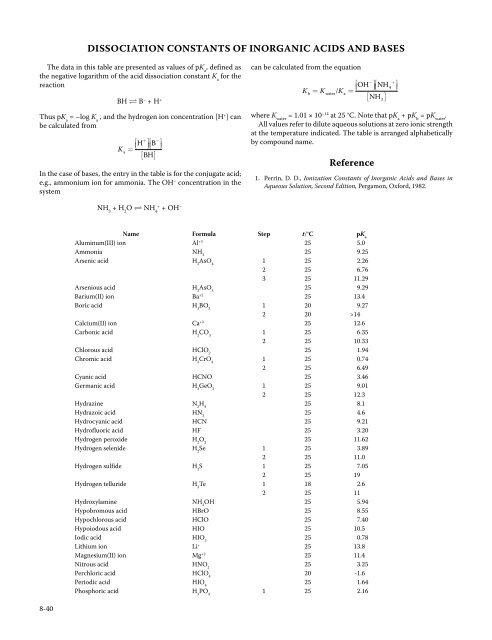
DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS OF INORGANIC ACIDS AND ...
DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS OF INORGANIC ACIDS AND ...
DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS OF INORGANIC ACIDS AND ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>DISSOCIATION</strong> <strong>CONSTANTS</strong> <strong>OF</strong> <strong>INORGANIC</strong> <strong>ACIDS</strong> <strong>AND</strong> BASESThe data in this table are presented as values of pK a, defined asthe negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant K afor thereactionBH B – + H +Thus pK a= –log K a, and the hydrogen ion concentration [H + ] canbe calculated from⎡+H ⎤ BK a= ⎣⎢ ⎦⎥ ⎡ −⎤⎣⎢ ⎦⎥[ BH]In the case of bases, the entry in the table is for the conjugate acid;e.g., ammonium ion for ammonia. The OH – concentration in thesystemcan be calculated from the equation⎡OH⎤ NHKb= KwaterKa= ⎣⎢ ⎦⎥ ⎡ /⎣⎢[ NH ]− +4where K water= 1.01 × 10 –14 at 25 °C. Note that pK a+ pK b= pK water.All values refer to dilute aqueous solutions at zero ionic strengthat the temperature indicated. The table is arranged alphabeticallyby compound name.Reference1. Perrin, D. D., Ionization Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases inAqueous Solution, Second Edition, Pergamon, Oxford, 1982.3⎤⎦⎥NH 3+ H 2O NH 4++ OH –Name Formula Step t/°C pK aAluminum(III) ion Al +3 25 5.0Ammonia NH 325 9.25Arsenic acid H 3AsO 41 25 2.262 25 6.763 25 11.29Arsenious acid H 2AsO 325 9.29Barium(II) ion Ba +2 25 13.4Boric acid H 3BO 31 20 9.272 20 >14Calcium(II) ion Ca +2 25 12.6Carbonic acid H 2CO 31 25 6.352 25 10.33Chlorous acid HClO 225 1.94Chromic acid H 2CrO 41 25 0.742 25 6.49Cyanic acid HCNO 25 3.46Germanic acid H 2GeO 31 25 9.012 25 12.3Hydrazine N 2H 425 8.1Hydrazoic acid HN 325 4.6Hydrocyanic acid HCN 25 9.21Hydrofluoric acid HF 25 3.20Hydrogen peroxide H 2O 225 11.62Hydrogen selenide H 2Se 1 25 3.892 25 11.0Hydrogen sulfide H 2S 1 25 7.052 25 19Hydrogen telluride H 2Te 1 18 2.62 25 11Hydroxylamine NH 2OH 25 5.94Hypobromous acid HBrO 25 8.55Hypochlorous acid HClO 25 7.40Hypoiodous acid HIO 25 10.5Iodic acid HIO 325 0.78Lithium ion Li + 25 13.8Magnesium(II) ion Mg +2 25 11.4Nitrous acid HNO 225 3.25Perchloric acid HClO 420 -1.6Periodic acid HIO 425 1.64Phosphoric acid H 3PO 41 25 2.168-40
Dissociation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases 8-41Name Formula Step t/°C pK a2 25 7.213 25 12.32Phosphorous acid H 3PO 31 20 1.32 20 6.70Pyrophosphoric acid H 4P 2O 71 25 0.912 25 2.103 25 6.704 25 9.32Selenic acid H 2SeO 42 25 1.7Selenious acid H 2SeO 31 25 2.622 25 8.32Silicic acid H 4SiO 41 30 9.92 30 11.83 30 124 30 12Sodium ion Na + 25 14.8Strontium(II) ion Sr +2 25 13.2Sulfamic acid NH 2SO 3H 25 1.05Sulfuric acid H 2SO 42 25 1.99Sulfurous acid H 2SO 31 25 1.852 25 7.2Telluric acid H 2TeO 41 18 7.682 18 11.0Tellurous acid H 2TeO 31 25 6.272 25 8.43Tetrafluoroboric acid HBF 425 0.5Thiocyanic acid HSCN 25 –1.8Water H 2O 25 13.995