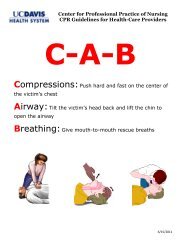
- Page 1 and 2:
Resident HandbookMercy Redding Fami
- Page 3 and 4:
PEDIATRICS/OB......................
- Page 5 and 6:
MASTER SCHEDULE:...................
- Page 7 and 8:
Resident HandbookMercy Redding Fami
- Page 9 and 10:
efore the start of the rotation tha
- Page 11 and 12:
Cardiology Competencies - PGY3Cogni
- Page 13 and 14:
Understand and describe Home care a
- Page 15 and 16:
Page 15 of 1532. OBRA "87 & "94 Reg
- Page 17 and 18:
Skills1. Monitor interpretation for
- Page 19 and 20:
Page 19 of 153Skills1. Diagnosis an
- Page 21 and 22:
1. Management of well child care2.
- Page 23 and 24:
3. Lab interpretation of joint flui
- Page 25 and 26:
5. Hemorrhoid I & D6. Fluid and Ele
- Page 27 and 28:
B. Service DescriptionC. DutiesA tw
- Page 29 and 30:
C. DutiesAttendance at the cardiolo
- Page 31 and 32:
Dermatology Clinic (C1 and C2 - MFH
- Page 33 and 34:
Vasectomy Clinic (C1 - FPI)Resident
- Page 35 and 36:
ability to maximize their health/he
- Page 37 and 38:
hospital care of common ENT conditi
- Page 39 and 40:
viii. Resident may be responsible f
- Page 41 and 42:
Rawlings or Dr. Bland so we can mak
- Page 43 and 44:
for EM occur once a month(on the th
- Page 45 and 46:
Emergency Medicine Rotation Require
- Page 47 and 48:
HOME VISITSEach resident is to make
- Page 49 and 50:
Practice preceptors who rotate onto
- Page 51 and 52:
A. Service GoalsAs a second and thi
- Page 53 and 54:
attending re: the patient’s statu
- Page 55 and 56:
Attending duties:• Be the attendi
- Page 57 and 58:
11-15: the night shift resident rou
- Page 59 and 60:
ED, and admitted, must be discussed
- Page 61 and 62:
D. Service Guidelines: OBSTETRICS S
- Page 63 and 64:
OPHTHALMOLOGYA. Service GoalsThe go
- Page 65 and 66:
CLIA testing & LunchEpisiotomy Trai
- Page 67 and 68:
10) Concussion11) Athlete’s heart
- Page 69 and 70:
Significant training continues duri
- Page 71 and 72:
. Hospital Leadership TrainingResid
- Page 73 and 74:
• Health systems training• Prac
- Page 75 and 76:
Alternative Scholarly Activities:1.
- Page 77 and 78: B. Service DescriptionC. DutiesThe
- Page 79 and 80: • Summarize areas of needed impro
- Page 81 and 82: as physicians, but especially inter
- Page 83 and 84: CHIEF RESIDENTS:The Chief Residents
- Page 85 and 86: . If the goal is not met as determi
- Page 87 and 88: • Complete, or provide evidence o
- Page 89 and 90: Grounds for Disciplinary Action:Gro
- Page 91 and 92: Appeal:include the reasons supporti
- Page 93 and 94: MFHC conducts a health center evalu
- Page 95 and 96: UNFINISHED BUSINESS:NEW BUSINESSDEP
- Page 97 and 98: must protect itself from possible s
- Page 99 and 100: MEDICAL STAFF BYLAWS / RULES AND RE
- Page 101 and 102: other educational items as approved
- Page 103 and 104: o Schedule II drugs may be written
- Page 105 and 106: GYNECOLOGY PROCEDURE LISTPROCEDURES
- Page 107 and 108: Breast FNA 0 5Wound Debridement 2 2
- Page 109 and 110: Addressing Patients’ Perceptions:
- Page 111 and 112: Reportable Diseases and Conditions:
- Page 113 and 114: admission (e.g., circumstances may
- Page 115 and 116: service for which the vacation is g
- Page 117 and 118: (i.e. Medicare, Medi-Cal, etc.) req
- Page 119 and 120: Call Expectations and Supervision R
- Page 121 and 122: Page 121 of 153WORK HOURSResidency
- Page 123 and 124: IV: ADDENDUM: Mercy Family Health C
- Page 125 and 126: 3. Privacy: Knock before entering i
- Page 127: All new warfarin patients will be g
- Page 131 and 132: Beef liver Garbanzo beans SeaweedBr
- Page 133 and 134: c. When C1 reviews lab and finds an
- Page 135 and 136: Colposcopy Clinics (C2 - MFHC and S
- Page 137 and 138: pertinent information. Dr. DeVlamin
- Page 140 and 141: 3. Perform a surgical “time out
- Page 142 and 143: • If in doubt, contact the Reside
- Page 144 and 145: Immediate feedback (Formative Evalu
- Page 146 and 147: Please note: If you have more than
- Page 148 and 149: chart holder that corresponding to
- Page 150 and 151: 1. According to the ACGME program r
- Page 152 and 153: 6. FPS resident if not the only sen