Scattering 1 Classical scattering of a charged particle (Rutherford ...
Scattering 1 Classical scattering of a charged particle (Rutherford ...
Scattering 1 Classical scattering of a charged particle (Rutherford ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
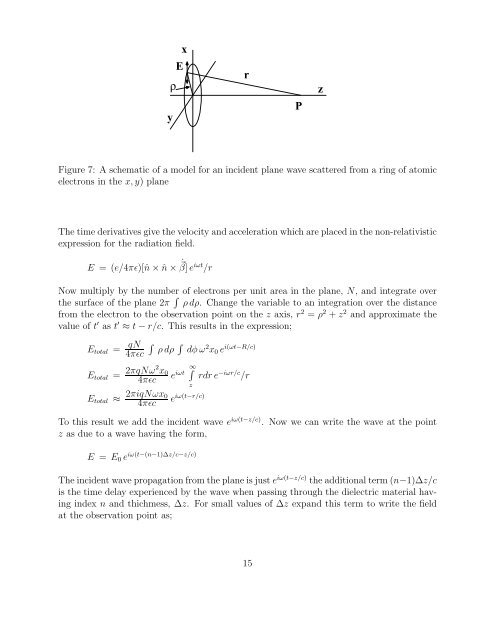
xEρyrPzFigure 7: A schematic <strong>of</strong> a model for an incident plane wave scattered from a ring <strong>of</strong> atomicelectrons in the x, y) planeThe time derivatives give the velocity and acceleration which are placed in the non-relativisticexpression for the radiation field.E = (e/4πǫ)[ˆn × ˆn × ˙⃗ β] e iωt /rNow multiply by the number <strong>of</strong> electrons per unit area in the plane, N, and integrate overthe surface <strong>of</strong> the plane 2π ∫ ρ dρ. Change the variable to an integration over the distancefrom the electron to the observation point on the z axis, r 2 = ρ 2 + z 2 and approximate thevalue <strong>of</strong> t ′ as t ′ ≈ t − r/c. This results in the expression;E total = qN4πǫcE total = 2πqNω2 x 04πǫcE total ≈ 2πiqNωx 04πǫc∫ρ dρ∫dφ ω 2 x 0 e i(ωt−R/c)e iωt ∞ ∫ze iω(t−r/c)rdr e −iωr/c /rTo this result we add the incident wave e iω(t−z/c) . Now we can write the wave at the pointz as due to a wave having the form,E = E 0 e iω(t−(n−1)∆z/c−z/c)The incident wave propagation from the plane is just e iω(t−z/c) the additional term (n−1)∆z/cis the time delay experienced by the wave when passing through the dielectric material havingindex n and thichmess, ∆z. For small values <strong>of</strong> ∆z expand this term to write the fieldat the observation point as;15