A Double ZVS-PWM Active-Clamping Forward Converter ... - Ivo Barbi
A Double ZVS-PWM Active-Clamping Forward Converter ... - Ivo Barbi
A Double ZVS-PWM Active-Clamping Forward Converter ... - Ivo Barbi
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
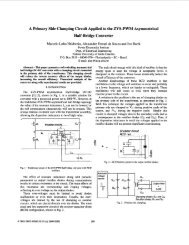
the output inductor filter Lo is large enough to beconsidered as a current source with a value equal to the loadcurrent I,;the voltage over input capacitors are equal (VI=V2=Vi);the resonant inductors are equal (LrI=LrZ=Lr);the clamping capacitors are equal (Ccl=Cc2=Cc);the resonant capacitors are equal (Crl=CrZ=Cr);0 the transformer leakage inductance is absorbed into Lland Lrz;0 there is no difference among the gate signals applied toeach pair the of switches (SI,S2 and S3,S4), they have identicalduty cycles.Fig. 2 shows the topological stages of the converter for ahalf-period and Fig. 3 shows the main theoretical waveformsfor one switching period. The six sequential circuit states aredescribed below:First Stage (to, tl): During this stage, the power istransferred to the load in two ways. Power is transferred fromthe input source VI through switch S1 and also, there is apower transfer to the load when capacitor Cc2 dischargesthrough switch S4. The switches S2 and S3 are in “off’ stateand the voltage over them is equal to the voltage over theclamping capacitors C,I and C,Z.Second Stage (tl, t2): At instant tl, switch SI is tuned-offwith zero voltage. Capacitor Crl begins to charge linearly witha constant current. This stage finishes when the voltage overSI is VI, and over S3 is Vc-VI.Third Stage (tz, t3): At instant t2, the transformer voltageis zero, in such a way that, the capacitor C,, begins theresonance with LrI. Also, the output current I, starts thefreewheeling process. When the voltage over Sl reaches V,this stage finishes.Fourth Stage (4, t4): At instant t3, diode D3 is directbiased and starts conducting the current through Lrl, whichdecreases linearly. In the same manner, the current throughLr2 decreases linearly. During this stage the load currentkeeps freewheeling through diodes DrI and Dn. Switch S3must be gated on before diode D3 is reverse biased. This stagefinishes when the switch S4 is turned OKFifth Stage (t4, t5): When switch S4 is turned off, thecurrent through L2 is deviated to resonant capacitor Cr2. Thiscapacitor is discharged in a resonant way. During this stagethe load current keeps freewheeling. This stage finishes whenvoltage over capacitor Cr2 is null and the diode D2 starts toconduct.Sixth Stage (t5, ts): At the instant t5, diode D2 is directbiased and begins conducting the Lr2 resonant inductorcurrent. During this condition, the switch S2 must be gated toconduct. The current through Lr2 decreases linearly until itreaches zero. Thereafter, this current changes direction andflow through switch S2. When the sum of the currents in LrIand Lr2 is equal to -nI, this stage finishes. During this stagethere is no power transferred to the load; therefore, only areduction in the duty cycle occurs.VIv2y2b -ERWLII,_I a ) - First Stageb ) - Second StageL.1c ) - Third Staged - Fourth StageU2laDI21”lrLlrrf) - Sixth StageFig. 2. States of operation of the converter.597