Chapter 9 Factors Influencing the Design of Vessels - FET
Chapter 9 Factors Influencing the Design of Vessels - FET
Chapter 9 Factors Influencing the Design of Vessels - FET
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
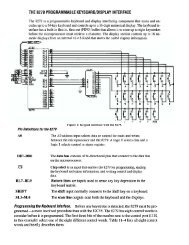
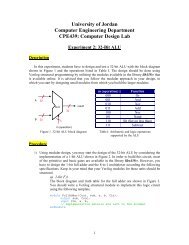
Department <strong>of</strong> Chemical EngineeringStrength <strong>of</strong> Materials for Chemical Engineers (0935381)<strong>Chapter</strong> 9<strong>Factors</strong> <strong>Influencing</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Design</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Vessels</strong>A- Most Common Types <strong>of</strong> <strong>Vessels</strong>:• Open tanks.• Flat-bottomed, vertical cylindrical tanks.• Vertical cylindrical and horizontal vessels with formed ends.• Spherical or modified spherical vesselsB- <strong>Factors</strong> <strong>Influencing</strong> <strong>the</strong> Choice <strong>of</strong> Vessel:• The function and location <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> vessel• The nature <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> fluid• Operating temperature and pressure• Necessary volume for storage or capacity for processing.C- Usage:• Large volume <strong>of</strong> no hazardous liquids, such as brine and o<strong>the</strong>r aqueous solutions,may be stored in pounds or in open tanks.• If <strong>the</strong> fluid is toxic, combustible, or gaseous in <strong>the</strong> storage condition or if <strong>the</strong>pressure is greater than atmospheric, closed system is required.• For storage <strong>of</strong> fluids at atmospheric pressure, cylindrical tanks with flat bottomand conical or domed ro<strong>of</strong>s are commonly used.• For small volumes under pressure, cylindrical tanks with formed heads are used.• For large volumes under pressure, spheres are used.D- Welding:1- T welds:
2- Butt welds:3- Plug welds:4- Lap welds:5- Edge welds:♣ The plates <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> shell may be butt or lap-welded depending upon <strong>the</strong> design andeconomic consideration.♣ 5/8 in is <strong>the</strong> maximum plate thickness for lap-welded horizontal joints.♣ 3/8 in is <strong>the</strong> maximum plate thickness for lap-welded vertical joints.♣ Butt-welded joints may be used for shell plates for all thicknesses up to and including1 ½ in.♣ The plates for butt-welded joints must be squared.
♣ Squaring <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> plates for lap-welded joints is not necessary♣ Plates for lap-welded joints are less expensive.