The LINOS Laseroptics and Lenses - Qioptiq Q-Shop
The LINOS Laseroptics and Lenses - Qioptiq Q-Shop
The LINOS Laseroptics and Lenses - Qioptiq Q-Shop
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
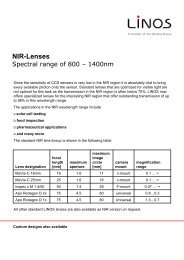
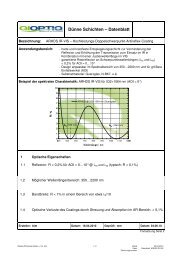
Singlets AchromatsF-<strong>The</strong>ta-Ronar <strong>Lenses</strong> 355 nm<strong>The</strong> following is valid for the overviewtables at the bottom:••<strong>The</strong> entrance beam diameter (beam-Ø)refers to the intensity 1/e 2 at Gaussianillumination. <strong>The</strong> image spot diameter(spot-Ø) refers to the intensity 1/e 2 atGaussian illumination. It can becalculated by the formula:Spot-Ø = 1.83 x λ x EFL / beam-ØSpot-Ø: image spot diameter [μm]1.83: factor of apodisationλ: wavelength [nm]EFL: focal length [mm]Beam-Ø: entrance beam diameter [mm]••<strong>The</strong> mirror distances m1 <strong>and</strong> m2 arerecommended values••<strong>The</strong> overall scan angle Ñ refers to themaximum diagonal scan angle••<strong>The</strong> scan length can be calculated withthe formula:••<strong>The</strong> listed F-<strong>The</strong>ta-Ronar lensesaccomplish the F-<strong>The</strong>ta-conditionbetterthan 0.1% except for a fewversions.<strong>The</strong>se lenses which have alarger scanfield due to distortion areindicated with**.••<strong>The</strong> effective focal length (EFL), flangefocal length (FFL) <strong>and</strong> back focallength(BFL) have been calculated bymeans ofparaxial relations (for raysclose to theoptical axis). In reality,they can slightlydeviate from the datashown in thefollowing tables by theactual entrancebeam diameters <strong>and</strong>mirror positionsused.• • <strong>The</strong> data for the entrance beamdiameter <strong>and</strong> the mirror positions arerecommended values. Changing theirvalues will affect both the image spotdiameter <strong>and</strong> the maximum possiblescanangle/diagonal.2y‘= EFL x 2Ð x π/1802y‘: scan length or diagonal [mm]EFL: focal length [mm]2Ð: overall scan angle [°]π/180: conversion factor into radiansF-<strong>The</strong>ta-Ronar 355 nmProtectiveglassNominal focallength [mm]Effective focallength [mm] EFLBack focal length (fromvertexof last element orfromprotective glasssurface) [mm]BFLFlange focal length(distancefrommechanical flange tofocus plane) [mm] FFLScanlengthordiagonal forareascans[mm]2y'PG3 160 160.1 183.8 189.2 139.7PG4* 161 161 202.9 208.3 140.5PG11* 255** 254.7 321 365.7 240.4* With fused silica lenses** Meets F-<strong>The</strong>ta condition better than 1%414US-Phone +1 585 223-2370 UK-Phone +44 2380 744 500