Frame Relay - for Faster and More Efficient Data Communications ...
Frame Relay - for Faster and More Efficient Data Communications ... Frame Relay - for Faster and More Efficient Data Communications ...
46Table 4SDH functions, Resources and Managed ObjectsFALFEBEFERFBELOPLOSMMPTMMSLMMSRKOOFLTUMFSFSDHMOFrame Alignment LossFar End Block ErrorFar End Remote FailureBlock ErrorLoss of PointerLoss of SignalMisMatch, Path TraceMisMatch, Signal LabelMisMatch between Sent and ReceivedK-bytesOut Of FrameLoss of TU MultiframeSignal FailSignal DegradeResourceManaged Objectof a synchronous digital multiplexer arematched to the transport functions definedin G.snal. Transport Functions 20 to 29are described in Table 4.SDH networks contain the following TransportFunctions (one direction):PI Physical Interface, required foradapting signals for transmissionover cables and vice versa. PI containsthe transport functions PPI,SLT and SLALPA Lower-order Path Adaptation,maps the payload into the containerLPT Lower-order Path Termination,adds VC Path overheadLPC Lower-order Path Connection, allowsflexible assignment betweenlower- and higher-order VCsHPAHigher-order Path Adaptation, processespointer to indicate phasebetween lower- and higher-orderVCs, assembles complete higherorderVCHPT Higher-order Path Termination,adds higher-order path overheadHPC Higher-order Path Connection, allowsflexible assignment betweenSAhigher-order VC and STM-NSection Adaptation, processespointer to indicate phase betweenhigher-order VCs and STM-N, andassembles complete STM-NMSP Multiplex Section Protection, providesswitching to another linesystem for protectionMST Multiplex Section Termination,adds/extracts rows 5 to 9 of theSection overheadRST Regenerator Section Termination,adds/extracts rows 1 to 3 of theSection overheadSPISynchronous Physical Interface,converts to/from in-station or interstationsignals.Networks with digital cross-connectionequipment can be modelled in a similarway. As shown in Fig. 17, N incoming andERICSSON REVIEW No. 1-2, 1992
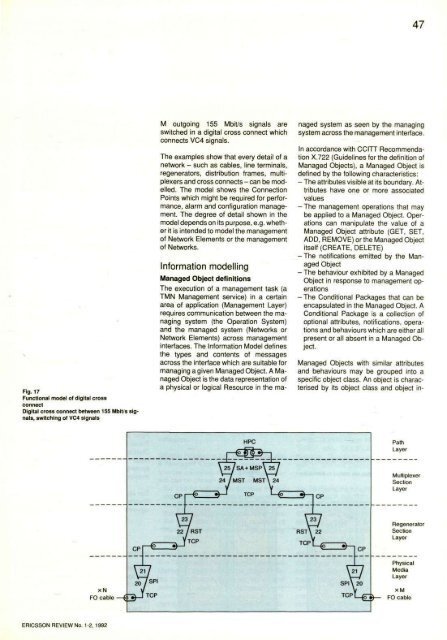
47Fig. 17Functional model of digital crossconnectDigital cross connect between 155 Mbit s signals,switching of VC4 signalsM outgoing 155 Mbit/s signals areswitched in a digital cross connect whichconnects VC4 signals.The examples show that every detail of anetwork - such as cables, line terminals,regenerators, distribution frames, multiplexersand cross connects - can be modelled.The model shows the ConnectionPoints which might be required for performance,alarm and configuration management.The degree of detail shown in themodel depends on its purpose, e.g. whetherit is intended to model the managementof Network Elements or the managementof Networks.Information modellingManaged Object definitionsThe execution of a management task (aTMN Management service) in a certainarea of application (Management Layer)requires communication between the managingsystem (the Operation System)and the managed system (Networks orNetwork Elements) across managementinterfaces. The Information Model definesthe types and contents of messagesacross the interface which are suitable formanaging a given Managed Object. A ManagedObject is the data representation ofa physical or logical Resource in the managedsystem as seen by the managingsystem across the management interface.In accordance with CCITT RecommendationX.722 (Guidelines for the definition ofManaged Objects), a Managed Object isdefined by the following characteristics:- The attributes visible at its boundary. Attributeshave one or more associatedvalues- The management operations that maybe applied to a Managed Object. Operationscan manipulate the value of aManaged Object attribute (GET, SET,ADD, REMOVE) or the Managed Objectitself (CREATE, DELETE)-The notifications emitted by the ManagedObject- The behaviour exhibited by a ManagedObject in response to management operations- The Conditional Packages that can beencapsulated in the Managed Object. AConditional Package is a collection ofoptional attributes, notifications, operationsand behaviours which are either allpresent or all absent in a Managed Object.Managed Objects with similar attributesand behaviours may be grouped into aspecific object class. An object is characterisedby its object class and object in-REVIEW No. 1-2, 1992
- Page 1: ERICSSONREVIEW1-21992Frame Relay -
- Page 4 and 5: ERICSSON REVIEWBO HEDFORSPublisher
- Page 6 and 7: 4Fig. 2Distributed computer environ
- Page 8 and 9: Fig. 7A company's data network shou
- Page 10 and 11: 8Fig. 11The frame format used for F
- Page 12 and 13: 10er (DE, Fig. 12) should be set to
- Page 14 and 15: Computerised System for QualityInsp
- Page 16 and 17: Box 1Code39, the first alphanumeric
- Page 18 and 19: 16Fig. 6Cable attenuation test at E
- Page 20 and 21: 18Fig. 9Installing the Dehlfi syste
- Page 22 and 23: Human Factors - A Key to ImprovedQu
- Page 24 and 25: 221 Use the user's model2 Introduce
- Page 26 and 27: 24Fig. 5Advanced Human Factors desi
- Page 28 and 29: Fig. 7User interface for PBX attend
- Page 30 and 31: Cell-voltage EqualisersSeries BMP 1
- Page 32 and 33: 30Box1CELL-VOLTAGE EQUALISER BMP 16
- Page 34 and 35: 32age, the faulty cell or the entir
- Page 36 and 37: In Search of Managed ObjectsWalter
- Page 38 and 39: Fig. 4The telecommunication network
- Page 40 and 41: Fig. 6Functional Model illustrating
- Page 42 and 43: 40Fig. 9Combination of layering and
- Page 44 and 45: 42Table 2Relationship between Funct
- Page 46 and 47: 44No1PPI2PPI3SLTTransport Function(
- Page 50 and 51: The Managed Objects and their prope
- Page 52 and 53: 50Fig. 21Information Model of PDH d
- Page 54 and 55: Fig. 25Information Model of SDH mul
- Page 56 and 57: 54Table 5Cross-connect functions, R
- Page 58: Fig. 32, leftCross-connect Fragment
47Fig. 17Functional model of digital crossconnectDigital cross connect between 155 Mbit s signals,switching of VC4 signalsM outgoing 155 Mbit/s signals areswitched in a digital cross connect whichconnects VC4 signals.The examples show that every detail of anetwork - such as cables, line terminals,regenerators, distribution frames, multiplexers<strong>and</strong> cross connects - can be modelled.The model shows the ConnectionPoints which might be required <strong>for</strong> per<strong>for</strong>mance,alarm <strong>and</strong> configuration management.The degree of detail shown in themodel depends on its purpose, e.g. whetherit is intended to model the managementof Network Elements or the managementof Networks.In<strong>for</strong>mation modellingManaged Object definitionsThe execution of a management task (aTMN Management service) in a certainarea of application (Management Layer)requires communication between the managingsystem (the Operation System)<strong>and</strong> the managed system (Networks orNetwork Elements) across managementinterfaces. The In<strong>for</strong>mation Model definesthe types <strong>and</strong> contents of messagesacross the interface which are suitable <strong>for</strong>managing a given Managed Object. A ManagedObject is the data representation ofa physical or logical Resource in the managedsystem as seen by the managingsystem across the management interface.In accordance with CCITT RecommendationX.722 (Guidelines <strong>for</strong> the definition ofManaged Objects), a Managed Object isdefined by the following characteristics:- The attributes visible at its boundary. Attributeshave one or more associatedvalues- The management operations that maybe applied to a Managed Object. Operationscan manipulate the value of aManaged Object attribute (GET, SET,ADD, REMOVE) or the Managed Objectitself (CREATE, DELETE)-The notifications emitted by the ManagedObject- The behaviour exhibited by a ManagedObject in response to management operations- The Conditional Packages that can beencapsulated in the Managed Object. AConditional Package is a collection ofoptional attributes, notifications, operations<strong>and</strong> behaviours which are either allpresent or all absent in a Managed Object.Managed Objects with similar attributes<strong>and</strong> behaviours may be grouped into aspecific object class. An object is characterisedby its object class <strong>and</strong> object in-REVIEW No. 1-2, 1992