University as follows:Academic Performance Letter Grades Grade Points (G)Outst<strong>and</strong>ing A+ 10Extra Ordinary A 09Excellent B+ 08Very Good B 07Good C+ 06Average C 05Poor D 04Very Poor E 03The award of grades based upon marks obtained out of 100 shall be made asfollows:Marks Grade Marks90 ≤ A+ ≤ 10080 ≤ A ≤ 8970 ≤ B+ ≤ 7960 ≤ B ≤ 6950 ≤ C+ ≤ 5940 ≤ C ≤ 4930 ≤ D ≤ 3920 ≤ E ≤ 29Note: 1. The pass percentage is 50%, Pass Grade is Grade C+ <strong>and</strong> highergrades.2. Grades C, D <strong>and</strong> E are fail grades.9.7.5 Calculation of Semester Grade Point Average (SGPA) &Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA):The Grade Point Average is calculated as follows:GPA= ∑ (Number of credits x Grade Points)∑ (Number of Credits Registered)For the purpose of calculation of GPA for SGPA only those papers (includingprojects) will be taken into account in which the student has been awardedpass grade. Here S st<strong>and</strong>s for the sum of(i) SGPA= ∑Ci Pi∑Ci16
10. Promotion:11. Division:WhereCi = Number of credits earned in the i th paper of a semester for whichSGPA is to be calculated.Pi = Grade point earned in i th paperI = 1, 2, 3,…………………..n, represent the number of papers in which astudent is registered in the concerned semester.(ii) CGPA= ∑Cj Pj∑CjWhereCj = Number of credits earned in the j th paper upto the semester for whichCGPA is calculated.Pj = Grade point earned in the j th paper. Any grade lower than the pass gradein a paper shall not be taken into account.J =1,2,3,………….n, represent the number of papers in which student wasregistered <strong>and</strong> obtained a grade not lower than C upto the semester for whichCGPA is to be calculated.9.7.6 If the c<strong>and</strong>idate is not satisfied with the evaluation of the answer sheetof Semester examination, she may apply to the controller of Examinations forre-evaluation in accordance with the rules laid down by the University in thisregard.10.1 A c<strong>and</strong>idate must qualify at least 50 % papers of B. Pharmacy I Sem., IISem., III Sem. & IV Semester (taken together) to be allowed to admit in B.Pharmacy V Semester.10.2. A c<strong>and</strong>idate must qualify at least 50 % papers of B. Pharmacy III Sem.,IV Sem., V Sem. & VI Semester (taken together) to be allowed to admit in B.Pharmacy VII Semester.The successful c<strong>and</strong>idates shall be classified in two divisions as under:(i)(ii)12. Scholarship:Those who obtained 60% or more of the aggregate number of marks,in all the subjects in all semesters taken together, shall be placed infirst division.Those who obtained less than 60% but not less than 50% of theaggregate number of marks, in all subjects in all semesters takentogether, shall be placed in the second division.A c<strong>and</strong>idate while appearing in the re-appear examination shall not be eligiblefor a scholarship, a prize or a medal.17
13. Declaration of Results:14. Improvement Case:Six weeks after the termination of the examination or as soon as possible, thecontroller of examination shall declare the result. After successful completionof the course, the c<strong>and</strong>idate shall be awarded a degree mentioning the division.(i)(ii)(iii)(iv)(v)A person who has qualified for the award of B. Pharmacy Course fromthis university may be allowed to re-appear as an ex-student in at themost two subject(s) in which she appeared earlier, with a view toimprove her previous performance. The c<strong>and</strong>idate shall be awardedonly two consecutive chances along with the re-appear students in thesubject(s) concern immediately after her passing for her degree.No c<strong>and</strong>idate shall be eligible for improvement after one year ofpassing the examination for the degree course.The C<strong>and</strong>idate will have to deposit fee <strong>and</strong> form for each examinationseparately.The higher score in the subject(s) in which she re-appears forimprovement will be taken into account towards the final result <strong>and</strong> themarks already obtained by the c<strong>and</strong>idate in the subjects in which shehas not opted to improve her result shall be carried forward. Thec<strong>and</strong>idate shall be awarded a new DMC clearly mentioning‘Improvement case’ subject(s) with improved marks, only <strong>and</strong> thenew gr<strong>and</strong> total.In case the c<strong>and</strong>idate does not improve her result, it shall be declaredas ‘Previous Result St<strong>and</strong>s’.15. Attendance:15.1 No c<strong>and</strong>idate shall be considered to have pursued a regular paper of thestudy unless she has attended not less than 75% of the classes in eachpaper. A deficiency up to 10% may be condoned by the Chairperson ofthe department. In some special cases the Hon’ble Vice-Chancellor maycondone a further 5%.15.2 If a student is absent from the Department for more than four weekswithout intimating to the Chairperson/Paper coordinator of thedepartment, her name will be struck off from the department rolls withinformation to the Academic Branch.15.3 In case the student name is struck off due to nonpayment of fee <strong>and</strong> is readmittedlater, her attendance shall not be counted for that period.18
16. General Guidelines:16.1 Where this document is silent about any rule, the UniversityPolicy/Regulations from time to time will be applicable.16.2 Admission, teaching schedule, preparatory holidays, examination, winter,summer vacation, shall be followed as specified in academic calendar ofthe university.16.3 A student is deemed to have completed the requirements for the degree<strong>and</strong> is eligible for the award of degree if:16.3.1 She has satisfied all the academic requirements as per theregulations; <strong>and</strong>16.3.2 She has pay all fees due from her; <strong>and</strong>16.3.3 There is no case of indiscipline pending against her.16.3.4 Satisfied the minimum academic <strong>and</strong> residence requirements;16.3.5 Satisfactorily completed the requirements for the sort durationacross-curricular paper, industry internship <strong>and</strong> NCC/NSS asmay be prescribed by the Academic council;16.3.6 A student who has completed the entire graduation requirementlisted above shall be eligible for award of degree / certificate.However, under extremely exceptional circumstances, wheregross violation of the graduation requirements is detected atany later stage, the Academic Council may recommend towithdraw the degree/PG diploma already awarded.16.4 The gap of one/two semesters missed by the student(s), as the case maybe, will count towards the total duration of the programme permissibleunder the regulations.16.5 Absence of registered students from classes during a semester shall bediscouraged. However, for bonafied reasons such as illness, maternity, astudent may grant leave of absence as per provision of leave rules forstudents framed by the Academic Council.16.5 All academic problems of the students other than those affecting theUniversity rules <strong>and</strong> regulations framed from time to time may be lookedinto by a committee constituted by the Dean Academic Affairs.19
Paper Code: BPL-101PHARMACEUTICS-I (Dispensing <strong>and</strong> Hospital Pharmacy)L -- T -- PTotal Credits:044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:Pharmaceutical dispensing, practice <strong>and</strong> pharmacy: It is essential for a pharmacist toknow while working in a pharmacy as how to prepare <strong>and</strong> supply medicines. This requiresthe knowledge of stability of medicines <strong>and</strong> their ingredients, principle of compounding,dosage, chemical, physical <strong>and</strong> therapeutic incompatibility, packaging methods, labelingprocedures, legal requirements affecting drug storage, supply <strong>and</strong> records, containers <strong>and</strong>labeling of substances <strong>and</strong> misuse of drugs.UNIT IDefinitions <strong>and</strong> General Dispensing Procedures.Sources of information required for Pharmacists <strong>and</strong> History of Pharmacopoeias (I.P.,B.P., <strong>and</strong> U.S.P.).Sources of error <strong>and</strong> care required in dispensing prescriptions.Pharmaceutical Latin-Latin Terms used in prescriptions <strong>and</strong> their English equivalents.Types of Dispensed products.Containers, closures <strong>and</strong> labelling for dispensed products.Colours, Flavours, Sweeteners <strong>and</strong> other additives used in prescriptions.UNIT IIPrinciples involved <strong>and</strong> procedures adopted in dispensing of typical preparations likemixtures, emulsion, creams, ointments, powders, pastes, jellies, suppositories,ophthalmics, pastilles, lozenges, pills, lotions, liniments, inhalations, paints, spraysetc.Incompatibilities: Physical <strong>and</strong> chemical, occurrence <strong>and</strong> methods adopted incorrections.UNIT III: Pharmaceutical CalculationsPercentage solutions, enlarging <strong>and</strong> reducing recipes, calculation of doses, alligation,alcohol dilutions, proof spirit, isotonic solutions, milli-equivalents, displacementvalue etc.UNIT IV: Hospital <strong>and</strong> its organisation:Pharmacy, organisation <strong>and</strong> personnelHospital formularyPurchasing <strong>and</strong> inventory controlDrug distributionDispensing to inpatientsDispensing to outpatients20
Drug chargesPre-packagingCentral sterile supplyDrug information centreMaintenance of recordsSafe use of medicinesNote: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions)1. Cooper <strong>and</strong> Gunn’s, “Dispensing for Pharmaceutical Students”, Delhi: CBSPublishers.2. R. M. Mehta, “Dispensing Pharmacy”, New Delhi: Vallabh Prakashan.3. B.M. Mithal, “A Text book of Pharmaceutical Formulations”, Delhi: VallabhPrakashan.4. John E. Hoover, “Dispensing of Medication”, Easton: Mack Publishing Co.5. William E. Hassan, “Hospital Pharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.6. M. J. Stoklosa, “Pharmaceutical Calculation”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.7. Joel L. Zatz, “Pharmaceutical Calculations”, New York: John Wiley <strong>and</strong> Sons.8. M. C. Attwood <strong>and</strong> J. T. Fell, “Text Book of Hospital Pharmacy”, Oxford: BlackwellScientific Publications.9. Mitchell J. Stklosa & Howard C. Ansel, “Pharmaceutical Calculations”, Philadelphia:Lippincott Williams & Wilkins publisher.21
Paper Code: BPL-103 PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY-I (Inorganic Chemistry)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Inorganic chemicals have been used in pharmacy <strong>and</strong> medicine for NewYork reasons ranging from therapeutic to nutritional supplements to pharmaceuticalnecessities. The paper is designed to study the principles of inorganic chemistry topharmaceuticals <strong>and</strong> to study those inorganic agents used as pharmaceutical aids <strong>and</strong>necessities or as therapeutics <strong>and</strong> diagnostic agents.UNIT IImpurities, Limit test for iron, lead, heavy metals, chloride & sulphate.An outline of the methods of preparation, uses, sources of impurities, tests for purity<strong>and</strong> identity <strong>and</strong> special tests if any, of the following classes of inorganicpharmaceuticals included in Indian Pharmacopoeia monograph details:• Gastrointestinal agents: Acidifying agents, antacids, protectives <strong>and</strong>adsorbents, cathartics;• Major extra <strong>and</strong> intra cellular electrolytes: Physiological anions,electrolytes used for replacement therapy, acid base balance <strong>and</strong> combinationtherapy.• Acids & Bases: Buffers, Water;UNIT IIEssential <strong>and</strong> trace elements: Transition elements <strong>and</strong> their compounds ofpharmaceutical importance: iron <strong>and</strong> haematinics, mineral supplements. Cationic <strong>and</strong>anionic compounds of inorganic drug useful for systemic effects.Topical agents: Protectives, astringents <strong>and</strong> anti-infectives.UNIT IIIGases <strong>and</strong> vapours: Oxygen, anesthetics <strong>and</strong> respiratory stimulants.8. Dentalproducts: dentifrices, anti-caries agent.Complexing <strong>and</strong> chelating agents used in therapy.Miscellaneous agents: Sclerosing agents, expectorants, emetics, poisons <strong>and</strong>antidotes, sedatives etc.UNIT IVPharmaceutical aids used in pharmaceutical industry: Antioxidants,preservatives,filter aids, adsorbents, diluents, excipients, suspending agents, colorants etc.Inorganic radiopharmaceuticals: Nuclear radiopharmaceuticals, reactions,nomenclature, methods of obtaining their st<strong>and</strong>ards <strong>and</strong> units of activity, measurementof activity, clinical applications <strong>and</strong> dosage, hazards <strong>and</strong> precautions.22
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A. I. Vogel, “Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis”, London: ELBS/Longman.2. J. H. Block, E. Roche, T. O. Soine <strong>and</strong> C. O. Wilson, “Inorganic Medicinal <strong>and</strong>Pharmaceutical Chemsitry”, Philadelphia PA: Lea <strong>and</strong> Febiger.3. “Pharmacopoeia of India”, Govt. of India, Ministry of Health.4. L.A. Diseher, “Modern Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry”. New Delhi:Pharmacopoeia of India, Govt. of India, Ministry of Health, (All Edns.)23
Paper Code: BPL-105PHARMACOLOGY- I (Anatomy, Physiology <strong>and</strong> HealthEducation)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: In this subject emphasis is given to anatomy of different organs of humanbody. The students are familiarized with basic structures, location of different organs whichplay a role in the normal function of human body <strong>and</strong> applied aspects of developmental, gross<strong>and</strong> microscopic anatomy without burdening the students with unnecessary details of basicanatomy. Students are taught the general principles of functions of human body withemphasis on practical applications <strong>and</strong> basic physiological consideration of different systemsof human body. Functional study of different organs <strong>and</strong> their inter-relationship <strong>and</strong> basichistological study of human cells <strong>and</strong> different organs is another important objective.UNIT IIntroduction• Scope of anatomy, physiology <strong>and</strong> basic Terminology used in these subjects.• Introduction to human body & organization of human body.• Functional & structural characteristics of cell, cell components <strong>and</strong> theirfunction.• Detailed structure of cell membrane & physiology of transport process.• Structural & functional characteristics of elementary tissues of human body:epithelial, connective, muscular <strong>and</strong> nervous tissue, <strong>and</strong> their sub-types.Osseous system: Structure, composition & functions of skeleton. Classification ofjoints, types of movements at joints, disorders of joints.Skeletal muscles: Their gross anatomy & physiology of muscle contraction,physiological properties of skeletal muscles <strong>and</strong> their disorders.Haemopoetic system: Composition & function of blood <strong>and</strong> its elements, theirdisorders, blood groups, <strong>and</strong> their significance, mechanism of coagulation, disordersof platelets <strong>and</strong> coagulation.Lymph <strong>and</strong> lymphatic system: Composition, formulation <strong>and</strong> circulation of lymph,disorders of lymph <strong>and</strong> lymphatic system, basic physiology <strong>and</strong> functions of spleen.Respiratory system: Anatomy of respiratory organs, functions of respirationmechanism <strong>and</strong> regulation of respiration, respiratory volumes <strong>and</strong> vital capacity.UNIT II Cardiovascular system: Basic anatomy of heart, physiology of heart, blood vessels <strong>and</strong>circulation. Basic underst<strong>and</strong>ing of cardiac cycle, heart sounds <strong>and</strong> electrocardiogram.Blood pressure <strong>and</strong> its regulation, Brief outline of cardiovascular disorders likehypertension, hypotension, arteriosclerosis, angina, myocardial infraction, congestiveheart failure <strong>and</strong> cardiac arrhythmias. Digestive system: Gross anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract, function of its differentparts including those of liver, pancreas <strong>and</strong> gallbladder, various gastrointestinalsecretions <strong>and</strong> their role in the absorption <strong>and</strong> digestion of food.24
Autonomic nervous system: Physiology <strong>and</strong> functions of the autonomic nervoussystem. Mechanism of neurohumoral transmission in the autonomic nervous system. Central nervous system: Functions of different parts of brain <strong>and</strong> spinal chord.Neurohumoral transmission in the central nervous system, reflux action,electroencephalogram, specialized functions of the brain, cranial nerves <strong>and</strong> theirfunctions.UNIT III Endocrine system: basic anatomy <strong>and</strong> physiology of pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid,adrenals, pancreas, testes <strong>and</strong> ovary, their hormones <strong>and</strong> functions. Urinary system: various parts, structures <strong>and</strong> functions of the kidney <strong>and</strong> urinary tract.Physiology of the urine formation <strong>and</strong> acid base balance. Disease of urinary system. Reproductive system: Male <strong>and</strong> female reproductive systems <strong>and</strong> their hormones,physiology of menstruation, coitus <strong>and</strong> fertilization. Sex differentiation, spermatogenesis<strong>and</strong> oogenesis. Pregnancy its maintenance <strong>and</strong> parturition. Sense organs: Basic anatomy <strong>and</strong> physiology of the eye (vision), ear (hearing), tastebuds, smell <strong>and</strong> skin (superficial receptors).UNIT IV: Health Education:Classification of food requirements, balance diet, nutritional deficiency disorders,their treatment <strong>and</strong> prevention, specification of drinking water.Demography <strong>and</strong> family planning: Demography cycle, family planning, <strong>and</strong> variouscontraceptive methods. Medical Termination of pregnancy.Communicable Diseases: Brief out line of communicable diseases, their causativeagents, modes of transmission <strong>and</strong> prevention (chicken pox, influenza, diphtheria,cough, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, hepatitis, cholera, typhoid, food poisoning,helminthiasis, malaria, filariasis, rabies, trachoma, tetanus, leprosy, syphilis,gonorrhea <strong>and</strong> AIDS).First aid: emergency treatment of shock, snakebites, burns, poisoning, fractures <strong>and</strong>resuscitation methods.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.25
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. C. C. Chatterjee, “Human Physiology”, Calcutta: Medical Allied Agency2. G. J. Tortora , “Principles of Anatomy <strong>and</strong> Physiology”, New York:Harper & rowPublishers,.3. N. S. Parmar, “Health Education <strong>and</strong> Community Pharmacy”, New Delhi: CBSPublishers <strong>and</strong> Distributors.4. Guyton, “Textbook of Medical Physiology”, New York: W B Sannders Company.5. “Samson Wright’s Applied Physiology”, Oxford University Press.6. “Best <strong>and</strong> Taylor’s Physiological Basis of Medical Practice”, Baltimore: William <strong>and</strong>Willkins.7. B. D. Chaurasia, “Human Anatomy”, New Delhi: CBS Publishers <strong>and</strong> Distributors.26
Paper Code: BPL-107 REMEDIAL BIOLOGY (REMEDIAL BIOLOGY)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 022 -- -- Total Marks: 50External Marks: 25Internal Marks: 25Paper Objectives: This paper is for the students who did not have Biology at 10+2 level.The paper envisages studying the elementary biological science which includes study ofgeneral botany, Biotechnology, evolution of human life, sex determination, structure <strong>and</strong>function of human systems which find further application is pharmaceutical science.UNIT IMethods of classification of plants.Plant cell: its structure <strong>and</strong> non-living inclusions, mitosis <strong>and</strong> meiosis, different typesof plant tissues <strong>and</strong> their functions.UNIT IIMorphology <strong>and</strong> histology of root, stem, bark, wood, leaf, flower, fruit <strong>and</strong> seed.Modification of root <strong>and</strong> stem.UNIT IIIGeneral survey of animal kingdom, structure <strong>and</strong> life history of parasites as illustratedby amoeba, trypanosoma, plasmodium, taenia, ascaris.UNIT IVGeneral structure <strong>and</strong> life history of insects like mosquito, houseflies <strong>and</strong> silkworm.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in this theory subject shall be of 25 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units & it would be compulsory. Two questions will be setfrom each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. Each Question shall be of05 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A Fahn , “Plant Anatomy”, London: Pergamon Press.2. B. M. Johri, “Reproductive Biology of Plants”, Mumbai: Narosa publishing House.3. S. C. Rastogi, “Concepts in Molecular Biology”, Mumbai: Willey eastern Ltd.4. Claude a. Villee, “Introduction to Animal Biology”, Philadelphia: W. D. Saunders co.27
Paper Code: BPL-109 REMEDIAL MATHEMATICS (REMEDIALMATHEMATICS)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: This paper is for the students who did not have Mathematics at 10+2level. Mathematics is the language of science. The study of mathematics is important as allthe equations used in pharmacokinetics <strong>and</strong> pharmaco-dynamics are in the mathematicalforms <strong>and</strong> studies of such results are in logarithmic <strong>and</strong> integration forms.UNIT-IAlgebra : Revision on equation reducible to quadratics <strong>and</strong> simultaneous equations (linear<strong>and</strong> quadratic) up to two variable only.Determinants <strong>and</strong> their six important properties, solutions of simultaneous equations byCramar's rule.UNIT-IIMatrices: Definition of special matrices (like unit, singular, diagonal matrices etc.) arithmeticoperation on matrices, transpose, adjoint reciprocal <strong>and</strong> inverse of a matrix, solution ofsimultaneous equations using matrices.Partial fractions <strong>and</strong> resolution of linear <strong>and</strong> quadratic (non-repeated) partial functions.Evaluation of En, En 2 <strong>and</strong> En 3UNIT-IIITrigonometry: Revision on angle measurement <strong>and</strong> T-ratios addition, subtraction <strong>and</strong>transformation formulae. T-ratio of multiple, sub multiple <strong>and</strong> allied angles, solution ofsimple trigonometric identities based on above concepts.UNIT-IVPharmaceutical application of logarithms. Analytical plane geometry: Cartesian co-ordinates,distance between two points, area of triangle, locus of a point, straight line, slope <strong>and</strong>intercept form, general equation of first degree.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.28
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Dinodoia, J <strong>and</strong> Chugh, “Elements of Pharmaceutical Mathematics” (Vol.I <strong>and</strong>Vol.II), New Delhi: Jeevonsons Publications.2. G. D. Dhall , S.N. Chhibbar , H.O. Trivedi <strong>and</strong> S. Ch<strong>and</strong>ra , “Frank Mathematics forB.Pharma”, New Delhi: Frank Bros. & Co. Ltd.3. Bradley <strong>and</strong> Smith, “Calculus”, New Jersey USA: Prentice Hall.4. W. Hungerford Thomas , “Algebra” ,New York: Springer.5. N. Piskunov , “Differtial <strong>and</strong> Integral Calculus”, Vol-II, Noida: G K Publishers Pvt.Ltd.6. S. T.Rizvi, “Algebra <strong>and</strong> its Applications”, New Delhi: Narosa Book Distributors Pvt.Ltd.29
Paper Code: BPP-111 PHARMACEUTICS-I Practical (Dispensing <strong>and</strong> HospitalPharmacy)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion including dispensing of preparations like Emulsions Suspensions Solutions Creams Ointments Inhalations Liniments Paints Syrups Mixtures Pastes PowdersSuggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Cooper <strong>and</strong> Gunn’s, “Dispensing for Pharmaceutical Students”, Delhi: CBSPublishers.2. M. C. Attwood <strong>and</strong> J. T. Fell, “Text Book of Hospital Pharmacy”, Oxford: BlackwellScientific Publications.3. Mitchell J. Stklosa & Howard C. Ansel, “Pharmaceutical Calculations”, Philadelphia:Lippincott Williams & Wilkins publisher.30
Paper Code: BPP-113Pharmaceutical Chemistry-I Practical (Inorganic Chemistry)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50 The background <strong>and</strong> systemic qualitative analysis of inorganic mixtures up to 4radicals. Six mixtures to be analyzed, preferably by semi-micro methods. Allidentification tests for pharmaceutical, inorganic pharmaceutical <strong>and</strong> qualitative testsfor cations <strong>and</strong> anions as included in the appendix of IP should be carried out. Limittests for iron, lead, heavy metals, chloride & sulphate should be performed..Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Y.D. Jigyasu, S.R. Upendra & B.B.Sharma,Systemic Modern Practical Chemistry,Part-I, New Delhi, Kalyani Publishers.2. “Pharmacopoeia of India”, Govt. of India, Ministry of Health.3. Dhake & Belsare, “Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry (Practical)”, U.S.A: OxfordUniversity Press.31
Paper Code: BPP-115PHARMACOLOGY- I Practical(Anatomy, Physiology <strong>and</strong> Health Education)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion, some of them may as follows:Study of human skeleton.Study of different systems with the help of charts <strong>and</strong> models.Microscopic study of different tissues.Estimation of hemoglobin in blood. Determination of bleeding time, clotting time,R.B. C. count, T. L. C., D. L. C., <strong>and</strong> E. S. R.Recording of body temperature, pulse rate <strong>and</strong> blood pressure, basic underst<strong>and</strong>ing ofelectrocardiogram-PQRST waves <strong>and</strong> their significance.Simple experiments involved in the analysis of normal <strong>and</strong> abnormal urine: collectionof specimen, appearance, <strong>and</strong> determination of pH, sugar, proteins, urea <strong>and</strong>creatinine.Physiological experiments on nerve-muscle preparations.Determinations of vital capacity, experiments on spirometery.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. G. J. Tortora , “Principles of Anatomy <strong>and</strong> Physiology”, New York:Harper & rowPublishers,.2. B. D. Chaurasia, “Human Anatomy”, New Delhi: CBS Publishers <strong>and</strong> Distributors.3. C. L. Ghai, “A text book of practical physiology”, New Delhi: Jaypee BrothersMedical Publishers (P) Ltd.4. Van de Graaff <strong>and</strong> J.L. Crewley, “A photographic atlas for the anatomy <strong>and</strong>physiology lab.” Englewood (U.S.A): Mortan Publishing.5. R. K. Goyal, “Practical anatomy Physiology <strong>and</strong> biochemistry”, Ahmedabad: B. S.Shah Prakashan.6. F.J. Baker <strong>and</strong> R.E, “Silverton, Introduction to Medical Laboratory Technology”,London: Butterworth & Co. Ltd.32
Paper Code: BPP-117REMEDIAL BIOLOGY Practical (REMEDIAL BIOLOGY)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 50External Marks: 25Internal Marks: 25Number of practicals based on theory portion, some of them may as follows:Morphology of plant parts indicated in theory.Care, use <strong>and</strong> type of microscope.Gross identification of slides of structures <strong>and</strong> life cycle of lower plants/animalsmentioned in theory.Preparation, microscopic examination of stem, root <strong>and</strong> leaf of monocot <strong>and</strong> dicotleaf.Structure of human parasite <strong>and</strong> insects mentioned in theory with the help ofspecimen.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A Fahn , “Plant Anatomy”, London: Pergamon Press.2. Claude a. Villee, “Introduction to Animal Biology”, Philadelphia: W. D. Saunders co.33
Paper Code: BPL-102Pharmaceutics-II (General Pharmacy)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:The objective of this subject is to give an exposure to the students about the basicTerminologies used in pharmacy, basic techniques used in the field of pharmacy, knowledgeabout history <strong>and</strong> origin of pharmacy, different types of properties of pharmaceuticals <strong>and</strong>knowledge about physical processes used in pharmacyUNIT IUNIT II Extraction: Various methods of extraction of crude drugs namely percolation(various types including processes for concentrated preparations, constant hotpercolation), maceration (various types including processes for organized <strong>and</strong>unorganized drugs, for concentrated preparations, double <strong>and</strong> triple macerationprocesses), Decoction. Formulation, preparation <strong>and</strong> uses of various Formulation,preparation <strong>and</strong> uses of pharmaceutical extracts.Liquid Preparations: Formulation, preparation <strong>and</strong> uses of various liquid productsnamely syrups, aromatic waters, spirits, solutions, mucilage, elixirs, glycerin,mouthwashes, gargles, nasal drops, ear drops.Semisolid dosage forms (ointments <strong>and</strong> suppositories): ointment, ointment bases,<strong>and</strong> factors governing selection of ideal base, preparation of ointments.Suppositories-suppositories bases, selection of ideal base, preparation ofsuppositories.UNIT IIIGl<strong>and</strong>ular Products: Introduction, extraction methods <strong>and</strong> preparation of thyroid,liver, pancreas <strong>and</strong> pituitary gl<strong>and</strong>.Surgical dressings: like fibers, fabrics, b<strong>and</strong>ages, surgical ligatures <strong>and</strong> sutures i.e.catgut <strong>and</strong> other absorbable <strong>and</strong> non-absorbable products.UNIT IVImmunology: General introduction, infection, factors influencing infection, kinds ofimmunity, vaccines (i.e. Tetanus vaccine, Diphtheria vaccine, BCG vaccine, smallpox vaccine), virus immunity, toxoids, toxins, diagnostic preparation, sera, antitoxins(i.e. Diphtheria antitoxins, Botulinium antitoxins), brief control of immunologicalproducts-identification tests, toxicity tests, sterility tests, potency tests <strong>and</strong> storage ofimmunological products.Blood <strong>and</strong> related products: Whole human blood, concentrated human RBC, driedhuman plasma, dried human serum, human plasma protein fraction, humanfibrinogen, human thrombin, plasma substitute, ideal plasma substitute properties,34
products i.e. PVP, Dextran, absorbable gelatin, sponge, oxidized cellulose, calciumgluconate.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Cooper <strong>and</strong> Gunn’s, “Tutorial Pharmacy”, Delhi: CBS Publishers.2. “Remington Pharmaceutical Sciences”, Mack Publishing Co.3. B.M. Mithal, “A Textbook of Pharmaceutical Formulations”, Delhi: VallabhPrakashan.4. “British National Formulary”, Great Britain: Published Jointly by British MedicalAssociation <strong>and</strong> Royal Pharmaceutical Society.5. “Pharmacopoiea of India”, Delhi: Published by the Controller of Publications.6. “British Pharmacopoiea”, Cambridge: Her Majesty Stationary Office, UniversityPress.7. “The United States Pharmacopoeia”, Easton, PA: The United States PharmacopoeialConvention, Mack Pub Co.35
Paper Code: BPL-104 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-II (Organic Chemistry I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 043 -- 2 -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: By studying this subject, the students usually underst<strong>and</strong> different organicreactions <strong>and</strong> their mechanisms. Knowledge about different organic molecules, their use inpharmacy <strong>and</strong> basic Terms <strong>and</strong> techniques in organic chemistry are highlighted.UNIT-IStructure <strong>and</strong> properties: Atomic structure, atomic orbital, molecular orbital, hybridization,sigma & pi bond, covalent, electrovalent & co-ordinate bond, inductive effect, resonance,Classification <strong>and</strong> Nomenclature of organic compounds.UNIT-IIIsomerism, geometric isomerism, stereochemistry including optical activity, stereoisomerism,specification of configuration & conformational analysis, Organometallic Compounds-Grignard reagent organo-lithium compounds, their preparation & synthetic application.UNIT-IIIImportant methods of preparation, reactions with special reference to mechanism of thefollowing classes of compounds: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes & dienes, free radical substitutionreaction, alkyl halides, alcohols.UNIT-IVAromatic compound ,aromatic character, structure of benzene, resonance, orientation ofaromatic substitution, arenes ,amines (aliphatic & aromatic), phenols, aryl halides.Aldehydes & ketones (aliphatic & aromatic), carboxylic acids &their derivatives, di &tricarboxylic acids , hydroxy acids.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.36
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. T. R. Morrison <strong>and</strong> R. Boyd, “Organic Chemistry”, New Delhi: Prentice Hall of IndiaPvt. Ltd.2. I. L. Finar, “Organic Chemistry”, (Vol. I <strong>and</strong> II) London: ELBS/ Longman3. P. Sykes, “A Guide Book to mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, New Delhi: OrientLongman.4. J. D. Roberts <strong>and</strong> M. C. Caserio, “Basic Principle of Organic Chemistry”, Inc.: NewYork.5. E. L. Eliel, “Stereochemistry of Carbon Compounds”, New York: Macgraw Hill BookCompany, Inc.6. P. Sykes, “A Guide Book to mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, New Delhi: OrientLongman.7. J. D. Roberts <strong>and</strong> M. C. Caserio, “Basic Principle of Organic Chemistry”, Inc.: NewYork.37
Paper Code: BPL-106Pharmacognosy-I (Pharmacognosy-I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: The study of Pharmacognosy is to give knowledge about crude drugs,their cultivation, evaluation <strong>and</strong> use etc. Different methods used for extraction <strong>and</strong>purification of crude drugs from different plant <strong>and</strong> animal source. The study includesmedicinal plants of Pakistan, their habitat, collection <strong>and</strong> biological source of the drug.Allergens <strong>and</strong> allergenic preparations, enzymes, plant growth hormones as well as pesticides<strong>and</strong> poisonous plants with special reference to Pakistan shall are also included.UNIT IIntroduction:Definition, history, development <strong>and</strong> scope of Pharmacognosy.Classification of drugs: Alphabetical, morphological, taxonomical, pharmacological,chemical <strong>and</strong> chemo taxonomical with their merits <strong>and</strong> demerits.Quality control of crude drugs: Adulteration of crude drugs <strong>and</strong> their detection byorganoleptic, microscopic, physical, chemical, <strong>and</strong> biological methods of evaluations.UNIT IIPlant taxonomy: Study of the following families with special reference to medicinallyimportant plants- Apocynaceae, Solanaceae, Rutaceae, Umbelliferae, Leguminosae,Rubiaceae, Liliaceae, Labiate, Cruciferae.Study of pharmaceutical aids like talc, diatomite, kaolin, bentonite, gelatin, <strong>and</strong> naturalcolorants.UNIT III An introduction to active constituents of drugs: Isolation, classification <strong>and</strong> propertiesof active constituents of drugs. Systematic Pharmacognostical study of the following:o Carbohydrates <strong>and</strong> derived products: Agar, Guar gum, Gum acacia, Honey, Isabgol,Pectin, Starch <strong>and</strong> Tragacanth.o Lipids: Bees wax, Castor oil, Cod liver oil, Linseed oil, Shark liver oil <strong>and</strong> Wool fat.UNIT IVStudy of drugs containing resins <strong>and</strong> resin combinations: ColophoNew York,Podophyllum, Jalap, Cannabis, Capsicum, Myrrh, Asafoetida, Balsam of tolu, Balsam ofperu, Benzoin, Turmeric, Ginger.Volatile oil: General methods of obtaining volatile oils from plants, study of volatile oilsof Mentha, Cori<strong>and</strong>er, Cinnamon, Lemon peel, Orange peel, Lemon grass, Caraway,Cumin, Dill, Spermint, Clove, Fennel, Nutmeg, Eucalyptus, Cardamom, Valerian,Palmarosa, Gaultheria, S<strong>and</strong>al wood.38
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions) :1. C. K. Kokate,A.P. Purohit <strong>and</strong> S.B. Kokhale, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”,Pune: Nirali Publication.2. G.E.Treese <strong>and</strong> Evans, W. C., “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, U. K.: BailliereTindall, Eastbourne.3. S.S.H<strong>and</strong>a <strong>and</strong> V.K.Kapoor, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, New Delhi: C.B.S.Publisher.4. Mohammad Ali, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, New Delhi: CBS Publishers &Distribution.5. Shah <strong>and</strong> Quadry, “Pharmacognosy” ,Ahmedabad: B. S. Shah Prakashan.6. A. Fahn, “Plant Anatomy”, Oxford: Pergamon Press.7. E.C.G.Clarke, “Isolation <strong>and</strong> Identification of Drugs”, London: the PharmaceuticalPress.8. Jean Brunton, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry <strong>and</strong> MedicinalPlants”, Engl<strong>and</strong>, U.K.: Intercept Limited.39
Paper Code: BPL-108Pharmaceutical Chemistry-III (Physical Chemistry)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 043 -- 2 -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: The aim is to learn about various Physico-Chemical factors involved withthe three states of matter.UNIT IBehavior of Gas: Kinetic Theory of Gas, deviation from ideal behavior &Explanation.Liquid State: Physical properties (Surface tension, parachor, viscosity, rheochor,refractive index, optical rotation, dipole moment.)Amorphous <strong>and</strong> Crystalline solids: Geometry of crystals, miller indices, types ofcrystals, physical properties of crystals, crystal diffraction.Thermodynamics: Fundamentals- First, Second, Third <strong>and</strong> Zeroth law, jouleThomson effect, absolute temperature scale.UNIT IIThermo Chemistry: Definition <strong>and</strong> convention –heat of reaction, heat of formation,heat of neutralization, heat of solution, heat of combustion, Hess’s law of constantsummation, Bombs calorimeter, <strong>and</strong> energy Kirchoff’s law.Electro Chemistry: Faraday’s law of electrolysis, Electrolytic conductance,& itsmeasurement, its variation with dilutions, Kolrausch law, Arrhenius theory, Degree ofionization, Ostwald dilution law, transport no., migration of ions, Hittorfs theoreticaldevice, Theory of strong electrolyte (DebyeHuckle theory)UNIT IIISolution: Ideal & real solution, Solution of gases in liquids, Colligative properties.PH: Its determination, buffer, theory of buffers.Adsorption: Freudlich <strong>and</strong> Gibbs adsorption isotherm theory, Langmuir theory ofadsorption.UNIT IVChemical Kinetics: Zero, first <strong>and</strong> second order reaction, complex reaction,elementary idea of reaction, kinetic characteristics, homogeneous <strong>and</strong> heterogeneouscatalysis, acid base <strong>and</strong> enzyme catalysis.Phase Equilibrium: Phase , component, degree of freedom, phase rule, (excludingdeviation, cooling curves, phase diagram for one & two component system involvingeutectics, congruent, incongruent melting point (examples- water , sulphur, KI-H 2 O,NaCl-H 2 O system), Distribution law & application to solvent extraction.40
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Bahl <strong>and</strong> Tuli, “Physical Chemistry”, New Delhi: S. Ch<strong>and</strong> & Co.2. W.S. Brey, “Physical Chemistry <strong>and</strong> its Biological Applications”, New York:Academic Press.3. K.J. Laidler, “Physical Chemistry with Biological Applications”, Benzman: AcademicPress.4. V. R. Williams <strong>and</strong> H. S. Williams, “Basic Physical Chemistry for Life Sciences”,San Francisco: W. H. Freeman.5. J. A. Kitckener, “Findly’s Physical Chemistry”, (Ed.), London: Green <strong>and</strong> Company.6. Jenkin’s, “Quantitative Pharmaceutical Chemistry”, New York: Mcgraw Hill BookCompany.41
Paper Code: BPP-110 PHARMACEUTICS-II Practical (General Pharmacy)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion, preparations of some of them may asfollows:Peppermint water, cinnamon water, camphor water, chloroform water, concentratedpeppermint water, concentrated cinnamon water.Simple syrup, syrup of ginger, syrup of orange, syrup of tolu, compound syrup offerrous sulphate, spirit of peppermint, spirit of chloroform, spirit of ether.Strong solution of ammonium acetate, surgical solution of chlorinated soda, solutionof cresol with soap, solution of ferric chloride, strong solution of iodine, solution ofhydrogen peroxide, tannic acid glycerin, boric acid glycerin, mouth washes, nasaldrops, ear drops, elixirs, mucilage of acacia, mucilage of tragacanthTincture of orange, capsicum tincture, strong tincture of ginger, tincture of lemon,tincture of tolu, tincture of nuxvomica.liquid extract of liquorice, liquid extract of ipecacuanha, liquid extract of belladona,liquid extract of senna, concentrated infusion of clove, concentrated infusion ofquassia, concentrated infusion of senna, liver extract.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Cooper <strong>and</strong> Gunn’s, “Tutorial Pharmacy”, Delhi: CBS Publishers.2. “Remington Pharmaceutical Sciences”, Mack Publishing Co.3. B.M. Mithal, “A Textbook of Pharmaceutical Formulations”, Delhi: VallabhPrakashan.4. “British National Formulary”, Great Britain: Published Jointly by British MedicalAssociation <strong>and</strong> Royal Pharmaceutical Society.5. “Pharmacopoiea of India”, Delhi: Published by the Controller of Publications.6. “British Pharmacopoiea”, Cambridge: Her Majesty Stationary Office, UniversityPress.7. “The United States Pharmacopoeia”, Easton, PA: The United States PharmacopoeialConvention, Mack Pub Co.8. Gaud & Gupta, “Practical Pharmaceutics”, New Delhi: CBS Publisher.42
Paper Code: BPP-112 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-II Practical (Organic Chemistry I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted, some of them may asfollows: Introduction of various laboratory techniques including :o Calibration of thermometero Determination of melting pointo Determination of boiling pointo Determination of mixed melting point.o Distillationo CrystallizationIdentification of organic compounds <strong>and</strong> their derivatization.The student should be introduced to the various laboratory techniques throughdemonstrations involving synthesis of selected organic compounds (e.g. Picric Acid,Acetanilide, Dibenzal acetone, Benzylidine aniline & Iodoform) Introduction to the use of stereomodels to study :o R <strong>and</strong> S configuration of enantiomers.o E <strong>and</strong> Z configuration of geometric isomers.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. F. C. Mann, <strong>and</strong> B. C. Saunders, “Practical Organic Chemistry”, London: The EnglishLanguage Book Society <strong>and</strong> Longman group Ltd.2. B.S. Furniss, A.J. Hannaford, P.W.G. Smith <strong>and</strong> A.R. Tatchell, “Vogel’s Textbook ofPractical Organic Chemistry”, Singapore: Pearson Education Limited.43
Paper Code: BPP-114 PHARMACOGNOSY-I Practical (PHARMACOGNOSY-I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted, some of them may asfollows:Morphological characteristics of plant families mentioned in theory.Microscopic measurements of cells <strong>and</strong> cell contents <strong>and</strong> determination of leafconstants.Morphological <strong>and</strong> microscopical study of crude drugs mentioned in theory.Chemical examination for the identification of crude drugs mentioned in theory.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. E.C.G.Clarke, “Isolation <strong>and</strong> Identification of Drugs”, London: the PharmaceuticalPress.2. Jean Brunton, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry <strong>and</strong> MedicinalPlants”, Engl<strong>and</strong>, U.K.: Intercept Limited.3. G. Malti Chauhan <strong>and</strong> A.P.G. Pillai , “Microscopic profile of powdered drugs usedin Indian systems of medicine, volume 1, Leaf drugs,” Gujarat Ayurved University,Jamnagar.4. G. Malti Chauhan <strong>and</strong> A.P.G. Pillai , “Microscopic profile of powdered drugs usedin Indian systems of medicine”, volume 2, bark drugs, Gujarat Ayurved University,Jamnagar.5. W. C. Evans, Trease <strong>and</strong> Evans, “Pharmacognosy , W. B. Saunders Limited.6. G. E. Trease, “A Textbook of Pharmacognosy”, London: Bailliere Tindall.44
Paper Code: BPP-116 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-III Practical (Physical Chemistry)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted, some of them mayas follows:Determination of Surface tension, Viscosity, Rheochor, Optical rotation, Dipolemoment.Determination of molar mass by Rast method.Determination of refractive index of given liquids <strong>and</strong> find out the contribution ofcarbon, hydrogen <strong>and</strong> oxygen in molar refraction of a compound.Determination of molar mass of volatile liquids by Victor-Meyer method.Determination of the specific rotation of sucrose at various concentrations <strong>and</strong>determination of the intrinsic rotation.Determination of the heat of solution, heat of hydration <strong>and</strong> heat of neutralization.Determination of the cell constant, verify Ostwald dilution law.Determination of rate constant of simple reaction.Determination of pH& study the influence of pH on degradation of a drug.Study of the solubility of binary system of phenol <strong>and</strong> water at different temperatures<strong>and</strong> concentrations.Study of influence of a third component on the UCT of phenol-water binary system.Study of ternary phase system using given solvent combinations.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. S. R. Pali <strong>and</strong> S. K.D.E. Prabartak, “Practical Physical Chemistry”, Calcutta: HaltoneLtd.2. Jenkin’s, “Quantitative Pharmaceutical Chemistry”, New York: Mcgraw Hill BookCompany.3. Yadav, “Advanced Practical Physical Chemistry”, Delhi: Goel Publications.4. R.C. Dass <strong>and</strong> B. Behere, “Experimental Physical Chemistry”, London: Tata McGraw-Hill.5. V.V. Nadkarnay, A. N. Kothore, Y. V. Law<strong>and</strong>e, “Practical Physical Chemistry”,Bombay: Popular Prakashan.6. J.A. Kitchener, “Findlay's Physical Chemistry”, London: Longmans, Green <strong>and</strong> Co.45
Paper Code: BPL-201 Pharmaceutics-III (Pharmaceutical Engineering-I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: This subject deals with the various techniques involved in development,commercialization <strong>and</strong> manufacturing of components within the pharmaceuticals industry.UNIT IUNIT IIFlow of fluids: Introduction, mechanism of fluid flow, Reynolds number <strong>and</strong> itssignificance, Bernoulli's theorem, manometers <strong>and</strong> friction losses in pipes,measurement of flow rate using direct weighing or measuring, hydrodynamicmethods, displacement meters <strong>and</strong> dilution methods. Regulation of flow using plugcocks, globe valves, gate valves, unidirectional valves, automatic regulating valve,butterfly valve <strong>and</strong> diaphragm valve, <strong>and</strong> water hammer.Refrigeration: Principle <strong>and</strong> equipment employed for vapor compressionrefrigeration, lithium bromide absorption refrigeration <strong>and</strong> steam jet refrigeration.Applications of refrigeration in Pharmacy.Heat Transfer: Modes of heat transfer, Fourier's law, overall heat transfercoefficient, Stefan-Boltzmann’s law, single pass heater, multi pass heater, liquidliquidheat interchanger <strong>and</strong> finned tubes.Drying: Theory, behavior of solids during drying, static bed dryers, moving beddryers, fluidized bed dryer <strong>and</strong> pneumatic bed dryers.UNIT IIIUNIT IVSize reduction: Mechanism, factors influencing, energy requirements, applications inpharmacy, grinders i.e. fluid energy mill, hammer mill, ball mill <strong>and</strong> its variants,centrifugal mill, attrition mill, edge runner mill, colloid mill, squirrel cagedisintegrator, Buhrstone mill.Centrifugation: theory, industrial centrifugal filters <strong>and</strong> industrial centrifugalsedimenters.Filtration: Theory, filter aids, filter media, industrial filters i.e. s<strong>and</strong> filter, washing<strong>and</strong> non-washing type filter presses, rotary drum filter, leaf filters, edge filter.Evaporation: Factors affecting evaporation, natural circulation evaporators e.g.evaporating pan, evaporating still, horizontal <strong>and</strong> vertical tube evaporators, forcedcirculation evaporators, film evaporators, multiple effect evaporation, material <strong>and</strong>energy balance of evaporators. Humidification, dehumidification <strong>and</strong> air conditioning: Principles ofHumidification, dehumidification <strong>and</strong> air conditioning, psychrometry, humidity46
measurement, large-scale equipment for humidification <strong>and</strong> dehumidification, coolingtowers.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. “Bentley’s Textbook of Pharmaceutics”, New York: ELBS Bacilliere Tindall.2. W. L. Badger <strong>and</strong> J T Banchero, “Introduction to Chemical Engineering”, London:McGraw Hill International Book Co.3. “Remington Pharmaceutical Sciences”, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co.4. Leon Lachman, H A Liberman <strong>and</strong> J L Kanig, “The Theory <strong>and</strong> Practice of IndustrialPharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.5. W. L. MaCabe <strong>and</strong> J C Smith, “Unit operations of Chemical Engineering”, London:McGraw Hill International Book Co6. R. H. Perry <strong>and</strong> C H Chilton, “Chemical Engineers H<strong>and</strong>book”, London: McGrawHill <strong>and</strong> Co.7. Cooper <strong>and</strong> Gunns, “Tutorial Pharmacy”, Delhi: CBS Publishers.47
Paper Code: BPL 203 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-IV (Pharmaceutical Analysis-I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Analysis of Pharmaceuticals play a very important role in industry as itrelies upon both qualitative <strong>and</strong> quantitative chemical analysis to ensure that the raw materialused meets Pharmacopoeial specifications <strong>and</strong> also ensures a quality of finished product inTerms of proportion of components.UNIT IIntroduction: Significance of quantitative analysis in quality control, differenttechniques of analysis, significant figures, rules for retaining significant digits, typesof errors, mean deviation <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ard deviation, precision <strong>and</strong> accuracy,fundamentals of volumetric analysis: law of mass action, activity <strong>and</strong> activitycoefficient, pH, buffers, method of expressing concentration, primary <strong>and</strong> secondaryst<strong>and</strong>ards.Neutralization Titrations: Acid base concepts, strength of acids <strong>and</strong> bases,hydrolysis of salts, ionic product of water, neutralization curves, neutralizationindicators, theory of indicators, choice of indicators, mixed indicators. Analysis ofboric acid, mixture of sodium carbonate <strong>and</strong> bicarbonate.UNIT IINon-aqueous Titrations: Theory of non-aqueous titrations, titration of alkali metalsalts of organic acids, titration of amines <strong>and</strong> amine salts of organic acids, titration ofhalogen acid salts of bases <strong>and</strong> titration of acidic substances.Oxidation Reduction Titrations: Concepts of oxidation <strong>and</strong> reduction, redoxreactions, strength <strong>and</strong> equivalent weights of oxidizing <strong>and</strong> reducing agents. Theoryof redox titrations, General principles of potassium permanganate titrations,potassium dichromate titrations potassium iodate titrations, potassium bromatetitrations, cerric sulphate titrations <strong>and</strong> iodometric titrations. Analysis of ferroussulphate, hydrogen peroxide, potassium bromide, ascorbic acid, sodium thiosulphate,copper sulphate, phenol, sodium sulphite.UNIT IIIPrecipitations Titrations: Precipitation reactions, common ion effect, solubilityproduct, effects of acids, temperature <strong>and</strong> solvent upon the solubility of a precipitate.Determination of end points in precipitation titrations by Mohr’s method, Volhardsmethod <strong>and</strong> Fajans method.Gravimetry: Introduction, precipitation methods, the colloidal state, supersaturation,co-precipitation, post-precipitation, conditions of precipitation, precipitation fromhomogeneous solution, precipitation reagents, washing <strong>and</strong> ignition of the precipitate.Determination of nickel as dimethylglyoximate <strong>and</strong> aluminium as 8-hydroxyquinolate.48
UNIT IVComplexometric Titrations: Complex ions, complexation, stability of complexes,factors influencing the stability of complexes, Warner’s co-ordination number,complexones, titration curves, types of EDTA titrations, titrations of mixturesincluding use of masking <strong>and</strong> demasking agents, metal ion indicators. Analysis ofmagnesium <strong>and</strong> calcium.Miscellaneous methods of analysis: Diazotization titration, Kjeldahl nitrogendetermination, Karl Fischer titration, determination of alcohol in liquid galenicals,oxygen flask combustion.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A. I. Vogel, “Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis”, London: ELBS/Longman.2. I. M. Kolthoff <strong>and</strong> V. A. Stenger, “Volumetric Analysis, Vol. II Titration Methods”,New York: Interscience Publishers, Inc.3. K. A. Connors, “A Textbook of Pharmaceutical Analysis”, New York: WileyInterscience.4. Skoog, Hollar <strong>and</strong> Nieman, “Principles of Instrumental Analysis”, Philadelphia:Harcourt College Publishers.5. T. Higchi, “Pharmaceutical Analysis”, New Delhi: CBS Publishers.6. A. H. Beckett <strong>and</strong> J. B. Stenlake, “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Vol. I <strong>and</strong>II”,London: The Athlon Press of the University of London.49
Paper Code: BPL-205Pharmacognosy-II (Pharmacognosy-II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: The study of Pharmacognosy is to give knowledge about crude drugs,their cultivation, evaluation <strong>and</strong> use etc. Different methods used for extraction <strong>and</strong>purification of crude drugs from different plant <strong>and</strong> animal source. The study includesmedicinal plants of Pakistan, their habitat, collection <strong>and</strong> biological source of the drug.Allergens <strong>and</strong> allergenic preparations, enzymes, plant growth hormones as well as pesticides<strong>and</strong> poisonous plants with special reference to Pakistan shall are also included. Separation<strong>and</strong> isolation of plant constituents by special techniques like chromatography, ion exchange,electrophoresis <strong>and</strong> high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is introduced. Detailedstudy of carbohydrates <strong>and</strong> related products, alkaloids, volatile oils, fixed oils, tannins,glycosides, etc., is included. The students know the Unani system of medicine, phytopharmacology,Traditional Medicine <strong>and</strong> Alternative System of Medicine.UNIT IUNIT IIPhytochemical screening: (a) Preparation of extracts. (b) Screening tests foralkaloids, glycosides, resins, tannins, saponins <strong>and</strong> flavonoids in plant extracts.Study of the biological sources, cultivation, collection, commercial verities,chemical constituents, substituents, adulterants, diagnostic microscopic <strong>and</strong>macroscopic features <strong>and</strong> specific chemical tests of following group of Glycosidescontaining drugs:Saponins: Liquorice, Ginseng, Dioscorea <strong>and</strong> Senega.Cardio-active sterols: Digitalis, Squill, strophanthus <strong>and</strong> Thevetia.Anthraquinones : Aloe, Senna, Rhubarb <strong>and</strong> Cascara.Study of Tannins <strong>and</strong> tannin containing drugs: Study of Tannins <strong>and</strong> tannincontaining drugs like gambir, black catechu, gall <strong>and</strong> myrobalan.Studies of traditional drugs, common vernacular names, botanical sources,morphology, chemical nature of chief constituents, pharmacology, categories <strong>and</strong>common uses <strong>and</strong> marketed formulations of following indigenous drugs:Amla, Shatavari, Aamarg, Gokhru, Shankhpushpi, Gaduchi, Brahmi, Arjuna, Methi,Lehsun, Guggal, Gymnema <strong>and</strong> Neem.Holistic concepts of Drugs administration in traditional systems of medicine.Introduction to Ayurvedic preparations like Arishtas, Asavas, Gutikas, Tailas,Churnas, Lehas <strong>and</strong> Bhasmas.UNIT IIISystematic study of source, cultivation, collection, processing, commercial varieties,chemical constituents, substitutes, adulterants, uses, diagnostic macroscopic <strong>and</strong> microscopicfeatures <strong>and</strong> specific chemical tests of following alkaloid containing drugs:50
Pyridine-piperidine: tobacco, areca <strong>and</strong> lobelia.Tropane: belladonna, hyoscymous, datura <strong>and</strong> withania.Quinoline <strong>and</strong> isoquinoline : Cinchona, ipecac, opium.Indole: ergot, rauwolfia, catharanthus <strong>and</strong> physostigma.Imidazoles: pilocarpus.Steroidal: vertrum, kurchi.Alkaloidal amines: ephedra <strong>and</strong> colchicum.Glycoalkaloids: solanum.Purines: Coffee, tea <strong>and</strong> cola.UNIT IVBiological sources, preparation, identification test <strong>and</strong> uses of the followingenzymes:Diastase, papain, pepsin, trypsin <strong>and</strong> pancreatin..Introduction <strong>and</strong> study of plant bitters <strong>and</strong> sweeteners.Plant based pesticides <strong>and</strong> insecticides.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. S.S. Agrawal <strong>and</strong> M. Paridhari, “Herbal Drug Technology”, New Delhi: UniversityPress.2. S.S. Agrawal <strong>and</strong> M. Paridhari, “Clinically Useful Herbal Drugs”, New Delhi: AhujaPublishers.3. C.K. Kokate , A.P. Purohit <strong>and</strong> S.B. Kokhale , “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, Pune:Nirali Publication.4. G.E. Trease <strong>and</strong> W.C. Evans, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, U. K: Bailliere Tindall,Eastbourne.5. V.C. Tyler, L.R. Brady <strong>and</strong> J.E. Robers, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, 8 th Ed. ,Philadelphia: Lea <strong>and</strong> Febiger.6. T.E. Wallis, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, London: J. <strong>and</strong> A Churchill limited.7. A. Fahn , “Plant Anatomy”, Oxford : Pergamon Press.8. Jean Brunton, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, Engl<strong>and</strong>, U.K.: Phytochemistry <strong>and</strong>Medicinal Plants, Intercept Limited.51
Paper Code: BPL-207 Pharmaceutics-IV (Forensic Pharmacy)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Study of this subject enables the students to become aware about theregulatory control of manufacturing <strong>and</strong> sale of drugs. The students are able to know aboutthe laws <strong>and</strong> procedures regarding Registration <strong>and</strong> sale of drugs, establishment of retail,wholesale <strong>and</strong> distribution set ups. Knowledge of Rules <strong>and</strong> legislation about controlled,poisonous <strong>and</strong> dangerous drugs is also provided.UNIT IA brief review of evolution of Pharmaceutical legislation in India. Pharmacy Act, 1948.UNIT IIDrugs <strong>and</strong> Cosmetics Act, 1940 <strong>and</strong> rules there under. AICTE Act, 1987. Medicinal <strong>and</strong> Toilet Preparations (Excise Duties Act), 1955.Shops <strong>and</strong> Establishments Act of the state. Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act 1970 <strong>and</strong> Rules 1975.UNIT IIINarcotic Drugs <strong>and</strong> Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 <strong>and</strong> rules. Drugs <strong>and</strong> Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954. DPCO, 1995.UNIT IVPharmaceutical EthicsPatents Act, 1970 <strong>and</strong> rules.Minimum Wages Act, 1948 <strong>and</strong> rules. Poisons Act, 1919. Prevention of Cruelty to Animal Act 1960.The teaching of all the above acts should cover the latest amendments.52
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions) :1. B. M. Mithal, “Text Book of Forensic Pharmacy”, Calcutta: National Bank Centre.2. N. K. Jain, “Text Book of Forensic Pharmacy”, Delhi: Vallabh Prakashan.3. Original Acts published on behalf of Government of India.4. H. K. Bharati, “Drug <strong>and</strong> Pharmacy Laws in India”, Indore: Sadhana M<strong>and</strong>ir.53
Paper Code: BPL-209Environmental Studies (Environmental Studies)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 004 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Paper Objectives is to become familiar with the Natural Resources,Ecosystems, Biodiversity <strong>and</strong> its Conservation, Environmental Pollution, EnvironmentProtection Act etc.UNIT IUNIT IIThe Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studies: Definition, scope <strong>and</strong>importance. Need for public awarenessNatural Resources: Renewable <strong>and</strong> non- renewable resources. Natural resources <strong>and</strong>associated problems, (a) Forest resources: Use <strong>and</strong> over-exploitation, deforestation,case studies. Timber extraction, mining, dams <strong>and</strong> their effects on forests <strong>and</strong> tribalpeople. (b) Water resources: Use <strong>and</strong> over-utilization of surface <strong>and</strong> ground water,floods, drought, conflicts over water, dams benefits <strong>and</strong> problems. (c) Mineralresources: Use <strong>and</strong> over-exploitation, environmental effects of extracting <strong>and</strong> usingmineral resources, case studies. (d) Food resources: World food problems, changescaused by agriculture <strong>and</strong> over-grazing, effects of modern agriculture, fertilizerpesticideproblems, water logging, salinity, case studies. (e) Energy resources:Growing energy needs, renewable <strong>and</strong> non- renewable energy sources, use ofalternate energy sources, case studies. (f) L<strong>and</strong> resources: L<strong>and</strong> as a resource, l<strong>and</strong>degradation man induced l<strong>and</strong> slides, soil erosion <strong>and</strong> desertification. Role of anindividual in conservation of natural resources. Equitable use of resources foesustainable life styles.Ecosystems: Concept of an ecosystem. Structure <strong>and</strong> function of an ecosystem.Producers, consumers <strong>and</strong> decomposers. Energy flow in the ecosystem. Ecologicalsuccession. Food chains, food webs <strong>and</strong> ecological pyramids. Introduction, types,characteristic features, structure <strong>and</strong> function of the following ecosystem: Forestecosystem, Grassl<strong>and</strong> ecosystem, Desert ecosystem, Aquatic ecosystem (ponds,streams, lakes, rivers, oceans, estuaries)Biodiversity <strong>and</strong> its Conservation: Introduction-Definition: genetic, species <strong>and</strong>ecosystem diversity. Biogeographically classification of India. Value of biodiversity:consumptive use, productive use, social, ethical, aesthetic <strong>and</strong> option values.Biodiversity at global, national <strong>and</strong> local levels. India as a mega-diversity nation. Hotspotsof biodiversity. Threats to biodiversity: habitat loss, poaching of wildlife, manwildlifeconflicts. Endangered <strong>and</strong> endemic species of India. Conservation ofbiodiversity: In-situ <strong>and</strong> Ex-situ conservation of biodiversity.UNIT IIIEnvironmental Pollution: Definition. Causes, effects <strong>and</strong> measures of Air pollution,Water pollution, Soil pollution, Marine pollution, Noise pollution, Thermal pollution,54
nuclear hazards, Solid waste management: Causes, effects <strong>and</strong> control measures ofurban <strong>and</strong> industrial wastes. Role of an individual in prevention of pollution. Pollutioncase studies. Disaster management: floods, earthquakes, cyclone <strong>and</strong> l<strong>and</strong>slides.Human Population <strong>and</strong> Environment: Population growth, variation among nations.Population explosion-Family Welfare Programme. Environment <strong>and</strong> human health.Human rights. Value education.HIV/AIDS. Women <strong>and</strong> Child Welfare. Pole ofInformation Technology in Environment <strong>and</strong> human health.UNIT IVSocial Issues <strong>and</strong> the Environment: From Unsustainable to Sustainabledevelopment. Urban problems related to energy. Water conservation, rain waterharvesting, water shed management. Resettlement <strong>and</strong> rehabilitation of people: itsproblems <strong>and</strong> concerns. Environmental ethics: Issues <strong>and</strong> possible solutions. Climatechange, global warming, acid rain, ozone layer depletion, nuclear accidents <strong>and</strong>holocaust. Case studies. Wastel<strong>and</strong> reclamation. Consumerism <strong>and</strong> waste products.Environment Protection Act: Air (Prevention <strong>and</strong> Control of Pollution) Act. Water(Prevention <strong>and</strong> Control of Pollution) Act. Wildlife Protection Act. ForestConservation Act. Issues involved in enforcement of environmental legislation. Publicawareness.Field Work: Visit to a local area to document environmental assets-river, forestgrassl<strong>and</strong>/hill/mountain. Visit to a local polluted site-Urban/ rural/ Industrial/Agricultural. Study of common plants, insects <strong>and</strong> birds. Study of simple ecosystemspond,river, hill slopes etc.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Y. Anjaneyulu, “Introduction to Environmental Science”, Hyderabad: BSPublications.2. H. Kaur, “Environmental Studies”, Meerut: Pragati Prakashan.3. R.W. Andrew, Jackson & M. Julie, “Environmental Science – The Natural4. Environment <strong>and</strong> Human Impact”, Engl<strong>and</strong>: Addison Wesley Longman5. S.C. Santra,“Environmental Science”, Kolkata: New Central Book Agency (P) Ltd.6. Richard T.Wright,“Environmental Chemistry”, South Asia: Pearson Education Inc.7. B.K. Sharma, “Environmental Chemistry”, Meerut: Goel Publ. House.8. K.D. Wanger,“Environmental Management”,Philadelphia,USA: W.B.Saunders Co.55
Paper Code: ENG-201Communication Skills in EnglishL -- T -- P Total Credits: 022 -- --- Total Marks:50External Marks: 25Internal Marks: 25Paper Objective: Paper objective is to improve the language proficiency of sciencegraduates as skill oriented. The main objectives are: To enable the learners to be able to communicate in real life contexts using video <strong>and</strong>audio teaching material. Enabling the learners to become communicatively competent by using listening,speaking, writing <strong>and</strong> reading. Introducing the learners to non verbal communication strategies. To prepare the learners for successfully clearing the international examinations ofproficiency in English like IELTS, BEC, <strong>and</strong> TOEFL etc.UNIT-I: BUSINESS COMMUNICATION – IBusiness English as a genreImportance of effective communication in business contextFace to face communication with customers <strong>and</strong> visitorsBasic skills for talking to people in transactional situationsBooking hotel accommodationMaking small talk <strong>and</strong> telling storiesUNIT-II: ENGLISH GRAMMERNeed for grammarParts of speechArticlesTensesSubject-verb ConcordCommon ErrorsUNIT-III: BASIC PHONETICSSounds of EnglishWord StressIntonationUNIT-IV: EFFECTIVE LISTENINGWhat is listening?56
NOTE:Types of listeningStrategies for effective listeningSemester will carry 50 marks with equal weightage ( 25 each ) to Theory &Practical assessment.Theory Assessment will be done by the University’s Controller ofExaminations by conducting a theory paper of 25 marks in each semester(External Marks).Practical Assessment will be done by the Learning Resource Centre byconducting Listening & Speaking tests of 25 marks in each semester(Internal Marks).57
Paper Code: BPP-211Pharmaceutics-III Practical (Pharmaceutical Engineering-I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Experiments based on different unit operations studied in theory such as: Flow of fluids,Refrigeration, Heat Transfer Humidification, dehumidification <strong>and</strong> air conditioningEvaporation, Filtration, Centrifugation, Drying, Size reduction etc. including some exerciseson Pharmaceutical Engineering Drawing like: Introduction: Significance of Engineering Drawing in Pharmaceutical Industry,drawing instruments <strong>and</strong> their uses, lines, lettering <strong>and</strong> dimensioning. Scales: Construction of plain scales, vernier scale, diagonal scale, comparative scale<strong>and</strong> isometric scale Isometric projections: Theory, isometric views <strong>and</strong> projections, construction ofisometric projections/views of two-dimensional <strong>and</strong> three-dimensional objects. Orthographic projections: Theory, types, <strong>and</strong> construction of drawing in both firstangle <strong>and</strong> third angle. Various methods of sectioning i.e. full section, half section,removed section, partial section, <strong>and</strong> offset section. Drawing of machine parts <strong>and</strong> simple pharmaceutical equipment Methods of depicting layouts of various sections of a pharmaceutical unit.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. N. D. Bhatt, “Machine Drawing”, Gujarat: Charotar Publishing House.2. N. D. Bhatt, “Engineering Drawing”, Gujarat: Charotar Publishing House.3. French <strong>and</strong> Vierck, “A Manual of Engineering Drawing for Students <strong>and</strong> Draftsman”,New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company.4. Giesecke, Mitchell <strong>and</strong> Spencer, “Technical Drawing”, New York: MacmillanPublishing Company.5. W. L. Badger <strong>and</strong> J T Banchero, “Introduction to Chemical Engineering”, London:McGraw Hill International Book Co.6. “Remington Pharmaceutical Sciences”, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co.7. Leon Lachman, H A Liberman <strong>and</strong> J L Kanig, “The Theory <strong>and</strong> Practice of IndustrialPharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.8. W. L. MaCabe <strong>and</strong> J C Smith, “Unit operations of Chemical Engineering”, London:McGraw Hill International Book Co9. R. H. Perry <strong>and</strong> C H Chilton, “Chemical Engineers H<strong>and</strong>book”, London: McGrawHill <strong>and</strong> Co.58
Paper Code: BPP-213 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-IV Practical (PharmaceuticalAnalysis-I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50The students should be introduced to the main analytical tools through demonstrations. Theyshould have a clear underst<strong>and</strong>ing of a typical analytical balance, the requirements of a goodbalance, weights, care <strong>and</strong> use of balance, methods of weighing <strong>and</strong> errors in weighing. Thestudents should also be acquainted with the general apparatus required in various analyticalprocedures. Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted, some of themmay as follows:St<strong>and</strong>ardization of analytical weights <strong>and</strong> calibration of volumetric apparatus.Acid Base Titrations : Preparation <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ardization of acids <strong>and</strong> bases; someexercises related with determination of acids <strong>and</strong> bases separately or in mixture form,some official assay procedures e.g. boric acid should also be covered.Oxidation Reduction Tltrations: Preparation <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ardization of some redoxtitrants e.g. potassium permanganate, potassium dichromate, iodine, sodiumthiosulphate, etc. Some exercises related to determination of oxidizing <strong>and</strong> reducingagents in the sample shall be covered. Exercises involving potassium iodate,potassium bromate, iodine solution, titanous chloride, <strong>and</strong> ceric ammonium sulphate.Precipitation titrations: Preparation <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ardization of titrants like silver nitrate<strong>and</strong>, ammonium thiocyanate, Titrations according to Mohr's, Volhard's <strong>and</strong> Fajan'smethods.Gravimetric Analysis: Some exercises related to gravimetric analysis should becovered.Non aqueous Titrations: Preparation <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ardization of perchloric acid <strong>and</strong>sodium/potassium/lithium methoxides solutions; Estimations of some pharmacopoeialproducts.Complexometric Titrations: Preparations <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ardization of EDT A solution,some exercises related to pharmacopoeial assays by complexometric titrations.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A. I. Vogel, “Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis”, London: ELBS/Longman.2. I. M. Kolthoff <strong>and</strong> V. A. Stenger, “Volumetric Analysis, Vol. II Titration Methods”,New York: Interscience Publishers, Inc.3. Skoog, Hollar <strong>and</strong> Nieman, “Principles of Instrumental Analysis”, Philadelphia:Harcourt College Publishers.4. A. H. Beckett <strong>and</strong> J. B. Stenlake, “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Vol. I <strong>and</strong>II”, London: The Athlon Press of the University of London.5. L. G. Chatten, “Pharmaceutical Chemistry”, New York: Marcel Dekker.59
Paper Code: BPP-215 PHARMACOGNOSY-II Practical (Pharmacognosy-II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted, some of them may asfollows:Identification of crude drugs mentioned in theory, Microscopic studies of selected crudedrugs & General chemical tests for the different classes of drugs.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. V.E. Tyler, L.R. Brady & J.E. Robbers, “Pharmacognosy”, Bombay: K.M. VargheseCompany.2. Egon Stahl, “Thin-Layer Chromatography”, New York: Springer Verlag.3. E.J. Shellard, “Quantitative Paper <strong>and</strong> Thin Layer Chromatography”, New York:Academic Press.4. C.K. Atal & B.M. Kapur, “Cultivation <strong>and</strong> Utilization of Medicinal Plants”, India:CSIR.5. H. Wagner, S. Bladt, E.M. Zgainski, “Plant Drug Analysis”, New York: Springer-Verlag.60
Paper Code: BPL-202Pharmaceutical Chemistry-V (Pharmaceutical Biochemistry)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Students are taught those areas of biochemistry which are important forthe underst<strong>and</strong>ing of metabolic disorders relevant to common disturbances of body functions,gene structure <strong>and</strong> functions. General introduction <strong>and</strong> basic biochemistry of proteins,carbohydrates, bioenergetics, lipids, etc., including biochemistry of enzymes <strong>and</strong> metabolicfate of nitrogen is also taught. The syllabus also includes replication <strong>and</strong> expression ofgenetic information. Metabolic basis of biochemistry in relation to human metabolism,digestion <strong>and</strong> intestinal absorption are also taught.UNIT IIntroduction: Biochemical organization of the cell <strong>and</strong> transport processes across cellmembrane.The concept of free energy, determination of change in free energy - fromequilibrium constant <strong>and</strong> reduction potential, bioenergetics, production of A TP <strong>and</strong>its biological significance.Enzymes: Nomenclature, enzyme kinetics <strong>and</strong> its mechanism of action, mechanismof inhibition, enzymes <strong>and</strong> iso-enzymes in clinical diagnosis, immobilization ofenzymes. Co-enzymes: Vitamins as co-enzymes <strong>and</strong> their significance. Metals as coenzymes<strong>and</strong> their significance.Carbohydrate Metabolism: Conversion of polysaccharide to glucose-I-phosphate,Glycolysis <strong>and</strong> fermentation <strong>and</strong> their regulation, Gluconeogenesis <strong>and</strong>glycogenolysis, Metabolism of galactose <strong>and</strong> galactosemia, Role of sugar nucleotidesin biosynthesis, <strong>and</strong> Pentosephosphate pathway.UNIT IIThe Citric Acid Cycle: Significance, reactions <strong>and</strong> energetic of the cycle,Amphibolic role of the cycle, <strong>and</strong> Glyoxalic acid cycle.Lipids Metabolism: Oxidation of fatty acids, oxidation & energetic, β-oxidation,Biosynthesis of ketone bodies <strong>and</strong> their utilization. Biosynthesis of saturated <strong>and</strong>unsaturated fatty acids, Control of lipid metabolism, Essential fatty acids &eicosanoids (prostagl<strong>and</strong>ins, thromboxanes <strong>and</strong> leukotrienes), phospholipids, <strong>and</strong>sphingolipids.Biological Oxidation : Redox-potential, enzymes <strong>and</strong> co-enzymes involved inoxidation reduction & its control, The respiratory chain, its role in energy capture <strong>and</strong>its control, Energetics of oxidative phosphorylation, Inhibitors of respiratory chain<strong>and</strong> oxidative phosphorylation, Mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation.UNIT IIINitrogen & Sulphur Cycle: Nitrogen fixation. ammonia assimilation, nitrification<strong>and</strong> nitrate assimilation, Sulphate activation. sulphate reduction. Incorporation ofsulphur in organic compounds, Release of sulphur from organic compounds.61
Metabolism of Ammonia <strong>and</strong> Nitrogen Containing Monomers: Nitrogen balance.Biosynthesis of amino acids. Catabolism of amino acids. Conversion of amino acidsto specialized products, Assimilation of ammonia. Urea. cycle, metabolic disorders ofurea cycle. Metabolism of sulphur containing amino acids. Porphyrin biosynthesis.formation of bile pigments. hyperbilirubinemia. Purine biosynthesis. Purinenucleotide interconversion. Pyrimidine biosynthesis. <strong>and</strong> Formation ofdeoxyribounucleotides.UNIT IVBiosynthesis of Nucleic Acids: Brief introduction of genetic organization of themammalian genome, alteration <strong>and</strong> rearrangements of genetic material, Biosynthesisof DNA <strong>and</strong> its replication. Mutation. Physical & chemical mutagenesis /carcinogenesis. DNA repair mechanism. Biosynthesis of RNA.Genetic Code <strong>and</strong> Protein Synthesis: Genetic code. Components of proteinsynthesis. <strong>and</strong> Inhibition of protein synthesis. Brief account of genetic engineering<strong>and</strong> polymerase chain reactions.Regulation of gene expression.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. “Harper’s Review of Biochemistry”, California: Lange Medical Publications.2. A. L. Lehninger, “Principles of Biochemistry”, New Delhi: CBS Publishers.3. L. Stryer, “An Introduction to Biochemsitry”, San Francisco: Freeman <strong>and</strong> Company.4. B. Harrow <strong>and</strong> A. Mazur, “Textbook of Biochemistry”, Philadelphia: W. B. SaundersCompany5. E. E. Conn <strong>and</strong> P. K. Stumpf, “Outlines of Biochemistry”, New York: Jone Wiley &Sons.62
Paper Code: BPL-204Pharmaceutical Chemistry-VI (Organic Chemistry-II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: The area of application of Organic Chemistry is vast <strong>and</strong> includesPharmaceuticals. The objective of the paper is to review <strong>and</strong> study fundamentals of OrganicChemistry in identifying <strong>and</strong> synthesizing organic compounds essentially employed as drugs<strong>and</strong> pharmaceuticals. By studying this subject, the students usually underst<strong>and</strong> differentorganic reactions <strong>and</strong> their mechanisms. Knowledge about different organic molecules, theiruse in pharmacy <strong>and</strong> basic Terms <strong>and</strong> techniques in organic chemistry are highlighted.UNIT I: Heterocyclic compounds:UNIT IIStudy of fundamentals of heterocyclic compounds, nomenclature, method of synthesis<strong>and</strong> important chemical reactions of the following: Five membered Heterocycles:Furan, Thiophene, Pyrrole, Thiazole, oxazole, imidazole, Pyrazole. Six memberedHeterocycles: Pyridine, pyridazine, Pyrimidine, Pyrazine, Pyrones. Benz-fusedHeterocycles: Quinoline, Isoquinoline, Indole.Carbohydrates: An account of the chemistry of Arabonose, Ribose, mannose,Glucose, fructose, Sucrose, Lactose, Cellulose, starch, Glycogen <strong>and</strong> dextrans,Structure elucidation of glucose, sucrose, starch.Lipids: Study of chemistry of fixed oils, fats <strong>and</strong> waxes.UNIT IIIProteins <strong>and</strong> Amino Acids: Isolation <strong>and</strong> general methods of synthesis of aminoacids <strong>and</strong> physico-chemical properties. General classification of proteins <strong>and</strong> endgroup analysis.Structural features of DNA <strong>and</strong> RNA.UNIT IVα,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds.Electrocyclic, Cycloaddition <strong>and</strong>sigmatropic reactions.Neighbouring group effects.Catalysis by transition metal complexes.Stereoselective <strong>and</strong> stereospecific reactions.63
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. I. L. Finar, “Organic Chemistry” (Vol. I <strong>and</strong> II), London: ELBS/ Longman.2. R. N. Acheson, “An Introduction to Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds”, NewDelhi: Interscience Publications.3. P. Sykes, “A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, New Delhi: OrientLongman.4. J. D. Roberts <strong>and</strong> M. C. Caserio, “Basic Principle of Organic Chemistry”, New York:W.A. Benjamin Inc.5. Jerry March, “Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reaction Mechanism <strong>and</strong> Structure NewChemistry”, U.S.A: Carrier publications.64
Paper Code: BPL-206Pharmaceutics-V (Pharmaceutical Microbiology)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:Students are taught the principles of Microbiology with special reference to PharmaceuticalMicrobiology including environmental Microbiology <strong>and</strong> other relevant aspects. The modernconcepts of microbiological application are taught to students. The staining of slides <strong>and</strong>preparation of culture media, etc., including microbiological assays of pharmaceuticals is alsotaught. Sensitivity test <strong>and</strong> other necessary pharmaceutical tests are also included. Thestudents are trained about sterilization, disinfection <strong>and</strong> fermentation with reference to theiruse <strong>and</strong> application in the pharmaceutical industry. Knowledge of immune system is alsoimparted.UNIT IIntroduction to the science of microbiology: ancient theories concerning the originof life, contribution of great scientists to this science, with particular reference to thecontributions of the following scientists: A.V. Leeuwenhoek, Louis Pasteur, EdwardJenner, Robert Koch, Alex<strong>and</strong>er Fleming, Joseph Lister.Microscopy: Microscopes, their magnification, resolution, illumination <strong>and</strong> filters,working of different types of microscopes, micrometry.UNIT IIClassification of microbes <strong>and</strong> their taxonomy.Bacteria, fungi <strong>and</strong> viruses: Nutrition, cultivation, isolation <strong>and</strong> identification.Bacterial enzymes – classification, nomenclature, production by fermentation,extraction methods, immobilization techniques <strong>and</strong> applications of bacterial enzymesin general <strong>and</strong> detailed account of following bacterial enzymes: alpha amylase(diastase) <strong>and</strong> proteases.UNIT IIIDisinfection: factors affecting disinfection, dynamics of disinfection, disinfectants<strong>and</strong> antiseptics <strong>and</strong> their evaluation.Sterilization: Different methods, applications <strong>and</strong> evaluation of sterilization methods,aseptic technique.UNIT IVMicrobial st<strong>and</strong>ardization: Microbial st<strong>and</strong>ardization of antibiotics (ampicillin,streptomycin), Vitamins (Vitamin B-12, Niacin) <strong>and</strong> calcium pentothenate.Fermentation: Types of media used; factors affecting, control of various parametersduring fermentation. A detailed account of the industrial fermentation process formanufacture of penicillin, streptomycin, glutamic acid; Lysine, citric acid, Vit.B 12 .65
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marksSuggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. L. E. Casida, “Industrial Microbiology”, New Delhi: New Age International (P) Ltd.2. Pelczar, Chan <strong>and</strong> Krieg, “Microbiology”, New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill PublishingCompany Ltd.3. R.Y. Stanier, Ingrham, Wheelis <strong>and</strong> Painter, “General Microbiology”, London:Macmillan Press Ltd.4. Hugo <strong>and</strong> Russel, “Pharmaceutical Microbiology”, Oxford: Blackwell ScientificPublications.5. G. Sykes, “Disinfection <strong>and</strong> Sterilization”, Engl<strong>and</strong>: Pitman Press.6. Davis, Dulbetco, Eisen, “Microbiology”, New Delhi: CBS Publishers.7. Benzamin Lewin, Gene V, “Microbiology”, New York: Jones <strong>and</strong> Barlett Publishers.8. Prescott <strong>and</strong> Dunn, “Industrial Microbiology”, New York: Mcgraw Hill BookCompany Inc.9. Peppler, “Microbiology Technology” (Vol.I & II), New York: Mcgraw Hill BookCompany Inc.66
Paper Code: BPL-208Computer Sciences (Computer Sciences)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Knowledge of FUNDAMENTALS & WINDOWS is essential for anyoneworking in the computer field. This paper is designed to meet the needs of beginners whowish to communicate with computers via windows. This paper gives the beginners a goodunderst<strong>and</strong>ing of windows & ms-office, which are now days the most important tools for thecomputer users. The students are required to learn basic introduction of computer withreference to their application in pharmacy.UNIT IIntroduction: Importance of computers, history of computers (generations), types ofcomputers, classification of computers, components of a computer, applications ofcomputers including Pharmaceutical applications, hardware description, Languageslike assembly, machine, <strong>and</strong> common high-level languages, computer viruses.Introduction to Internet: Concepts of Internet, WWW, Gopher, e-mail <strong>and</strong>applications of Internet.UNIT IIProgramming in BASIC: Introduction to BASIC, flowcharting, BASIC statements,constants <strong>and</strong> variables, expressions in BASIC, print control, jumping <strong>and</strong> looping,subscripted variables, functioning <strong>and</strong> subroutines, histogram <strong>and</strong> graphs, programmedesign, file management in BASIC <strong>and</strong> computer graphics.UNIT III Introduction to operating system with a special emphasis on Windows. MS-Word- Introduction to Word processing, Introduction to MS word, Editing,formatting,, previewing <strong>and</strong> printing a document, advanced features of MS word(Find <strong>and</strong> replace, grammar <strong>and</strong> spelling, auto correct, word count, mail merge, table<strong>and</strong> charts.UNIT IVMS- excel- Worksheet basics, creating, formatting, previewing <strong>and</strong> printing aworksheet, graphs <strong>and</strong> charts, working with formulas <strong>and</strong> cell referencing, databasecreation, sorting, database functions (Mathematical <strong>and</strong> trigonometrical, statistical <strong>and</strong>logical functions).MS-PowerPoint- Features <strong>and</strong> various versions, creating presentations, working withdifferent views <strong>and</strong> menus of PowerPoint, editing <strong>and</strong> formatting a text, working withslides, printing a presentation, inserting objects, slide sorter <strong>and</strong> animation effects.67
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. E. Balaguruswamy , “Programming in ANSI”, New Delhi: Tata Mac Graw Hill.2. S. Thakur Praveen , “Computers in Pharmacy”, New Delhi: Birla Publication PVTLtd.3. P. K. Sinha , “Computer Fundamentals”, New Delhi: BPB Publications.4. V.K. Jain ,“Basic Computer Programming”, New Delhi: Pusthak Mahal Publications.5. Gottfried S. Byron , “Schaum’s Outline series: Programme With Basic”, New York:Mcgraw-Hill, INC6. R.P.Soni, Harshal Arolkar <strong>and</strong> Sonal Jain, “Working with personal computersoftware”, New Delhi: Books India Publications.7. Ed. Bott. & Woddy Leohad, “MS – Office”, New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India.68
Paper Code: BPL-210Pharmaceutical Mathematics <strong>and</strong> Statistics(Pharmaceutical Mathematics <strong>and</strong> Statistics)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:Mathematics is the language of science. The study of mathematics is important as all theequations used in pharmacokinetics <strong>and</strong> pharmaco-dynamics are in the mathematical forms<strong>and</strong> studies of such results are in logarithmic <strong>and</strong> integration forms.UNIT IMatrices <strong>and</strong> Determinants: Definition of matrix, types of matrices, arithmeticoperations on matrices, determinants <strong>and</strong> its expansion, important properties ofdeterminants, solutions of simultaneous equations by Cramer’s rule.Differentiation: Concepts of functions, limits <strong>and</strong> differentiation; differentiation ofst<strong>and</strong>ard functions (without using first principle), including function of a function(chain rule), differentiation of implicit functions, logarithmic differentiation,parametric differentiation, elements of successive differentiation.UNIT IIIntegration: Integration as inverse of differentiation, indefinite integrals of st<strong>and</strong>ardfunctions, integration- by parts <strong>and</strong> substitution methods, formal evaluation of definiteintegrals.Differential equations: definition, formation <strong>and</strong> solution of ordinary differentialequations of first order <strong>and</strong> first degree (variable separable technique only).Laplace transforms: definition, properties of linearity <strong>and</strong> shifting, transforms ofelementary function (without proof) <strong>and</strong> inverse Laplace transforms not involvingEuler’s theorem.UNIT IIIMeasures of central tendency <strong>and</strong> dispersion: Requisites of an ideal measure,arithmetic mean, median, mode, range, mean deviation, st<strong>and</strong>ard deviation,coefficients of variation.Linear correlation: Bi-variant data scatter diagrams, correlation, types of correlation,Karl Pearson’s <strong>and</strong> Spearman’s methods, coefficients of correlation <strong>and</strong> its importantproperties (without proof).Linear regression: Regression, method of least squares, lines of regression,regression coefficients <strong>and</strong> their important properties (without proof).UNIT IVProbability: Events, classical <strong>and</strong> statistical definitions of probabilities, addition <strong>and</strong>multiplication laws of probability, conditional probability, Bayer’s theorem (statementonly) <strong>and</strong> its applications.69
St<strong>and</strong>ard probability distribution: Definitions, important properties (without proof)<strong>and</strong> applications of binomial, Poisson <strong>and</strong> normal distribution/ normal curves. Centrallimit theorem (statement only).Statistical inference: Concepts of parameter, statistic, sampling distribution, st<strong>and</strong>arderror, hypothesis, type-I <strong>and</strong> type-II errors; testing of hypothesis, t- test (paired <strong>and</strong>unpaired), Z-test(for means only).Note: Emphasis on Pharmaceutical applications, wherever possible, of the above-mentionedconcepts <strong>and</strong> results (without proof).Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A. M. Goon,M. K. Gupta <strong>and</strong> B. Dasgupta , “Basic Statistics”, Kolkata: World Press.2. S. P. Gupta , “Statistical Methods”, New Delhi: Sultan Ch<strong>and</strong> & Sons.3. Dinodoia, J <strong>and</strong> Chugh, “Elements of Pharmaceutical Mathematics” (Vol.I <strong>and</strong>Vol.II), New Delhi: Jeevonsons Publications.4. G. D. Dhall , S.N. Chhibbar , H.O. Trivedi <strong>and</strong> S. Ch<strong>and</strong>ra , “Frank Mathematics forB.Pharma”, New Delhi: Frank Bros. & Co. Ltd.5. Bradley <strong>and</strong> Smith, “Calculus”, New Jersey USA: Prentice Hall.6. W. Hungerford Thomas , “Algebra” ,New York: Springer.7. A.M. Mood , F.A. Graybill ,D.C. Boes , “Introduction of the Theory of Statistics”,New Delhi: Tata Mcgraw Hill.8. P.L. Meyer, “Introductory Probability <strong>and</strong> Statistical Applications”, New Delhi:Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Ltd.9. N. Piskunov , “Differtial <strong>and</strong> Integral Calculus”, Vol-II, Noida: G K Publishers Pvt.Ltd.10. S. T.Rizvi, “Algebra <strong>and</strong> its Applications”, New Delhi: Narosa Book Distributors Pvt.Ltd.70
Paper Code: BPP-212Pharmaceutical Chemistry-V Practical (PharmaceuticalBiochemistry)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted; some of them may asfollows:Quantitative reactions for carbohydrates, color reactions of proteins <strong>and</strong> amino acids,estimations of blood-cholesterol, blood sugar (glucose) blood-urea <strong>and</strong> blood-creatinine,Quantitative estimation of glucose <strong>and</strong> uric acid in urine, Quantitative analysis of sugar,ketone bodies, bile salts, bile pigments, albumin, creatinine in clinical urine samples.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. J. Jayaraman, “Laboratory Manual in Biochemsitry”, Delhi: Wiley Eastern Ltd.2. D. T. Plumer, “An Introduction to Practical Biochemstry”, New Delhi: Tata McgrawHill.3. S.K. Sawhney, “Introductory to Practical Biochemistry”, New Delhi: NarosaPublications.4. E. E. Conn <strong>and</strong> P. K. Stumpf, “Outlines of Biochemistry”, New York: Jone Wiley &Sons.71
Paper Code: BPP-214 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-VI Practical (Organic Chemistry-II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted; some of them mayas follows:Analysis of different organic binary mixtures.Preparation of some pharmaceutically important organic compounds havingheterocyclic moiety mentioned in the theory syllabus.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A. I. Vogel, “A Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry”, London: The EnglishLanguage Book Society <strong>and</strong> Longman group Ltd.2. R. N. Acheson, “An Introduction to Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds”, NewDelhi: Interscience Publications.3. P. Sykes, “A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, New Delhi: OrientLongman.4. F. C. Mann, <strong>and</strong> B. C. Saunders, “Practical organic Chemistry”, London: The EnglishLanguage Book Society <strong>and</strong> Longman group Ltd.5. Brian Furnis <strong>and</strong> Antony Hannaford, “Vogel’s Text Book of Practical OrganicChemistry”, Singapore: ELBS Publication.6. K. S. Jain, P. B. Miniyar & T. S. Chitre, “Experimental Pharmaceutical OrganicChemistry”, U.S.A: Carrier publications.72
Paper Code: BPP-216Pharmaceutics-V Practical (Pharmaceutical Microbiology)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted, some of them may asfollows:Preparation of various types of culture media, sub culturing of common aerobic <strong>and</strong>anaerobic bacteria, fungus <strong>and</strong> yeast, various staining methods, various methods of isolation<strong>and</strong> identification of microbes, sterilization techniques <strong>and</strong> their validation, evaluation ofantiseptics <strong>and</strong> disinfectants, testing the sterility of pharmaceutical products as per I.P.requirements, microbial assay of antibiotics <strong>and</strong> vitamins, etc.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Hugo <strong>and</strong> Russel, “Pharmaceutical Microbiology”, Oxford: Blackwell ScientificPublications.2. G. Sykes, “Disinfection <strong>and</strong> Sterilization”, Engl<strong>and</strong>: Pitman Press.3. Prescott <strong>and</strong> Dunn, “Industrial Microbiology”, New York: Mcgraw Hill BookCompany Inc.4. K. R. Aneja , “Experiments in Microbiology, Plant Pathology & Biotehnology”, NewDelhi: New Age International (P) Ltd.73
Paper Code: BPP-218 Computer Sciences Practical (Computer Sciences)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of experiments based on theory including Computer operating systems like Unix, MS DOS, etc. Simple programming in BASICStudy of soft-ware packages like WORD-STAR, LOTUS-123 etc.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. E. Balaguruswamy , “Programming in ANSI”, New Delhi: Tata Mac Graw Hill.2. V.K. Jain, “Basic Computer Programming”, New Delhi: Pusthak Mahal Publications.3. Gottfried S. Byron , “Schaum’s Outline series: Programme With Basic”, New York:Mcgraw-Hill, INC4. R.P.Soni, Harshal Arolkar <strong>and</strong> Sonal Jain, “Working with personal computersoftware”, New Delhi: Books India Publications.5. R. K. Taxali, “P.C. Software for Windows 98 made simple”, New Delhi: TataMcgraw Hill Publications.74
Paper Code: BPL-301 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-VII (Pharmaceutical Analysis-II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:Study of this subject gives knowledge about different techniques used for the estimation ofdrugs. Students are given the basic knowledge regarding the components of these techniques.It includes the study of column, thin layer, gas-liquid chromatography, HPLC <strong>and</strong> GC-MS,potentiometry, polarography, radiochemical techniques <strong>and</strong> differential scanningcolorimetry.UNIT I Electrochemistry: The electric cell, electrode potential, half cells, types of half cells,sign convention, Nernst equation, the salt bridge, activity series, st<strong>and</strong>ard potential,st<strong>and</strong>ard hydrogen electrode, measuring the relative voltage of half cells, calculationsof st<strong>and</strong>ard potential, reference electrodes, indicator electrodes. Potentiometry: Theoretical considerations, ion-selective electrodes, measurement ofpotential, location of end point equipment, analytical application, direct measurementof a metal concentration, differential curve, determination of ksp, pH measurementdead-stop titrations; pH meter, pH definition, relation to pH to potential, equipment<strong>and</strong> applications. Conductometry: Conductometric titrations <strong>and</strong> their applications.UNIT IIPolarography <strong>and</strong> its applications: theory of mass transport processes, currentprocesses, current potential relationship, polarization, choice of electrodes, effect ofoxygen, instrumentation, calculation of concentration, laboratory design <strong>and</strong> safety.Amperometric tirations <strong>and</strong> its applications.Coulometry: Coulometric titrations, its principles <strong>and</strong> applications, controlledpotential coulometry, cell design, instrumentation, advantages <strong>and</strong> limitations, <strong>and</strong>electrode selection.Extraction: Extraction procedure, separation of drug from Excipients, liquid-liquidextraction, separation of mixtures by extraction, distribution law, successiveextraction, the Craig method of multiple extraction, continuous counter-currentextraction, effect of temperature, pH, inert solute, association, ion-pair formation, theemulsion problem in extraction.UNIT III Fundamentals of Chromatography: Introduction <strong>and</strong> theory of underlying differenttypes of chromatography techniques like- Column chromatography, thin layerchromatography, paper <strong>and</strong> circular chromatography, adsorbents <strong>and</strong> solvents used inthese techniques. TLC: TLC in quantitative estimation.75
Ion exchange <strong>and</strong> molecular sieve processes: Theory of ion exchange, types ofexchangers, ion-exchange equilibria, ion-exchange capacity, ion-exchangeseparation, applications in pharmaceutical analysis, molecular sieve separation <strong>and</strong>application.UNIT IVGas chromatography: Introduction, principles of gas chromatography, basic GLCapparatus, sample introduction, column, column efficiency, solid support, liquidphases, branches of gas chromatography, detectors, temperature effect, application ofGLC in pharmaceutical analysis.HPLC: Introduction <strong>and</strong> nomenclature, instrumentation, liquid solid chromatography,liquid liquid chromatography, exclusion chromatography, HPLC columns, solventselection in HPLC, data h<strong>and</strong>ling in HPLC, application of HPLC.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A. I. Vogel “Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis”, London: ELBS/Longman.2. M. Kolthoff <strong>and</strong> V. A. Stenger, “Volumetric Analysis, Vol. II TitrationMethods”, New York: Interscience Publishers, Inc.3. K. A. Connors, “A Textbook of Pharmaceutical Analysis”, New York: WileyInterscience.4. P. D. Sethi , “HPLC”,New Delhi: CBS Publishers.5. A. H. Beckett <strong>and</strong> J. B. Stenlake, “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Vol. I <strong>and</strong>II”, London: The Athlon Press of the University of London.76
Paper Code: BPL-303 Pharmaceutics-VI (Pharmaceutical Engineering- II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: By studying this subject, the students are able to underst<strong>and</strong> that howdifferent dosage forms at large scale are manufactured. This subject also deals with thevarious techniques that involved in development, commercialization <strong>and</strong> manufacturing ofcomponents within the pharmaceuticals industry.UNIT IDistillation: Raoult's law, volatility, boiling point diagrams, azeotropic mixtures,equilibrium diagrams, types of distillation, rectification, rectifying columns,downcomers, material <strong>and</strong> energy balance of a rectifying column, reflux ratio,determination of number of theory plates, H.E.T.P. <strong>and</strong> steam distillation.Extraction: Factors affecting, equipment for extraction of solids i.e. fixed beddiffusion battery, continuous diffusion battery, basket extractor, Rotocel extractor <strong>and</strong>Dorr agitator; equipment for liquid-liquid extraction i.e. extraction towers <strong>and</strong>Podbielniak extractor.UNIT IIMixing: Definition, objectives, mechanism, uniformity index, factors influencingselection of suitable mixer. Study of equipment employed for solid-solid, liquid-liquid<strong>and</strong> solid-liquid mixing. Emulsification equipment.Size separation: Screening equipment i.e. trammels, rotex <strong>and</strong> hummer; airsuspension methods i.e. air separator <strong>and</strong> cyclone separators; hydraulic separation i.e.elutriation <strong>and</strong> double cone emulsifier.UNIT IIICrystallization: Crystal forms, habit, Mier's super saturation theory, crystallizersbased on super saturation, by cooling (i.e. tank crystallizers, agitated batchcrystallizers <strong>and</strong> Swenson-Walker), adiabatic cooling (i.e. vacuum crystallizers) <strong>and</strong>evaporation (i.e. Krystal crystallizers). Material <strong>and</strong> energy balance of crystallizer.Transportation of materials:Liquids: Pumps i.e. airlift, ejector, piston plunger, egg, diaphragm, gear, screw,centrifugal <strong>and</strong> self-priming.Gases: Ejectors, compressors, fans <strong>and</strong> blowers.Solids: InTermittent <strong>and</strong> continuous methods in vertical, horizontal <strong>and</strong> inclined planeUNIT IVCorrosion <strong>and</strong> its prevention: Types of corrosion, causes of corrosion <strong>and</strong> methodfor combating corrosion.77
Materials for pharmaceutical plant construction: Factors affecting the selection ofa material for pharmaceutical plant, ferrous metals (i.e. cast iron, steel <strong>and</strong> stainlesssteels), nonferrous metals (i.e. Copper <strong>and</strong> its alloys, aluminum, tin sliver, nickel <strong>and</strong>alloys), nonmetals i.e. glass, slate, asbestos, rubber, plastics <strong>and</strong> timber.Industrial hazards <strong>and</strong> safety precautions: Mechanical-chemical-electrical-firedusthazards, safety requirements, accident records etc.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Cooper <strong>and</strong> Gunns, “Tutorial Pharmacy”, Delhi: CBS Publishers.2. H. A. Liberman <strong>and</strong> J L Kanig, Leon Lachman, “The Theory <strong>and</strong> Practice of IndustrialPharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.3. Bentley, “Textbook of Pharmaceutics”, ELBS Bacilliere Tindall.4. W. L. Badger <strong>and</strong> J T Banchero, “Introduction to Chemical Engineering”, London:McGraw Hill International Book Co.5. W. L. MaCabe <strong>and</strong> J C Smith, “Unit operations of Chemical Engineering”, London:McGraw Hill International Book Co.6. R. H. Perry <strong>and</strong> C H Chilton, “Chemical Engineers H<strong>and</strong>book”, London: McGraw Hill<strong>and</strong> Co.78
Paper Code: BPL-305Pharmaceutics-VII (Physical Pharmacy)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: This subject gives main emphasis on various physical phenomena thatexist behind the formulation of different dosage forms.UNIT IMicromeretics <strong>and</strong> Powder Rheology: Particle size <strong>and</strong> distribution, averageparticle size, number <strong>and</strong> weight distribution, particle number, method of determiningparticle volume, optical microscopy, sieving, sedimentation, measurement, particleshape, specific surface, methods of determining surface area, permeability,adsorption, derived properties of powders, porosity, packing arrangement, densities,bulkiness <strong>and</strong> flow properties.Matter- State <strong>and</strong> selected properties: State of matter, change in the state of matter,latent heats <strong>and</strong> vapour pressure, sublimation-critical point, eutectic mixtures, relativehumidity, liquid complexes, liquid crystals, glassy state, solid-crystalline <strong>and</strong>amorphous polymorphism.UNIT IISurface <strong>and</strong> Interfacial Phenomenon: Liquid interface, surface <strong>and</strong> interfacialtensions, surface free energy measurement of surface <strong>and</strong> interfacial tensions,spreading coefficient, adsorption at liquid interfaces, surface active agents, HLBclassification, solubilization, detergency, electric properties of interface.Viscosity <strong>and</strong> Rheology: Newtonian systems, laws of flow, kinematic viscosity,effect of temperature, non Newtonian systems, pseudoplastic, dilatent, plastic,thixotropy, thixotropy in formulation, determination of viscosity, capillary, fallingball, rotational viscometers.UNIT III Dispersion system: Colloidal dispersions: Definition, types, properties of colloids,protective colloids, applications of colloid in pharmacy. Suspensions <strong>and</strong> Emulsions: Interfacial properties of suspended particles, settling insuspensions, theory of sedimentation, effect of Brownian movement, sedimentationof flocculated particles, sedimentation parameters, wetting of particles, controlledflocculation, flocculation in structured vehicles, rheological considerations,emulsions; types, theories <strong>and</strong> physical stability. Complexation: Classification of complexes, method of preparation <strong>and</strong> analysis,application.79
UNIT IVKinetics <strong>and</strong> drug stability: General considerations & concepts, half lifedetermination, influence of temperature, light, solvent, catalytic species <strong>and</strong> otherfactors, accelerated stability study, expiration dating.Buffers: Buffer equation <strong>and</strong> buffer capacity in general, buffer in pharmaceuticalsystems- buffered isotonic solutions, measurement of tonicity calculations, methodsof adjusting isotonicity.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A. N. Martin, “Physical Pharmacy”, Mumbai: K M Varghese& Co.2. Remington, “Pharmaceutical Sciences”, P.A.: Mack Publishing Co.3. E. Shotton & K. Ridgway, “Physical Pharmaceutics”, London: Oxford UniversityPress.4. H.A. Liberman <strong>and</strong> J L Kanig, Leon Lachman, “The Theory <strong>and</strong> Practice ofIndustrial Pharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.5. H.C. Ansel, “Introduction to Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms”, Mumbai: K MVarghese& Co.80
Paper Code: BPL-307Pharmacology-II (Pathophysiology of Common Diseases)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: The teaching of Pharmacology is aimed at different aspects of drugs <strong>and</strong>pharmaceuticals used in different diseases. The therapeutic/pharmacological group of drugs istaught according to the classification of World Health Organization. The students are able toknow the relationship between drug concentration <strong>and</strong> biological response, drug actionovertime, factors affecting absorption, distribution, binding, metabolism <strong>and</strong> elimination ofchemicals, structure activity relationship, biological changes that result from repeated druguse, tolerance, addiction <strong>and</strong> adverse effects. Process of drug interaction with cellularmacromolecules to alter physiological function <strong>and</strong> site of action including knowledge aboutproper selection of drugs is also covered.UNIT IBasic Principles of Cell Injury <strong>and</strong> Adaptation: Causes of Cellular injury,pathogenesis, <strong>and</strong> morphology of cell injury. Intercellular alterations in lipids,proteins <strong>and</strong> carbohydrates, Cellular adaptation, atrophy, hypertrophy.Basic Mechanisms involved in the process of inflammation <strong>and</strong> repair:Alterations in vascular permeability <strong>and</strong> blood flow, migration of WBCs, acute <strong>and</strong>chronic inflammation, mediators of inflammation, brief outline of the process ofrepair.UNIT II Pathophysiology of following Common Diseases: Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy,psychosis, depression, mania, hypertension, angina, congestive heart failure,atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, diabetes.UNIT IIIWherever applicable the molecular basis should be discussed. Pathophysiology of following Common Diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis, gout, Pepticulcer, asthma, ulcerative colitis, various types of Hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, acute <strong>and</strong>chronic renal failure.UNIT IVWherever applicable the molecular basis should be discussed. Pathophysiology of following Common Diseases:Tuberculosis, urinary tractinfections, sexually transmitted diseases, AIDS, anemia, iatrogenic diseases, <strong>and</strong>common types of neoplasm.Wherever applicable the molecular basis should be discussed.81
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. B.G. Katzung , “Basic <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacology”, London: Prentice HallInternational2. Davidson’s, “Principles <strong>and</strong> Practice of Medicine”, United Kingdom: ChurchillLivingstone3. Goodman <strong>and</strong> Gilman’s, “The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics”, NewYork: Pregman Press.4. L. Paul, “Principles of Pharmacology”, Chapman <strong>and</strong> Hall.5. H. P. Rang <strong>and</strong> M M Dale, “Pharmacology”, United Kingdom: ChurchillLivingstone.6. Harsh Mohan, “Textbook of Pathology”, India: Jaypee Brothers MedicalPublishers.7. E. T. Herfindal <strong>and</strong> J L Hirschman, “Clinical Pharmacy <strong>and</strong> Therapeutics”,Baltimore: Williams <strong>and</strong> Willkins Co.8. Edward C. Klatt Edward C., M. D. Klatt Vinay & M. D. Kumar, “Robbins Reviewof Pathology”, U. K.: W.B. Saunders Company.9. J. L. Dipiro, “Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiological Approach”, UnitedKingdom: Elsevier.82
Paper Code: ENG-301Communication Skills in EnglishL -- T -- P Total Credits: 022 -- -- Total Marks:50External Marks: 25Internal Marks: 25Paper Objective: Paper objective is to improve the language proficiency of sciencegraduates as skill oriented. The main objectives are: To enable the learners to be able to communicate in real life contexts using video <strong>and</strong>audio teaching material. Enabling the learners to become communicatively competent by using listening,speaking, writing <strong>and</strong> reading. Introducing the learners to non verbal communication strategies. To prepare the learners for successfully clearing the international examinations ofproficiency in English like IELTS, BEC, <strong>and</strong> TOEFL etc.UNIT-I: BUSINESS COMMUNICATION – IIAgreeing <strong>and</strong> disagreeingPresentationsIntraorganizational communicationH<strong>and</strong>ling complaint callsH<strong>and</strong>ling after sales problemsTele interviewsNon-Verbal communicationUNIT-II: WRITINGMinutes of meetingsSt<strong>and</strong>ard business lettersDrafting emailsShort reportsTechnical writingPreparing resumes <strong>and</strong> covering lettersUNIT-III: TEAM SKILLSTaking part in business meetingsPreparing agenda for meetingsMaking notes of business conversationsDebates <strong>and</strong> discussionsSoft skills for team building83
UNIT-IV: READINGWhat is reading?Types of readingStrategies for effective readingNOTE:Semester will carry 50 marks with equal weightage ( 25 each ) to Theory &Practical assessment.Theory Assessment will be done by the Controller ofExaminations by conducting a theory paper of 25 marks (External Marks).Practical Assessment will be done by the Learning Resource Centre by conductingListening & Speaking tests of 25 marks (Internal Marks).84
Paper Code: FFA-100Communicative French-1AL -- T -- P Total Credits: 033 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Paper Objective is to develop the following language skills:Listening: Enabling the learners to listen <strong>and</strong> underst<strong>and</strong> the spoken French language whichuses the elementary spoken structures.Speaking: Enabling the learners to speak <strong>and</strong> engage in simple dialogues in French.Reading <strong>and</strong> textual comprehension: Enabling learners to read <strong>and</strong> underst<strong>and</strong> the simpleelementary short texts in French.Writing: Enabling learners to use simple grammatical structures <strong>and</strong> the most essentiallexique in French.Exposing the learners to the culture of France.Contentsa. Phonetics:i. Soundii. Intonationb. Grammatical Components:Ii. Nouns <strong>and</strong> Articles: Gender <strong>and</strong> numberii. Pronounsiii. Adjectivesiv. Negationv. Numbers, Days of the week, Months of the year, Time, Date etc.IISimple conversationSimple paragraph writingEvaluation:There shall be one written Examination at the end of the semester. The evaluation consists oftwo aspects, namely continuous evaluation <strong>and</strong> semester Examination. Minimum percentagefor both the evaluation is 50%. Total mark for final paper is 100 <strong>and</strong> the ratio of continuousevaluation <strong>and</strong> semester examination is 50:50.Continuous evaluation includes:General Performance (Active classroom participation, Attendance etc.): 10 MarksHome assignments:20 MarksInternal Tests:20 MarksSemester Examination contains:50 Marks85
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Le Nouveau Sans Frontières – I, CLE International2. Panorama – I, CLE International3. Connexions – I, Didier4. Café Crème – I, Didier5. Campus – I, CLE InternationalNote: Audit paper in French offered by Department of Foreign Languages, BPSMV is a noncredit paper where the credits of the paper shall not be considered for calculation of SGPA(semester Grade point Average)/ CGPA (cumulative Grade Point average) of a particularsemester result whereas the credits <strong>and</strong> Grade of the audit paper shall be mentioned in theDMC (detailed Mark Certificate) of a student, in a semester in which she has appeared for thesame.86
Paper Code: LAW- 001Legal LiteracyL -- T -- PAudit Paper3 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Have a brief knowledge of laws of India <strong>and</strong> an underst<strong>and</strong>ing of theformal dispute redressal mechanism that exist in India.UNIT I Law relating to Hindu Marriage- conditions of valid marriage, Prohibited degrees,ground of divorce, Rights of wife. Dowry- definition, outlines of law relating to dowry. Sexual Harassment of Women- guidelines by Supreme Court in Vishaka <strong>and</strong> othersV. State of Rajasthan <strong>and</strong> others. Consumer Protection Act, 2000- meaning of consumer, Rights of consumer,Remedies available in the Act, Consumer Forums.UNIT II Fundamental Rights of Citizens- meaning, types & enforcement of fundamentalrights. Rights in relation to police- rights in relation to arrest, bail, search & seizure <strong>and</strong>rights of Women against police. Right to Information- meaning, how we can ask for information, which informationcan be denied, remedies for not furnishing the information. Lokayukt- object, Function, powers <strong>and</strong> duties. Right of Children to Free <strong>and</strong> Compulsory Education Act, 2009- Object, Scope <strong>and</strong>main features.UNIT IIIProperty Rights- Women’s property rights, right of inheritance, stridhan.Human Rights- what is human rights, international conventions on human rights.Right to Maintenance- maintenance under Hindu law. Under Section 125 of CriminalProcedure code.Object <strong>and</strong> scope of Motor Vehicle Act, 1988, Third party Insurance, No faultliability, Motor Vehicle Claim Tribunals, Procedure of Obtaining Driving License.UNIT IVEnvironment <strong>and</strong> Pollution- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986- What isenvironment, Outlines of different Indian Laws on Environment.87
Labour Laws- Object <strong>and</strong> scope of Workmen Compensation Act, Trade Union Act,Payment of Wages Act, Minimum Wages Act, Equal Remuneration Act, MaternityBenefit Act.Trafficking in Human Beings- Human trafficking <strong>and</strong> sexual exploitation, UnitedNations Global Initiative to Fight Human Trafficking, Forced Labor <strong>and</strong> HumanTrafficking,Note: Instruction for External Examiner:The paper will be divided in four units. Each unit must have two questions <strong>and</strong> theexaminee is required to attempt one question from each unit & four questions at all.All questions carry equal marks.Instruction for Internal Examiner: The internal assessment marks will bedistributed as follows:1. Attendance 5 marks.2. Two assignment of 5 marks each 10 marks3. Mid term examination 20 marks4. Article writing & presentation 15 marksTotal Marks50 MarksSuggested Readings:-Towards Legal Literacy: An Introduction to Law in India, Kamala Sankaran & UjjwalKumar <strong>Singh</strong> ISBN: 9780195692228Creating Legal Awareness, edited by Kamala Sankaran <strong>and</strong> Ujjwal <strong>Singh</strong> (Delhi:OUP, 2007)Multiple Action Research Group, Our Laws Vols 1-10, Delhi. Available in Hindi also.S.P. Sathe, Towards gender Justice, Research Center for Women’s Studies, SNDWomen’s University, Bombay, 1993.Indian Social Institute, New Delhi, Legal Literacy Series Booklets. Available in Hindialso.88
Paper Code: BPP-309Pharmaceutical Chemistry-VII Practical (PharmaceuticalAnalysis-II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted; some of them may asfollows:Quantitative determinations of official drugs <strong>and</strong> pharmaceuticals by differentmethods discussed in theory.Chromatography experiments by different methods to know the homogeneity ofsubstances <strong>and</strong> separation of drugs.Determination of alcohol <strong>and</strong> moisture content in the pharmaceutical preparations <strong>and</strong>crude drugs.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. M. Kolthoff <strong>and</strong> V. A. Stenger, “Volumetric Analysis, Vol. II Titration Methods”,New York: Interscience Publishers, Inc.2. P. D. Sethi , “HPLC”,New Delhi: CBS Publishers.3. A. H. Beckett <strong>and</strong> J. B. Stenlake, “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry” Vol. I <strong>and</strong>II,The Athlon Press of the University of London.4. E. Stahl “Thin Layer Chromatography, A Laboratory H<strong>and</strong>book”, New York:Springer- Verlag.5. “Indian Pharmacopoeia”, Delhi: Govt. of India, Ministry of Health.89
Paper Code: BPP-311Pharmaceutics-VI Practical (Pharmaceutical Engineering- II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted, some of them coveringdifferent unit operations studied in theory such as: distillation, extraction, mixing, sizeseparation, size reduction, crystallization etc.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. W. L. MaCabe <strong>and</strong> J C Smith, “Unit operations of Chemical Engineering”, London:McGraw Hill International Book Co.2. R. H. Perry <strong>and</strong> C H Chilton, “Chemical Engineers H<strong>and</strong>book”, London: McGraw Hill<strong>and</strong> Co.3. V. S. Subhramanyam, “Laboratory Manual of Pharmaceutical Engineering”, Delhi:CBS Publishers.90
Paper Code: BPP-313Pharmaceutics-VII Practical (Physical Pharmacy)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted; some of them may asfollows:Determination of bulk density, true density <strong>and</strong> porosity. Study of flow properties ofpowders, effects of particle size <strong>and</strong> lubricants, Surface tension - determination of CMC,Solubility: solvent <strong>and</strong> co solvent effect, ternary phase diagram, water number etc.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Remington, “Pharmaceutical Sciences”, P.A.: Mack Publishing Co.2. E. Shotton & K. Ridgway, “Physical Pharmaceutics”, London: Oxford UniversityPress.3. Gaud & Gupta, “Practical Physical Pharmacy”, Delhi: CBS Publishers.4. V. S. Subhramanyam, “Laboratory manual of Physical Pharmacy”, Delhi: VallabhPrakashan.91
Paper Code: BPL-302Pharmaceutical Chemistry-VIII (Medicinal Chemistry-I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:Objective of this subject is to underst<strong>and</strong> the Basic Principles of Medicinal Chemistry& modern approaches for drug designing. Paper also covers synthetic procedures,mode of action, uses, structure activity relationship including physicochemicalproperties of some classes of drugs.UNIT IBasic Principles of Medicinal Chemistry: Physico-chemical aspects (Optical,geometric <strong>and</strong> bio-isosterism) of drug molecules <strong>and</strong> biological action, Drug-receptorinteraction including transduction mechanisms.Principles of Drug Design (Theoretical Aspects): Traditional analog (QSAR) <strong>and</strong>mechanism based approaches (Introduction of graph theory, applications of quantummechanics, Computer Aided Drug Designing (CADD) <strong>and</strong> molecular modeling.UNIT IISynthetic procedures of selected drugs, mode of action, uses, structure activityrelationship including physicochemical properties of the drugs acting at Synaptic<strong>and</strong> neuro-effector junction sites:Cholinergics <strong>and</strong> Anticholinesterases.Adrenergic drugs.Antispasmodic <strong>and</strong> anti ulcer drugs.Neuromuscular blocking agents.UNIT IIISynthetic procedures of selected drugs, mode of action, uses, structure activityrelationship including physicochemical properties of the following classes ofdrugs:Antihistamines.Eicosanoids.Analgesic-antipyretics, anti-inflammatory (non-steroidal) agents.Drugs affecting uterine motility: Oxytocics (including oxytocin, ergot alkaloids <strong>and</strong>prostagl<strong>and</strong>ins).Biochemical approaches in drug designing wherever applicable should be discussed.UNIT IV Synthetic procedures of following selected drugs: Adrenaline, Phenylephrine,Edorphonium Chloride, Dicyclomine, Neostigmine bromide, Cyclopentolate HCl,92
Propanthaline bromide, Benzhexol, Omeprazole, Pentoprazole, Rabeprazole,Ranitidine, Roxatidine, Diphenhydramine, Chlorpheneramine, Promethazine,Mepyramine, Cyclizine, Sodium chromoglycollate, Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Indomehtacin,Phenazone, Phenyllbutazone, Oxyphenbutazone, Diclofenac, Piroxicam, Tenoxicam,Celecoxib, Valdecoxib,Allopurinol, Probenecid.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Wilson <strong>and</strong> Gisvold’s, “Textbook of Organic Medicinal <strong>and</strong> PharmaceuticalChemistry”, Philadelphia: J. Lippincot Co.2. W. O. Foye, “Principles of Medicinal Chemistry”, Philadelphia: Lea <strong>and</strong> Febiger.3. C. Hansch, “Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry”, Pregman Press Oxford.4. Y. C. Martin, “Quantitative Drug Design”, New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.5. Exploring QSAR• Vol. I- C. Hansch <strong>and</strong> A. Leo.,“Fundamentals <strong>and</strong> Applications in Chemistry<strong>and</strong> Biology”, Washington: American Chemical Society.• Vol.II- C. Hansch, A. Leo <strong>and</strong> D. Hockman, “Hydrophobic, Electronic <strong>and</strong>Steric Constants”, Washington: ACS Books Catalog.6. M. E. Wolff, “Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry”, New York: John Wiley & Sons.7. T. Nogardy, “Medicinal Chemistry – A Biochemical Approach”, New York, Oxford:Oxford University Press.93
Paper Code: BPL-304Pharmaceutics-VIII (Dosage Form Design)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:The objective of the paper is to instill skills among students for designing various dosageforms. Design of dosage form is important in achieving predictable therapeutic response to adrug included in a drug delivery system, which is subjected to large-scale manufacture. Thereproducibility of a product should not differ with its quality <strong>and</strong> efficacy. The studyencompasses formulation aspects with variety of additives available in context with release ofa drug from the drug delivery system.UNIT IPreformulation studies: Study of physical properties of drug like physical form,particle size, shape, density, wetting dielectric constant, solubility, dissolution <strong>and</strong>organoleptic properties <strong>and</strong> their effect on formulation, stability <strong>and</strong> bioavailability.Study of chemical properties of drugs: Study of chemical properties of drugs likehydrolysis, oxidation, reduction, racemisation, polymerization etc. <strong>and</strong> their influenceon formulation <strong>and</strong> stability of products.UNIT II Study of prodrugs: Study of prodrugs in solving problems related to stability,bioavailability <strong>and</strong> elegancy of formulation. Radiopharmaceuticals: Fundamentals of radio pharmacy, therapeutic applicationsof isotopes, diagnostic applications of isotopes, use of radioisotopes in basic research,product development, product production, process control <strong>and</strong> quality control.UNIT III Liquid formulations: Formulation <strong>and</strong> industrial production of liquid <strong>and</strong> semi-solidformulation like suspension, syrup, emulsions <strong>and</strong> ointments. Skin: Structure <strong>and</strong> physiology, physiology of sweating, physiology of skin secretionsformulations, preparations for skin of face <strong>and</strong> h<strong>and</strong>s, formulation, preparation <strong>and</strong>evaluation of cleansing creams, cold creams, cleansing lotions, foundation creams,moisturizing creams, skin tonics, h<strong>and</strong>y <strong>and</strong> body lotion.UNIT IVHairs: Structure <strong>and</strong> functions, formulation, preparation <strong>and</strong> evaluation of shampoos,d<strong>and</strong>ruff preparation, hair creams, <strong>and</strong> fixers, hair colorants, hair remover(depilatories), shaving sticks <strong>and</strong> after shave lotion.Lipsticks: Formulation, preparation <strong>and</strong> evaluation of lipsticks.Formulation, preparation <strong>and</strong> evaluation of other cosmetics like nail lacquers, antiperspirants<strong>and</strong> deodorants, tooth powders <strong>and</strong> tooth paste.94
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. H.C. Ansel, “Introduction to Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms <strong>and</strong> Drug DeliverySystems”, Mumbai: K M Varghese& Co.2. Remingtons , “Practice of Pharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.3. Shah, “SOP”, New Delhi: Business Horizons.4. Banker <strong>and</strong> Rhodes, “Modern Pharmaceutics”, New York: Marcel Dekker5. Swarbrick, “Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology”, New York : M. Dekker6. “Pharmacopoeia of India”, Govt. of India, Ministry of Health.7. Leon Lachman, H. A. Liberman <strong>and</strong> J. L. Kanig, “The Theory <strong>and</strong> Practice ofIndustrial Pharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.8. K.A. Connores, G.L. Amiden <strong>and</strong> V.J.Stella, “Chemical stability of Pharmaceuticals”,New York: Wiley & Sons.9. A. Owunwonne, “H<strong>and</strong> Book of Radiopharmaceuticals”, New Delhi: NarosaPublishing House.10. H. S. Bean, A. H. Beckett <strong>and</strong> J. E. Carless, “Advance in Pharmaceutical Sciences”,London: Academic Press.11. Sanju N<strong>and</strong>a, Arun N<strong>and</strong>a <strong>and</strong> Roop K. Khar, “Cosmetic Technology”, Delhi: BirlaPublications Pvt. Ltd.95
Paper Code: BPL-306Pharmacognosy-III (Chemistry of Herbal Drugs)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:The Objective of the paper is to study medicinally important plants & marine drugsscientifically along with chemistry & biosynthesis of different phytoconstituents obtainedfrom crude drugs. The paper also envisages the biotechnological techniques for obtaining <strong>and</strong>improving the quality of natural products.”UNIT I General techniques: General techniques of biosynthetic studies <strong>and</strong> basic metabolicpathways. An introduction to biogenesis of secondary metabolites of pharmaceuticalimportance. Study of chemical <strong>and</strong> spectral approaches: Study of chemical <strong>and</strong> spectralapproaches to simple molecules of natural origin. Concept of stereoisomerism: Concept of stereoisomerism taking examples of naturalproducts.UNIT IITerpenes: Biogenesis of monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes <strong>and</strong> triterpenoids.Chemistry of at least two medicinally important terpenoids from each class.Irridoids: Chemistry of medicinal important irridoids.UNIT IIICarotenoids: Carotenoids beta-carotenoids, alpha-carotenes, vitamin A, xanthophyllsof medicinal importance.Steroids <strong>and</strong> cardiac glycosides: Utilization of plants as a source of raw material forthe production of steroids, biosynthesis <strong>and</strong> chemistry of diosgenin, sarasapogenin,digitoxin <strong>and</strong> digoxin.UNIT IVAlkaloids: Chemistry <strong>and</strong> biogenesis of atropine <strong>and</strong> related compounds, quinine,reserpine, morphine, papaverine, ephedrine, ergot <strong>and</strong> vinca-alkaloids.Chemistry of antibiotics: Penicillins, streptomycin <strong>and</strong> tetracyclines.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.96
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. S. S. Agrawal <strong>and</strong> M. Paridhari, “Herbal Drug Technology”, New Delhi: UniversityPress2. S. S. Agrawal <strong>and</strong> M. Paridhari, “Clinically Useful Herbal Drugs”, New Delhi: AhujaPublishers.3. C. K. Kokate, A.P. Purohit <strong>and</strong> S.B. Kokhale., “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, Pune:Nirali Publication.4. G. E. Trease <strong>and</strong> W. C Evans, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, U. K.: BailliereTindall.5. V. C. Tyler, L. R.Brady <strong>and</strong> J.E. Robers, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”,Philadelphia: 8 th Ed. Lea <strong>and</strong> Febiger.6. T.E. Wallis, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, London: Churchill limited.7. A. Fahn, “Plant Anatomy”, Oxford : Pergamon Press.8. Jean Brunton, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, Engl<strong>and</strong>, U.K: Phytochemistry <strong>and</strong>Medicinal Plants, Intercept Limited.9. L. Finar, “Organic Chemistry” (Vol. I <strong>and</strong> II), London: ELBS/ Longman.10. Gurdeep R Chatwal, “Organic Chemistry of Natural Products” (Vol. I <strong>and</strong> II), Bombay:Himalya Publication House.11. O. P. Agarwal, “Organic Chemistry of Natural Products” (Vol. I <strong>and</strong> II), U. P.: GoelPublication House.97
Paper Code: BPL-308Pharmacology-III (Pharmacology-III)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:The teaching of Pharmacology is aimed at different aspects of drugs <strong>and</strong> pharmaceuticalsused in different diseases. The therapeutic/pharmacological group of drugs is taughtaccording to the classification of World Health Organization. The students are able to knowthe relationship between drug concentration <strong>and</strong> biological response, drug action overtime,factors affecting absorption, distribution, binding, metabolism <strong>and</strong> elimination of chemicals,structure activity relationship, biological changes that result from repeated drug use,tolerance, addiction <strong>and</strong> adverse effects. Process of drug interaction with cellularmacromolecules to alter physiological function <strong>and</strong> site of action including knowledge aboutproper selection of drugs is also covered.UNIT IGeneral Pharmacology: Introduction to Pharmacology, Sources of drugs, Dosageforms <strong>and</strong> routes of administration, mechanism of action, Combined effect of drugs,Factors modifying Drug action, tolerance <strong>and</strong> dependence, Pharmacogenetics.Principles of Basic <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacokinetics: Adverse Drug Reactions <strong>and</strong>treatment of poisoning, ADME drug interactions, Bioassay of Drugs <strong>and</strong> BiologicalSt<strong>and</strong>ardization, Discovery <strong>and</strong> development of new drugs.UNIT II: Pharmacology of Peripheral Nervous System: Neurohumoral transmission (autonomic <strong>and</strong> Somatic). Parasympathomimetics, Parasympatholytics, Sympathomimetics, AdrenergicReceptor <strong>and</strong> neuron blocking agents, Ganglionic, stimulants <strong>and</strong> blocking agents. Neuromuscular blocking Agents.UNIT III: Autocoids: Histamine, 5- HT <strong>and</strong> their antagonists. Prostagl<strong>and</strong>ins, thromboxanes <strong>and</strong> leukotrienes. Pentagastrin, Cholecystokinin, Angiotensin, Bradykinin <strong>and</strong> Substance P. Analgesics, Antipyretics, Anti-inflammatory <strong>and</strong> Anti-gout drugs.UNIT IV: Drugs Acting on the Respiratory System:Anti-asthmatic drugs.Anti-tussives <strong>and</strong> expectorants.Respiratory stimulants.98
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. H. P. Rang <strong>and</strong> M M Dale, “Pharmacology”, New York: Churchill Livingstone.2. F. S. K. Berar, “Textbook of Experimental Pharmacology”, New Delhi: Interprint.3. Goodman <strong>and</strong> Gilman’s, “The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics”, NewYork: Pregman Press.4. L. Paul, “Principles of Pharmacology”, New York: Chapman <strong>and</strong> Hall.5. B. G. Katzung, “Basic <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacology”, New York: Prentice HallInternational.99
Paper Code: BPL-310Pharmaceutics-IX (Pharmaceutical Management)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:Pharmaceutical management enables the students to learn about different principles ofmanagement <strong>and</strong> marketing. This prepares the students as how to manage different tasks,planning of objectives, how to manage long Term <strong>and</strong> short Term targets in industry,marketing <strong>and</strong> retail set-ups, strategies to accomplish different goals <strong>and</strong> management ofdifferent tasks within a specified period of time.UNIT IPrinciples of Management (Co-ordination, Communication, Motivation,decision making, Leadership, innovation, Creativity, Delegation ofAuthority/Responsibility, Record Keeping., Managerial qualities. Identification ofkey points to give maximum thrust for development <strong>and</strong> perfection.UNIT IIAccountancy: Principles of Accountancy, Ledger posting <strong>and</strong> book entries.Economics: Principles of economics with special reference to the laws of dem<strong>and</strong><strong>and</strong> supply.UNIT IIIPharmaceutical Marketing: Functions; buying, selling, transportation, storage,finance, feedback information, channels of distribution, wholesale, retail,departmental store, multiple shop.Salesmanship: Principles of sale promotion, advertising, ethics of sales.UNIT IVManagement: The concept, scope, functions <strong>and</strong> principles of management,Management <strong>and</strong> administration, Evolution of management.Human Resource Management: A brief exposure of human resourcemanagement - HR planning, recruitment, selection, training, performanceappraisal, positive attitude.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.100
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. G. W. Plossl <strong>and</strong> O W Wight, “Production <strong>and</strong> Inventory Control, Principles <strong>and</strong>Techniques”, New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.2. Banerjee, “Principle <strong>and</strong> Practice of Management”, New Delhi: Oxford <strong>and</strong> I B HPublishing Company.3. Rustam S. Pavel, “Salesmanship <strong>and</strong> Publicity”, Mumbai: Progressive CorporationPvt. Ltd.4. S.P. Ganguly, “Principles <strong>and</strong> Practice of Management”, Calcutta: ChatterjeePublishing Concern.5. K. S. menon, “Purchasing <strong>and</strong> Inventory Control”, Allahabad: Wheeler Publishing.6. C.B. Gupta, “Principles <strong>and</strong> Practice of Management”, New Delhi: Nationalpublishing House.101
Paper Code: BPP-312Pharmaceutical Chemistry-VIII Practical (MedicinalChemistry-I)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of experiments based on theory topics should be conducted likeSynthesis of some important medicinal compounds involving at least two steps in theirsynthesis.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. B.S. Furniss, A.J. Hannaford, P.W.G. Smith <strong>and</strong> A.R. Tatchell, “Vogel’s Textbook ofPractical Organic Chemistry”, Singapore: Pearson Education Limited.2. F.G. Mann <strong>and</strong> B.C. Saunders, “Practical Organic Chemistry”, Hyderabad: OrientLongman Limited.3. T. Nogardy, “Medicinal Chemistry – A Biochemical Approach”, New York, Oxford:Oxford University Press.4. “Pharmacopoeia of India”, Govt. of India, Ministry of Health.102
Paper Code: BPP-314Pharmaceutics-VIII Practical (Dosage Form Design)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted; some of them may asfollows:Preformulation studies, Synthesis <strong>and</strong> characterization of some Prodrugs, Formulation,preparation, packing, labeling <strong>and</strong> evaluation of the following class of dosage forms usinglaboratory scale equipments: Syrups (including dry syrups), Suspensions, Emulsions <strong>and</strong>Topical Preparations, Preparation <strong>and</strong> evaluation of (a) Cold cream (b) Vanishing cream (c)Sunscreen cream (d) Hair creams (e) Shampoos (f) Shaving cream (g) Tooth powder (h)Tooth paste (i) Mouth wash (j) Lipsticks etc. as per BIS or other methods <strong>and</strong> otherexperiments illustrative of the portion covered in the theory portion of the syllabus.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. H.C. Ansel, “Introduction to Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms <strong>and</strong> Drug DeliverySystems”, Mumbai: K M Varghese& Co.2. “Pharmacopoeia of India”, Govt. of India, Ministry of Health.3. K.A. Connores, G.L. Amiden <strong>and</strong> V.J.Stella, “Chemical stability of Pharmaceuticals”,New York: Wiley & Sons.4. Sanju N<strong>and</strong>a, Arun N<strong>and</strong>a <strong>and</strong> Roop K. Khar, “Cosmetic Technology”, Delhi: BirlaPublications Pvt. Ltd.103
Paper Code: BPP-316Pharmacognosy-III Practical (Chemistry of Herbal Drugs)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of experiments based on theory topics should be conducted includingLaboratory experiments on isolation, separation, purification of various groups ofchemical constituents of pharmaceutical significance. Exercises on paper <strong>and</strong> thinlayer chromatographic evaluations of herbal drug constituents.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. T. E. Wallis, “Practical Pharmacognosy”, London: Churchill limited.2. K. R. Brain <strong>and</strong> T. D. Turner, “The Practical Evaluation of Phyto Pharmaceutical”,Bristol: Scientechnica Publications.3. V. E. Jr. Tyler & A.E. Schwarting, “Experimental Pharmacognosy”, Minneapolis:Burgess Pub. Co.104
Paper Code: BPP-318Pharmacology-III Practical (Pharmacology-III)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of experiments based on theory topics should be conducted, some of them may asfollows (As per regulatory bodies guidelines Animals Experiments should be replaced withexperiments through Software): To study the experimental animal & basic equipments (for isolated tissues) used inexperimental pharmacology. To prepare & submit the various Physiological Salt Solution (PSS). To study various st<strong>and</strong>ard solution used in pharmacology. To study various agonist <strong>and</strong> antagonist used in pharmacology. To study the various route of drug administration in experimental pharmacology. To study the st<strong>and</strong>ard methods for scarifying & making animal unconscious & thest<strong>and</strong>ard techniques for injection of drugs. To record a Dose Response Curve (DRC) or Concentration Response Curve (CRC) ofacetylcholine/ histamine using rat ileum preparation (Demonstration throughSoftware). To obtain a graded dose response curve of histamine & determine the concentrationsame in solution (Unknown Concentration) using matching type bio-assay.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. “Pharmacological Experiments on Isolated Preparations”, Livingstone: EdinburgUniversity Pharmacology Staff.2. S.K. Kulkarni, “H<strong>and</strong>book of Experimental Pharmacology”, Delhi: VallabhPrakashan.3. L. Paul, “Principles of Pharmacology”, New York: Chapman <strong>and</strong> Hall.4. B. G. Katzung, “Basic <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacology”, New York: Prentice HallInternational.5. M. N. Ghosh, “Fundamentals of Experimental Pharmacology”, Calcutta: ScientificBook Agency.6. Goyal ,”Practical in Pharmacology”, Ahmedabad: B S Shah Publications.7. Ghose, “Fundamentals of Experimental Pharmacology”, New Delhi: Amit BookCompany.105
Paper Code: BPL-401Pharmaceutical Chemistry-IX (Medicinal Chemistry-II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Study of this subject covers the theory of drug action, stereochemistry <strong>and</strong>drug action, alkaloids <strong>and</strong> relation of structure <strong>and</strong> biological activity of organic medicinalagents. Protein <strong>and</strong> steroidal hormones, antibiotics, <strong>and</strong> synthetic drugs of differentpharmacological activity are also included.Synthetic procedures of selected drugs, mode of action, uses, structure activityrelationship including Physico-Chemical properties of the following classes of drugs:UNIT I Steroids <strong>and</strong> related drugs: Steroidal nomenclature <strong>and</strong> stereochemistry, <strong>and</strong>rogens<strong>and</strong> anabolic agents, estrogens, <strong>and</strong> progestational agents, adrenocorticoids.UNIT IIGeneral AnestheticsLocal AnestheticsHypnotics <strong>and</strong> SedativesOpioid analgesicsAntitussivesAnticonvulsantsAntiparkinsonism drugsCNS stimulantsPsychopharmacological agents (neuroleptics, antidepressants, anxiolytics).UNIT IIIDiureticsCardiovascular drugsAnticoagulant <strong>and</strong> Antiplatelet drugs.Biochemical approaches in drug designing wherever applicable should be discussed.UNIT IV Synthetic procedures of following selected drugs: Procaine, Benzocaine,Lignocaine, Cinchocaine, Thiopentone, Phenobarbitone, Hexobarbitone, Diazepam,Mehtaqualone, PheNew Yorktoin, Troxidone, Pethidine, N-methylmorphine,Chlorpromazine, Trifluoperazine, Amitryptiline, Nikethamide, Cholesterol,Dihydroepi<strong>and</strong>rosterone, Oestradiol, Diethylstilbosterol, Progesterone, Cortisoneacetate, Stigmasterol, Norethisterone, Testosterone, Triamcinolone, Furosemide,Acetazolamide, Chlorthiazide, Hydrochlorthiazie, Spironolactone, Triametrene,106
Nifedipine, Procainamide, Verapamil, Propranolol, Methyldopa, Clonidine,Guanethidine, Hydrallazine, Phentolamine, Clofibrate, Warfarin, Phenindione.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Wilson <strong>and</strong> Gisvold’s, “Textbook of Organic Medicinal <strong>and</strong> PharmaceuticalChemistry”, Philadelphia: J. Lippincot Co.2. W. O. Foye, “Principles of Medicinal Chemistry”, Philadelphia: Lea <strong>and</strong> Febiger.3. C. Hansch, “Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry”, Pregman Press Oxford.4. Y. C. Martin, “Quantitative Drug Design”, New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.5. M. E. Wolff, “Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry”, New York: John Wiley & Sons.6. T. Nogardy, “Medicinal Chemistry – A Biochemical Approach”, New York, Oxford:Oxford University Press.107
Paper Code: BPL-403Pharmaceutics –X (Pharmaceutical Technology)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:The students learn the techniques <strong>and</strong> methods of formulation development especially withreference to advanced formulation techniques, novel drug delivery systems, introduction ofpharmaceutical bio-technology <strong>and</strong> role of pharmacist in the development of different usefulbiotechnological products.UNIT ITablets: Types of tablets, formulation of tablets, various granulation techniquesincluding slugging, chilsonator, extruder <strong>and</strong> granulator. Tableting machinery forproduction of single layer, multilayer <strong>and</strong> compression coated tablets. Physics oftablet compression, strain gauge.Tablet coating: Sugar coating, film coating <strong>and</strong> compression coating, coatingprocesses i.e. air suspension coating <strong>and</strong> pan coating (using conventional, rear vented<strong>and</strong> perforated pans). Quality control of tablets. Process validation.UNIT IICapsules: Advantages, applications, formulation, large scale production <strong>and</strong> qualitycontrol of hard <strong>and</strong> soft capsules.Microencapsulation: Terminology, advantages <strong>and</strong> applications. Study of variousprocesses employed for microencapsulation i.e. coacervation phase separation,multiorifice centrifuge, electrostatic deposition, vacuum deposition, spray drying,spray congealing, polymerization, complex emulsion, air suspension technique <strong>and</strong>pan coating.UNIT IIIAerosols: Definitions, advantages <strong>and</strong> applications, liquified-gas system, compressedgas system, propellants, containers, valves, cold-filling process, pressure fillingprocess <strong>and</strong> quality control of aerosols.108
Packaging of Pharmaceutical Products: Packaging components, types,specifications <strong>and</strong> methods of evaluation, stability aspects of packaging. Packagingequipments, factors influencing choice of containers, legal <strong>and</strong> other officialrequirements for containers, package testing.UNIT IVParenterals: Types of parenteral products, formulation, production facilities,production procedures for small volume <strong>and</strong> large volume Parenterals, large scaleproduction of injectable grade water <strong>and</strong> quality control of parenterals. Design,development, production <strong>and</strong> evaluation of oral controlled release preparations.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. G. S. Banker <strong>and</strong> C. T. Rhode, “Modern Pharmaceutics”, New York: Marcel DekkerInc.2. S. J. Carter, Cooper <strong>and</strong> Gunn's, “Dispensing for Pharmaceutical Students”, Delhi:CBS Publishers.3. Remington's, “The science <strong>and</strong> Practice of Pharmacy”, Pernsybrania: MackPublishing Co. Easton.4. L. Lachman, H. A. Lieberman <strong>and</strong> J. L .Kanig, “The Theory <strong>and</strong> Practice of IndustrialPharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.5. J. C. KacChensney, “Packaging of Cosmetics <strong>and</strong> Toiletories”, London: NewnessButterworth.109
Paper Code: BPL-405Pharmacognosy-IV (Pharmacognosy-IV)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:Pharmacognosy is a paper which contribute to rational relationship between chemicalmoieties of naturally occurring drugs <strong>and</strong> biological <strong>and</strong> therapeutic effects they generate.The objective of the paper is to study with sufficient knowledge of classical botaNew Yorkassociated with scientific study of medicinally important plants arranged on a taxonomicsystem including chemical tests along with newer methods of analysis.UNIT IRole of medicinal <strong>and</strong> aromatic plants in national economy.World-wide trade in medicinal plants <strong>and</strong> derived products with special referenceto the status <strong>and</strong> potential of diosgenin (dioscorea), taxol (taxus sps), digitalis,podophyllum, vinca, papain, cinchona, liquorice, ginseng, aloe vera, rauwolfia <strong>and</strong>plant containing laxatives.UNIT IIPlant based industries <strong>and</strong> institutions involved in research <strong>and</strong> analysis ofmedicinal <strong>and</strong> aromatic plants in India.Economic utilization <strong>and</strong> production of phytoconstituents of aloes, senna,ispaghula, digitalis, dioscorea, poppy, ergot, cinchona, tropane <strong>and</strong> vinca alkaloids.Chemotaxonomy: Chemotaxonomy of medicinal plants.UNIT IIIMarine pharmacognosy: Novel medicinal agents from marine sources.Aromatic plants: Utilization of aromatic plants <strong>and</strong> derived products with specialreference to the isolation methods <strong>and</strong> chemical profile of mentha oil, s<strong>and</strong>alwood oil,fennel oil, geranium oil <strong>and</strong> eucalyptus oil.UNIT IVPlant tissue culture: Historical development of plant tissue culture, types of cultures,nutritional requirements, growth <strong>and</strong> their maintenance. Application of plant tissueculture in pharmacognosy.Natural allergens <strong>and</strong> photosensitizing agents.110
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. C. K. Atal <strong>and</strong> B. M. Kapur, “Cultivation <strong>and</strong> utilization of Medicinal plants”,Jammu: RRL.2. W. Barz, Reinhard E <strong>and</strong> Zenk M H, “Plant Tissue Culture <strong>and</strong> Its BiotechnologicalApplication”, Berlin: Springer.3. R. N. Chopra, S. L. Nayar <strong>and</strong> I. C. Chopra, “Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants”,New Delhi: CSIR.4. K. L. Chadha <strong>and</strong> R.Gupta, “Advances in Horticulture-Vol. II-Medicinal <strong>and</strong>Aromatic Plants”, New Delhi: Malhotra Publishing House.5. O. L. Gamborg <strong>and</strong> L. R. Wetter, “Plant Tissue Culture Methods, National ResearchCouncil of Canada”, Saskatchewan.111
Paper Code: BPL-407Pharmacology-IV (Pharmacology-IV)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:The teaching of Pharmacology is aimed at different aspects of drugs <strong>and</strong> pharmaceuticalsused in different diseases. The students are able to know the relationship between drugconcentration <strong>and</strong> biological response, drug action overtime, factors affecting absorption,distribution, binding, metabolism <strong>and</strong> elimination of chemicals, structure activityrelationship, biological changes that result from repeated drug use, tolerance, addiction <strong>and</strong>adverse effects. Process of drug interaction with cellular macromolecules to alterphysiological function <strong>and</strong> site of action including knowledge about proper selection of drugsis also covered.UNIT I: Pharmacology of Cardiovascular System:Digitalis <strong>and</strong> cardiac glycosides.Antihypertensive drugs.Antianginal <strong>and</strong> Vasodilator drugs.Antiarrhythmic drugsAntihyperlipidemic drugsDrugs used in the therapy of shock.UNIT II:Drugs Acting on the Hemopoietic System:HematinicsAnticoagulants, Vitamin K <strong>and</strong> hemostatic agents.Fibrinolytic <strong>and</strong> anti-platelet drugs.Blood <strong>and</strong> plasma volume exp<strong>and</strong>ers.Drugs acting on urinary system:Fluid <strong>and</strong> electrolyte balanceDiureticsUNIT IIINeurohumoral transmission in the C.N.S.General AnestheticsLocal anestheticAlcohols <strong>and</strong> disulfiram.Sedatives <strong>and</strong> hypnoticsAnti-anxiety agentsCentrally acting muscle relaxants.Psychopharmacological agents (antipsychotics, antidepressants <strong>and</strong> antimaniacs)112
UNIT IVAnti-epileptics drugs.Anti-Parkinsonian Drugs.Analgesics, Antipyretics, Anti-inflammatory <strong>and</strong> Anti-gout drugs.Narcotic analgesics <strong>and</strong> antagonists.C.N.S. stimulantsDrug Addiction <strong>and</strong> Drug Abuse.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. J. Crossl<strong>and</strong> <strong>and</strong> J. H. Thomson, “Essentials of Pharmacology”, New York: Harper<strong>and</strong> Row Publishers.2. C. R. Craig <strong>and</strong> R. R. Stitzel, “Modem Pharmacology”, Little Brown <strong>and</strong> Company.3. M. N. Ghosh, “Fundamentals of Experimental Pharmacology”, Calcutta: ScientificBook Agency.4. Goodman <strong>and</strong> Gilman's, “The Pharmacological basis of Therapeutics”, New York:Pergamon Press.5. D.R. Laurence <strong>and</strong> P. N. Bennet, “Clinical Pharmacology”, London: ChurchillLivingstone.113
Departmental ElectivePaper Code: BPL-409Packaging TechnologyL -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Objective of this paper is to give the knowledge about Packaging ofvarious Pharmaceutical Formulations with detailed study with regard to history, purpose,hazards, composition, types etc.UNIT IIntroduction: Definition, life history of a package, qualities of the package, purposeof packaging, hazards encountered by the package, various types of inner <strong>and</strong> outerpackages, selection of a suitable package <strong>and</strong> child resistant package.Packaging materials: Detailed study with regard to composition packagingcharacteristics, advantages, economics <strong>and</strong> limitations of paper, glass, plastics, metals<strong>and</strong> rubber as packaging materials.UNIT IIStrip Packing: Significance of Strip Packing, advantages, economics <strong>and</strong> limitationof Strip Packing, Strip Packing machinery, films employed in Strip Packing(including composites <strong>and</strong> laminates) <strong>and</strong> evaluation of films <strong>and</strong> strips packs.Blister Packaging: Blister packing materials, significance of Blister packing,advantages, economics <strong>and</strong> limitation of blister packing, blister packing machinery,various types of blister packages, evaluation of blister package.Pouch packaging: Materials used, advantages, economics <strong>and</strong> limitation of pouchpacking, pouch packing machinery, spectrum of applications, evaluation of pouchpacking.UNIT IIILiquid Formulation Packaging: Various containers/closures employed for liquidformulations. Machinery employed for liquid filling – constant level, volumetric,gravimetric etc. Evaluation of liquid formulation packages.Semi-Solid Packaging: Various types of containers/packages used for semi-solidproducts, filling <strong>and</strong> sealing machinery (including collapsible tube filling <strong>and</strong> sealingmachine) merits <strong>and</strong> limitations of various packages, evaluation of semi-solid productpackage.UNIT IVSterile Product Packaging: General principles of packaging of sterile products.Various types of containers used for sterile products including small volume <strong>and</strong> largevolume parenterals.114
Types of closures used for the sterile products: Sterile product filling <strong>and</strong> sealingmachinery i.e. ampoule filling <strong>and</strong> sealing machine. Limitations <strong>and</strong> merits of variouspackages. Evaluation of the sterile product packages.Labeling: Types of label, labeling requirements as per Drugs <strong>and</strong> Cosmetics act,packaging inserts <strong>and</strong> machinery employed for labeling.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question.Each Question shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. A.I. Brody & K. S. Marsh, “The Wiley Encyclopedia of Packaging Technology”,New York: John Wiley & Sons.2. Leon Lachman, H. A. Liberman <strong>and</strong> J. L. Kanig, “The Theory <strong>and</strong> Practice ofIndustrial Pharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.3. Sanju N<strong>and</strong>a, Rakesh Pahwa <strong>and</strong> Arun N<strong>and</strong>a, “Pharmaceutical PackagingTechnology”, New Delhi: New Age Publications.4. T. C. KacChesney, “Packaging of Cosmetics <strong>and</strong> Toiletries”, London: Newness-Butterworth.5. “Remington Pharmaceutical Sciences”, P.A: Mack Publishing Co.115
Departmental ElectivePaper Code: BPL-411Advanced PharmacognosyL -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50UNIT IIndigenous systems of medicines with emphasis on Ayurveda.UNIT II Some important techniques associated with quality control of Herbal Drugs:o Adulteration & deteriorationo Factors affecting Herbs qualityo TLC / HPTLCo Sampling procedureso Morphological examinationo Microscopical evaluationo Chemical evaluationUNIT IIIPharmacological Screening of herbal drugs.Quality assurance & stability testing of herbal drugs.UNIT IV Extraction of herbal drugso Basic Principleo Pre extraction operation for crude drugso Effect of solvent, solvent mixture & solution of extractiono Procedure of extractiono Treatment of dry residue after extraction.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.116
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Pulok K. Mukherjee, “Quality control on Herbal Drugs”,New Delhi: EasterrnPublishers(Business Horizons)2. S.S. Agrawal <strong>and</strong> M. Paridhari, “Herbal Drug Technology”, New Delhi: UniversityPress.3. S.S. Agrawal <strong>and</strong> M. Paridhari, “Clinically Useful Herbal Drugs”, New Delhi: AhujaPublishers.4. C.K. Kokate , A.P. Purohit <strong>and</strong> S.B. Kokhale , “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, Pune:Nirali Publication.5. G.E. Trease <strong>and</strong> W.C. Evans, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, U. K: Bailliere Tindall,Eastbourne.6. V.C. Tyler, L.R. Brady <strong>and</strong> J.E. Robers, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, 8 th Ed. ,Philadelphia: Lea <strong>and</strong> Febiger.7. T.E. Wallis, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, London: J. <strong>and</strong> A Churchill limited.8. A. Fahn , “Plant Anatomy”, Oxford : Pergamon Press.9. Jean Brunton, “Text Book of Pharmacognosy”, Engl<strong>and</strong>, U.K.: Phytochemistry <strong>and</strong>Medicinal Plants, Intercept Limited.10. V.E. Tyler <strong>and</strong> A.E. Schwarting “Experimental Pharmacognosy”, Minnesota: BurgessPub. Co., Minneapolis.11. E.C.G. Clarke., “Isolation <strong>and</strong> Identification of Drugs”, London: the PharmaceuticalPress.117
Departmental ElectivePaper Code: BPL-413Advanced BiotechnologyL -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50UNIT IUNIT IIUNIT IIIUNIT IVIntroduction & Historical Background Scientific & technological foundations Micro & nano- technology for medicineBio- technology & Medicines Vitamins Steroids Amino acid Proteins Antibiotics Natural CompoundsRecombinant DNA technology Concept Cutting & rejoining of DNA DNA segregating PCR in gene amplification Isolation & amplification of gene.Bio-informatics Molecular pharmaceutical biotechnology Moral & ethical questions (safety-medical, biological, chemical)Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.118
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. S. P. Vyas & V. Dixit, “Pharmaceutical Biotechnology”, New Delhi: CBS Pblishers.2. B. R. Glick & J.J. Pasternak, “Medical Biology, The Principle & Applications ofRecombinant DNA”, Washington: ASM Press.3. “Harper’s review of Bio Chemistry”, Washington: Lange Medical Publications.4. Prescott & Dunn, “Industrial Microbiology”, New York: MC Graw Hill Book CompanyInc.5. Kulkarni, “Biotechnology & its Applications”, New Delhi: CBS Publishers.119
Paper Code: BPP-415Pharmaceutical Chemistry-IX Practical (MedicinalChemistry-II)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of experiments based on theory topics should be conducted, some of them may asfollows: Workshop on stereomodel use of some selected drugs.Synthesis of selected drugs from the paper content involving two or more steps.Establishing the Pharmacopoeial st<strong>and</strong>ards of the drugs synthesized.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. B.S. Furniss, A.J. Hannaford, P.W.G. Smith <strong>and</strong> A.R. Tatchell, “Vogel’s Textbook ofPractical Organic Chemistry”, Singapore: Pearson Education Limited.2. F.G. Mann <strong>and</strong> B.C. Saunders, “Practical Organic Chemistry”, Hyderabad: OrientLongman Limited.3. T. Nogardy, “Medicinal Chemistry – A Biochemical Approach”, New York, Oxford:Oxford University Press.4. “Pharmacopoeia of India”, Govt. of India, Ministry of Health.120
Paper Code: BPP-417Pharmaceutics -X Practical (Pharmaceutical Technology)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of experiments based on theory topics should be conducted, some of them may asfollows:Microencapsulation by coacervation phase separation brought about by change oftemperature. Microencapsulation by coacervation phase separation brought about byaddition of nonsolvent. Formulation, preparation <strong>and</strong> evaluation of pediatric tablets.Preparation <strong>and</strong> evaluation of aspirin tablets. Coating of tablets. Evaluation ofcoatings. Granulation by slugging. Determination of BA <strong>and</strong> M/G factor. Formulationof hard capsules. Quality control of soft <strong>and</strong> hard capsules. Preparation of smallvolume parenterals. Test for pyrogen. Preparation <strong>and</strong> evaluation of large volumeparenteral. Formulation, preparation <strong>and</strong> evaluation of aerosol. Microencapsulation bycomplex emulsion method.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. G. S. Banker <strong>and</strong> C. T. Rhode, “Modern Pharmaceutics”, New York: Marcel DekkerInc.2. Remington's, “The science <strong>and</strong> Practice of Pharmacy”, Pernsybrania: MackPublishing Co. Easton.3. L. Lachman, H. A. Lieberman <strong>and</strong> J. L .Kanig, “The Theory <strong>and</strong> Practice of IndustrialPharmacy”, Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.121
Paper Code: BPP-419Pharmacognosy-IV Practical (Pharmacognosy-IV)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of experiments based on theory topics should be conducted; some of them may asfollows:Isolation of some selected Phytoconstituents studied in theory.Extraction of volatile oils <strong>and</strong> their chromatographic profiles.Demonstration of some experiments in plant tissue culture.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. G. Malti Chauhan <strong>and</strong> A.P.G. Pillai , “Microscopic profile of powdered drugs usedin Indian systems of medicine, volume 1, Leaf drugs,” Gujarat Ayurved University,Jamnagar.2. G. Malti Chauhan <strong>and</strong> A.P.G. Pillai , “Microscopic profile of powdered drugsused in Indian systems of medicine”, volume 2, bark drugs, Gujarat AyurvedUniversity, Jamnagar.3. W. C. Evans, Trease <strong>and</strong> Evans, “Pharmacognosy , W. B. Saunders Limited.4. G. E. Trease, “A Textbook of Pharmacognosy”, London: Bailliere Tindall.122
Paper Code: BPP-421Pharmacology-IV Practical (Pharmacology-IV)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of experiments based on theory topics should be conducted, some of them may asfollows (As per regulatory bodies guidelines Animals Experiments should be replaced withexperiments through Software):To record the CRC of histamine on guinea pig ileum preparation (Through Software).To study the center nervous system depressants property of drug on the locomotoractivity by actophotometer.To study the effect of drug on the muscle grip strength of mice using rota-rodapparatus.To study the effect of drug on the isolated heart of frog (Through Software).Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. J. Crossl<strong>and</strong> <strong>and</strong> J. H. Thomson, “Essentials of Pharmacology”, New York: Harper<strong>and</strong> Row Publishers.2. C. R. Craig <strong>and</strong> R. R. Stitzel, “Modem Pharmacology”, Little Brown <strong>and</strong> Company.3. M. N. Ghosh, “Fundamentals of Experimental Pharmacology”, Calcutta: ScientificBook Agency.4. Goodman <strong>and</strong> Gilman's, “The Pharmacological basis of Therapeutics”, New York:Pergamon Press.5. S.K. Kulkarni, “H<strong>and</strong>book of Experimentals Pharmacology”, Delhi: VallabhPrakashan.6. D.R. Laurence <strong>and</strong> P. N. Bennet, “Clinical Pharmacology”, London: ChurchillLivingstone.123
Paper Code: BPL-423Independent Study/ Seminar/ ProjectL -- T -- P Total Credits: 04-- -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 00Internal Marks: 100Paper Objectives: Objective of this paper is to improve the Independent Study nature in thestudents by performing some project work/presenting the seminar.124
Paper Code: BPL-402Pharmaceutical Chemistry-X (Medicinal Chemistry-III)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives: Medicinal chemistry is a branch of chemistry also involving aspects ofbiological, medical <strong>and</strong> pharmaceutical sciences. It is concerned with the invention,discovery, design, identification <strong>and</strong> preparation of biologically active compounds, theinterpretation of their mode of interaction at the molecular level, the construction of theirstructure-activity relationships, <strong>and</strong> study of their metabolism.UNIT IDrug metabolism <strong>and</strong> Concepts of Prodrugs.Synthetic procedures of selected drugs, mode of action, uses, structure activityrelationship (including physicochemical aspects) of the following classes of drugs.(Biochemical approaches in drug designing wherever applicable should be discussed):Antineoplastic agents.UNIT IIAntimetabolites (including sulfonamides).Chemotherapeutic agents used in Protozoal, Parasitic <strong>and</strong> other infectionAnti-viral including anti - HIVagents.Immunosuppressives <strong>and</strong> immunostimulants.UNIT IIIAmino acids, peptide, nucleotides <strong>and</strong> related drugs:Thyroid <strong>and</strong> Anti thyroid drugsInsulin <strong>and</strong> oral hypoglycemic agents.Peptidomimetics <strong>and</strong> nucleotidomimetics.Diagnostic agents.Pharmaceutical Aids.UNIT IV Synthetic procedures of following selected drugs: Diethyl carbamazine,Thiabendazole, Sulphadiazine, Sulphamethoxazole, Trimethoprim,Cycloserine,Chloramphenicol, Nalidixic acid, Norfloxacin, Nitorfurantoin, Isoniazid, Ethambutol,Ethonamide, Clofazimine, Ketoconazole, Clotrimazole, Chlorambucil, Melphalan,Thio-TEPA, 5-Fluorouracil, Cisplatin, Tolbutamide, Rosiglitazone, Pioglitazone, L-Thyroxine, Methylthiouracil, Methimazole, Azathioprone, Primaquine, Amodiaquine,Pyrimethamine, Metronidazole, Thioacetazole, Pyrazinamide.125
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. Wilson <strong>and</strong> Gisvold’s, “Textbook of Organic Medicinal <strong>and</strong> PharmaceuticalChemistry”, Philadelphia: J. Lippincot Co.2. W. O. Foye, “Principles of Medicinal Chemistry”, Philadelphia: Lea <strong>and</strong> Febiger.3. C. Hansch, “Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry”, New York: Pregman Press.4. M. E. Wolff, “Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry”, New York: John Wiley & Sons.5. T. Nogardy, “Medicinal Chemistry – A Biochemical Approach”, New York: OxfordUniversity Press.6. B. N. Ladu, H. G. M<strong>and</strong>el <strong>and</strong> E. L. Way, “Fundamentals of Drug metabolism <strong>and</strong>Disposition”, Baltimore: William <strong>and</strong> Walkins Co., Preston Street.126
Paper Code: BPL-404Pharmaceutical Chemistry-XI (Pharmaceutical Analysis-III)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objectives:The objective of the paper is to further skills of pharmaceutical analysis by studying variousprinciples involved in instrumental methods of chemical analysis, interpreting the data ofspectroscopic analysis including atomic absorption & emission spectroscopy, X-Raydiffraction, mass spectrometry <strong>and</strong> chromatography & their applications. After completion ofthis paper student will be able to do validation of instruments, trouble shooting in operationsrelated to analytical instruments, interpretation of results obtained from data or spectra,designing of appropriate analytical method for newer or known drug or drug material.UNIT IQuality assurance.GLP, ISO 9000, TQM, Quality Review <strong>and</strong> Quality Documentation.Regulatory control, regulatory drug analysis, interpretation of analytical data.Validation, quality audit: quality of equipment, validation of equipment, validation ofanalytical procedures.UNIT IIThe theoretical aspects, basic instrumentation, elements of interpretation of spectra <strong>and</strong>applications of the following analytical techniques should be discussed:Ultraviolet <strong>and</strong> Visible SpectrophotometryFluorimetry.Infrared Spectrophotometry including FTIR.UNIT IIINuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy including 13C NMR.Flame PhotometryAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy.Emission SpectroscopyUNIT IVMass SpectrometryX -ray Diffraction.Radio immunoassay.127
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. William Kemp, “Organic Spectroscopy”, London: Macmillan Press Ltd.2. Willard, Merritt, Dean <strong>and</strong> Settle, “Instrumental Method of Analysis”, New Delhi:CBS Publishers.3. K. A. Conners, “A Textbook of Pharmaceutical Analysis”, New York: WileyInterscience.4. Silverstein et al., “Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds”, UnitedKingdom: John Wiley.5. Skoog, “Fundamental of Analytical Chemistry”, New York: Saunders CollegePublishing.6. John R. Dyer, “Applications of Absorption Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds”,New Delhi: Prentice Hall.128
Paper Code: BPL-406Pharmaceutics –XI (BioPharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objective:The concepts of bioavailability <strong>and</strong> administration, absorption, distribution, metabolism <strong>and</strong>excretion of drugs are required to study the drug pharmacokinetic parameters, dosage regimedesign, therapeutic drug monitoring, in-vivo evaluation of drugs <strong>and</strong> bioavailability studies.Also the studies relating for population pharmacokinetics, determination of frequency,duration <strong>and</strong> quantity of drugs given for particular disease <strong>and</strong> schedule of drugs in variousailments & in different age groups.UNIT IIntroduction to Biopharmaceutics <strong>and</strong> Pharmacokinetics <strong>and</strong> their role in formulationdevelopment <strong>and</strong> clinical setting.Biopharmaceutics: Passage of drug across biological barrier (passive diffusion, activetransport, facilitated diffusion <strong>and</strong> pinocytosis).Factors influencing absorption: Physiochemical, physiological <strong>and</strong> pharmaceutical.Drug distribution in the body, plasma protein binding.UNIT II Pharmacokinetics, Significance of plasma drug concentration measurement,Compartmental model: definition <strong>and</strong> scope. Pharmacokinetics of drug absorption: Zero order <strong>and</strong> first order absorption rateconstant using wagner-Nelson <strong>and</strong> Loo-Riegelman method. Volume of distribution<strong>and</strong> distribution coefficient. Compartment kinetics: One compartment <strong>and</strong> two compartment models.Determination of pharmacokinetics parameters from plasma <strong>and</strong> urine data after drugadministration by intravascular <strong>and</strong> oral route.UNIT IIICurve fitting (method of residuals), regression procedures. Clearance concept,mechanism of renal clearance, clearance ratio, determination of renal clearance.Hepatic elimination of drugs, first pass effect, extraction ratio, hepatic clearance,billiary excretion, enterohepatic circulation.Non-linear pharmacokinetics with special reference to one compartment model afterI.V. drug administration, Michales Menten equation, determination of non-linearity(saturation mechanism).UNIT IVDosage regimen adjustment for repeated therapy.Clinical pharmacokinetics: Definition <strong>and</strong> scope, Dosage adjustment in patients with<strong>and</strong> without renal <strong>and</strong> hepatic failure.129
Introduction to Pharmacokinetics, drug interactions <strong>and</strong> its significance incombination therapy.Bioavailability <strong>and</strong> bioequivalence: Measures of bioavailability, C max , t max <strong>and</strong> Areaunder Curve (AUC). Design of single dose bio-equivalence study <strong>and</strong> relevantstatistics. Overview of regulatory requirements for conduction of bio-equivalencestudy.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. L. Shargel <strong>and</strong> B. C. Andrew, “Applied Biopharmaceutics <strong>and</strong> Pharmacokinetics”,USA: Prentice Hall International.2. Brahmankar, New Delhi: CBS Publishers.3. J. G. Wagner, “Fundamental of Clinical Pharmacokinetics”, Hamilton: DrugIntteligence Publications.4. R. E. Notari, “Biopharmaceutics <strong>and</strong> Pharmacokinetics- an Intoduction”, New York:Marcel Dekker Inc.5. Sarfaraz Niazi, “Textbook of Biopharmaceutics <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacokinetics”, NewYork: Appelton – Century Crofts.6. M. Gibaldi <strong>and</strong> D. Parrier, “Pharmacokinetics”, New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.7. J. G. Wagner, “Pharmacokinetics for the Pharmaceutical Scientist”, Switzerl<strong>and</strong>:Technomic Publishing.8. Milo Gibaldi, “Biopharmaceutics <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacokinetics”, Philadelphia: Lea<strong>and</strong> Fibiger.130
Paper Code: BPL-408Pharmacology-V (Pharmacology-V)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objective:The teaching of Pharmacology is aimed at different aspects of drugs <strong>and</strong> pharmaceuticalsused in different diseases. The therapeutic/pharmacological group of drugs is taughtaccording to the classification of World Health Organization. The students are able to knowthe relationship between drug concentration <strong>and</strong> biological response, drug action overtime,factors affecting absorption, distribution, binding, metabolism <strong>and</strong> elimination of chemicals,structure activity relationship, biological changes that result from repeated drug use,tolerance, addiction <strong>and</strong> adverse effects.UNIT I: Drugs Acting on the Gastrointestinal Tract:Anti- ulcer drugs.Laxatives <strong>and</strong> antidiarrhoeal drugs.Appetite Stimulants <strong>and</strong> SuppressantsEmetics <strong>and</strong> anti- emetics.Miscellaneous- Carminatives, demulcents, protectives, adsorbents, astringents,digestants, enzymes <strong>and</strong> mucolytics.UNIT II: Pharmacology of Endocrine System: Hypothalamic <strong>and</strong> pituitary hormones. Thyroid hormones <strong>and</strong> anti thyroid drugs, parathormone, calcitonin <strong>and</strong> Vitamin D. Insulin, oral hypoglycaemic agents <strong>and</strong> Glucagon. ACTH <strong>and</strong> corticosteroids Androgens <strong>and</strong> anabolic steroids Estrogens, progesterone <strong>and</strong> oral contraceptives Drugs acting on the uterus.UNIT III:ChemotherapyGeneral Principles of ChemotherapySulfonamides <strong>and</strong> cotrimoxazoleAntibiotics- penicillins, cephalosporins, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, Quinolones.Chemotherapy of tuberculosis, leprosy, fungal diseases, viral diseases, urinary tractinfections <strong>and</strong> sexually transmitted diseases.Chemotherapy of malignancy <strong>and</strong> immunosuppressive agents.UNIT IV: ToxicologyPrinciples of ToxicologyDefinition of poison, general principles of treatment of poisoning with particularreference to barbiturates, opioids, organophosphorous <strong>and</strong> atropine poisoning.Heavy metals (arsenic, lead <strong>and</strong> mercury) <strong>and</strong> heavy metal antagonists.131
Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. B.G. Katzung, “Basic <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacology”, London: Prentice HallInternational.2. Davidson’s Principles <strong>and</strong> Practice of Medicine”, London: Churchill Livingstone.3. Goodman <strong>and</strong> Gilman’s, “The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics”, New York:Pregman Press.4. L. Paul, “Principles of Pharmacology”, New York: Chapman <strong>and</strong> Hall.5. H. P. Rang <strong>and</strong> M. M. Dale, “Pharmacology”, London: Churchill Livingstone.6. E. T. Herfindal <strong>and</strong> J. L. Hirschman, “Clinical Pharmacy <strong>and</strong> Therapeutics”,Baltimore: Williams <strong>and</strong> Willkins.7. J. L. Dipiro, “Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiological Approach”, New York:Elsevier.8. D. R. Laurence <strong>and</strong> P.N. Bennet, “Clinical Pharmacology”, London: ChurchillLivingstone.”132
Paper Code: BPL-410Pharmacology-VI (Clinical Pharmacy & Drug Interaction)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 044 -- -- Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Paper Objective:Clinical pharmacy is the practice of Pharmacy in clinical setting especially in ahospital. The concept of clinical pharmacy <strong>and</strong> the role that the pharmacists areplaying internationally is to be introduced. Study of clinical pharmacy is important intherapeutic drug monitoring, deTermining toxicities, drug interactions, adverse drugreactions <strong>and</strong> dosage regimen establishment. It helps in proper selection of drugs,administration route, as well as guiding patients about the drug therapy.UNIT IIntroduction to Clinical Pharmacy.Basic Concepts of Pharmacotherapy.Clinical Pharmacokinetics <strong>and</strong> individualization of Drug Therapy.UNIT IIDrug use during Infancy <strong>and</strong> in the Elderly (Pediatrics <strong>and</strong> Geriatrics).Drug use during pregnancy.Drug-induced Diseases.UNIT IIIThe Basics of Drug Interactions.General Principles of Clinical Toxicology.UNIT IVInterpretation of Clinical Laboratory Tests.Therapeutic Drug Monitoring.Concept of Essential Drugs <strong>and</strong> Rational Drug use.Note: Instruction for Examiner:The Semester examination in each theory subject shall be of 50 marks. The examiner will setnine questions. Student will attempt five questions. First question would be of short answertype question covering all four Units (2.5 Marks per Unit) & it would be compulsory. Twoquestions will be set from each unit & out of which c<strong>and</strong>idate will attempt one question. EachQuestion shall be of 10 marks.133
Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. B. G. Katzung, “Basic & Clinical Pharmacology”, London: Prentice HallInternational.2. Davidson’s Principles <strong>and</strong> Practice of Medicine”, New York: Churchill Livingstone.3. Goodman <strong>and</strong> Gilman’s, “The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics”, New York:Pregman Press.4. L. Paul, “Principles of Pharmacology”, New York: Chapman <strong>and</strong> Hall.5. H. P. Rang <strong>and</strong> M. M. Dale, “Pharmacology”, New York: Churchill Livingstone.6. E. T. Herfindal <strong>and</strong> J. L. Hirschman, “Clinical Pharmacy <strong>and</strong> Therapeutics”,Baltimore: Williams <strong>and</strong> Willkins.7. J. L. Dipiro, “Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiological Approach”, Elsevier.8. D. R. Laurence <strong>and</strong> P. N. Bennet, “Clinical Pharmacology”, New York: ChurchillLivingstone.”134
Paper Code: BPP-412Pharmaceutical Chemistry-X Practical(Medicinal Chemistry-III)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of Syntheses involving two or more steps in the synthesis.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. B.S. Furniss, A.J. Hannaford, P.W.G. Smith <strong>and</strong> A.R. Tatchell, “Vogel’s Textbook ofPractical Organic Chemistry”, Singapore: Pearson Education Limited.2. F.G. Mann <strong>and</strong> B.C. Saunders, “Practical Organic Chemistry”, Hyderabad: OrientLongman Limited.3. “Pharmacopoeia of India”, Govt. of India, Ministry of Health.135
Paper Code: BPP-414Pharmaceutical Chemistry-XI Practical (PharmaceuticalAnalysis-III)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted; some of them may asfollows: Quantitative estimation of at least ten formulations containing single drug or morethan one drug, using instrumental techniques. Estimation of Na+, K+, Ca++ ions using flame photometry. IR of samples with different functional groups (-COOH, -COOR.-CONHR; -NH2, -NHR, -OH, etc.).Workshop to interpret the structure of simple organic compounds using UV, IR. NMR<strong>and</strong> MS.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. William Kemp, “Organic Spectroscopy”, London: Macmillan Press Ltd.2. Silverstein et al., “Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds”, UnitedKingdom: John Wiley.3. Skoog, “Fundamental of Analytical Chemistry”, New York: Saunders CollegePublishing.4. John R. Dyer, “Applications of Absorption Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds”,New Delhi: Prentice Hall.5 A. H. Beckett <strong>and</strong> J. B. Stenlake, “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Vol. I <strong>and</strong>II”, London: The Athlon Press of the University of London.136
Paper Code: BPP-416Pharmaceutics –XI Practical(Bio Pharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted; some of them may asfollows:Experiments designed for the estimation of various pharmacokinetic parameters withgiven data.Analysis of biological specifications for drug content <strong>and</strong> estimation of thepharmacokinetic parameters.In vitro evaluation of different dosage forms for drug release.Absorption studies - in- vitro <strong>and</strong> in -situ.Statistical treatment of pharmaceutical data.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. L. Shargel <strong>and</strong> B. C. Andrew, “Applied Biopharmaceutics <strong>and</strong> Pharmacokinetics”,USA: Prentice Hall International.2. J. G. Wagner, “Fundamental of Clinical Pharmacokinetics”, Hamilton: DrugIntteligence Publications.3. J. G. Wagner, “Pharmacokinetics for the Pharmaceutical Scientist”, Switzerl<strong>and</strong>:Technomic Publishing.4. Milo Gibaldi, “Biopharmaceutics <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacokinetics”, Philadelphia: Lea<strong>and</strong> Fibiger.137
Paper Code: BPP-418Pharmacology-V Practical (Pharmacology-V)L -- T -- P Total Credits: 02-- -- 4 Total Marks: 100External Marks: 50Internal Marks: 50Number of practicals based on theory portion should be conducted, some of them may asfollows (As per regulatory bodies guidelines Animals Experiments should be replaced withexperiments through Software):To study the various types of bio assay.To record a Dose Response Curve (DRC) or Concentration Response Curve (CRC) ofacetylcholine/ histamine using rat ileum preparation (Demonstration throughSoftware).To study the effect of drugs on the rabbit eye (Through Software).To obtain a graded dose response curve of histamine & determine the concentrationsame in solution (Unknown Concentration) using matching type bio-assay.Some reports may be collected from human volunteers regarding the effects offollowing clinically useful drugs:• Antihistaminics• Anti-anxiety <strong>and</strong> sedative drugs• Analgesics & Anti inflammatory agents• Anti Hypertensives.Suggested Readings (Latest Editions):1. “Pharmacological Experiments on Isolated Preparations”, Livingstone: EdinburgUniversity Pharmacology Staff.2. S.K. Kulkarni, “H<strong>and</strong>book of Experimental Pharmacology”, Delhi: VallabhPrakashan.3. L. Paul, “Principles of Pharmacology”, New York: Chapman <strong>and</strong> Hall.4. B. G. Katzung, “Basic <strong>and</strong> Clinical Pharmacology”, New York: Prentice HallInternational.5. M. N. Ghosh, “Fundamentals of Experimental Pharmacology”, Calcutta: ScientificBook Agency.6. Goyal ,”Practical in Pharmacology”, Ahmedabad: B S Shah Publications.7. Ghose, “Fundamentals of Experimental Pharmacology”, New Delhi: Amit BookCompany.8. E. T. Herfindal <strong>and</strong> J. L. Hirschman, “Clinical Pharmacy <strong>and</strong> Therapeutics”,Baltimore: Williams <strong>and</strong> Willkins.----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------138