Year 3 Block A: - Suffolk Learning
Year 3 Block A: - Suffolk Learning
Year 3 Block A: - Suffolk Learning
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
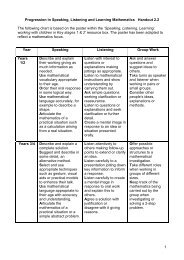
15 of 20 The National Strategies ⏐ Primary<strong>Year</strong> 3 <strong>Block</strong> A: Counting, partitioning and calculatingAssessment opportunity: Ma2, Solving numerical problemsAs children solve word problems, notice how they interpret the language of the problem toidentify the steps that they need to take. Look for evidence of children being able to identify andcomplete both steps in a problem that involves addition and subtraction or multiplication andanother operation.Children use counting strategies and partitioning to add and subtract combinations of one- andtwo-digit numbers. They add two-digit numbers by partitioning one or both of the numbers. Forexample, they work out 58 + 74 by partitioning 58 into 50 and 8 then adding 50 and 8 to 74.Children use a similar strategy for subtraction, for example, working out 94 – 58 or 294 – 58 bypartitioning the 58 and subtracting 50, then 8. They use counting-up strategies whereappropriate, as in 124 – 68 where they count up from 68 to 70, to 100, to 124, recording andadding the steps 2, 30 and 24. Children use a number line to note the steps and to explain howthey did the calculation. Children also subtract by counting on from the smaller to the largernumber, in their heads, when the difference is small, as in 305 – 297, making notes to supportcalculation.Assessment opportunity: Ma2, Mental methodsAs they add and subtract two-digit numbers mentally, look out for children who can explain howthey are solving the calculations. In particular, look for evidence of children making their owndecisions about whether to partition numbers or to count up.Children develop their use of the empty number line to support their calculations. They begin torecord vertically addition and subtraction calculations that cannot be easily done mentally.They partition one of the numbers and add or subtract the units, tens and hundreds separately:76+47267-149Children recognise the relationship between the vertical presentation and the steps on thenumber line. They begin to use an expanded layout that underpins the standard written method.For example, for 76 47 and 83 48 children use:00543-2008DOM-EN-11 © Crown copyright 2009