CHEM3331: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry I Final Exam Prof ...
CHEM3331: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry I Final Exam Prof ...
CHEM3331: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry I Final Exam Prof ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
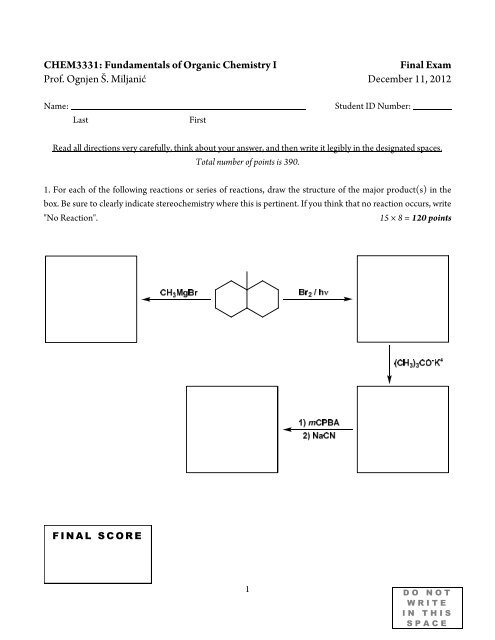
<strong>CHEM3331</strong>: <strong>Fundamentals</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Organic</strong> <strong>Chemistry</strong> I<strong>Final</strong> <strong>Exam</strong>Pr<strong>of</strong>. Ognjen Š. Miljanić December 11, 2012Name:LastFirstStudent ID Number:Read all directions very carefully, think about your answer, and then write it legibly in the designated spaces.Total number <strong>of</strong> points is 390.1. For each <strong>of</strong> the following reactions or series <strong>of</strong> reactions, draw the structure <strong>of</strong> the major product(s) in thebox. Be sure to clearly indicate stereochemistry where this is pertinent. If you think that no reaction occurs, write"No Reaction".15 × 8 = 120 pointsF I N A L S C O R E1D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
2D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
2. Give detailed mechanisms for the two reactions presented below. Show all charges and intermediates, and usecurved arrows to indicate the flow <strong>of</strong> electrons. Do not draw transition states.40 + 20 = 60 points4D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
3. Name the following compound according to IUPAC's systematic nomenclature. Indicate the stereochemistry<strong>of</strong> chiral centers and/or C=C double bonds where needed.5 × 8 = 40 points5D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
4. For each <strong>of</strong> the following two conversions, give a step-by-step outline <strong>of</strong> a synthetic sequence which wouldefficiently accomplish the required transformation. You may use any organic compound with two or lesscarbons, and any inorganic reagent. Do not give mechanisms.2 × 30 = 60 points6D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
5. Draw both chair conformations for the molecule shown below (D stands for deuterium, the heavier isotope <strong>of</strong>hydrogen). Circle the more stable conformation. Then, predict the product <strong>of</strong> E2 elimination <strong>of</strong> this precursor.Explain your reasoning in one brief sentence.30 pointsHINT: does H or D get eliminated?7D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
6. This question has several parts. In each segment, circle only one answer. 5 × 4 = 20 pointsCircle the strongest base among the following anions:OO S NHOCircle the most electronegative element:Na B N Li Pb Hg CCircle the most stable radical:Circle the only enyne among the following four compounds:Which compounds produce tertiary alcohols when reacted with Grignard reagents?alkanes aldehydes ketones alcohols ethers8D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
7. Molecule A has molecular formula C 8H 10. Its 1 H NMR spectrum shows a doublet at 1.28 ppm (integrates for6H), a quartet at 2.70 ppm (integrating for 2H), and a singlet integrating for 2H at 2.83 ppm. Its 13 C NMRspectrum contains four peaks, and its characteristic IR bands are found at 2215 (weak), 2950, and 3300 cm −1 .Oxymercuration <strong>of</strong> compound A produces compound B, which has molecular formula C 8H 14O 2. Compound Balso has four peaks in its 13 C NMR spectrum, and its IR spectrum is characterized by strong bands at 1725 and2950 cm −1 . 1 H NMR spectrum <strong>of</strong> compound B shows a doublet at 1.11 ppm (integrating for 6H), a singlet at1.98 ppm (integrating for 6H), and a quartet at 2.74 ppm which integrates form 2H.. Based on this information,draw the structures <strong>of</strong> compounds A and B in the provided boxes, and show your reasoning.40 points9D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
8. Order the three compounds A–C listed below by increasing acidity, and rationalize your answer usingresonance structures.30 points10D O N O TW R I T EI N T H I SS P A C E
APPENDICES1H NMR-OH-NH12 1110 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1ppm0ROCOHOCR HH-C-XAr-H C=C-H H-C-OH-C-ArH-C-NH-C-SHCH 3CH 2CHX = an electronegative atomH-C-C=OH-C-C=C1H NMR CHARACTERISTIC CHEMICAL SHIFTS / ppmmethyl methylene methyneCH 3- -CH 2- CHotherRC0.9 1.4 1.5-OH1-5RC COCR1.6 2.3 2.62.1 2.4 2.5CC-NHCHHCAr-H1-32.55.57.3R NR-ArR BrR Cl2.2 2.5 2.92.3 2.7 3.02.7 3.3 4.13.1 3.4 4.1ROCROCHOH109-12RO3.3 3.4 3.7
APPENDICESINFRA-RED GROUP ABSORPTION FREQUENCIESTYPE OF VIBRATION FREQUENCY (cm -1 ) WAVELENGTH (µ) INTENSITY (1)C−H Alkanes (stretch) 3000-2850 3.33-3.51 s−CH 3 (bend) 1450 and 1375 6.90 and 7.27 m−CH 2 − (bend) 1465 6.83 mAlkenes (stretch) 3100-3000 3.23-3.33 m(bend) 1700-1000 5.88-10.0 sAromatics (stretch) 3150-3050 3.17-3.28 s(out-<strong>of</strong>-plane bend) 1000-700 10.0-14.3 sAlkyne (stretch) ca. 3300 ca.3.03 sAldehyde 2900-2800 3.45-3.57 w2800-2700 3.57-3.70 wC−C Alkane not usually usefulC=C Alkene 1680-1600 5.95-6.25 m-wAromatic 1600-1400 6.25-7.14 m-wC≡C Alkyne 2250-2100 4.44-4.76 m-wC=O Aldehyde 1740-1720 5.75-5.81 sKetone 1725-1705 5.80-5.87 sCarboxylic acid 1725-1700 5.80-5.88 sEster 1750-1730 5.71-5.78 sAmide 1700-1640 5.88-6.10 sAnhydride ca. 1810 ca. 5.52 sca. 1760 ca. 5.68 sAcyl chloride 1800 5.55 sC−O Alcohols, Ethers, Esters,Carboxylic acids 1300-1000 7.69-10.0 sO−H Alcohols, PhenolsFree 3650-3600 2.74-2.78 mH-Bonded 3400-3200 2.94-3.12 mCarboxylic acids (2) 3300-2500 3.03-4.00 mN−H Primary and secondary amines ca. 3500 ca. 2.86 mC≡N Nitriles 2260-2240 4.42-4.46 mN=O Nitro (R−NO 2 ) 1600-1500 6.25-6.67 s1400-1300 7.14-7.69 sC−X Fluoride 1400-1000 7.14-10.0 sChloride 800-600 12.5-16.7 sBromide, Iodide 16.7 s___________________________________________________________________________________(1) s = strong, m = medium and w = weak(2) note that the -OH absorption <strong>of</strong> solid carboxylic acids which run as a nujol mull can be difficult to see as they maybe very broad
NOTHING WRITTEN ON THIS PAGE WILL BE GRADED12