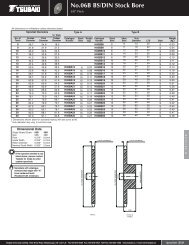
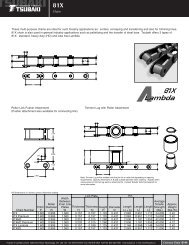
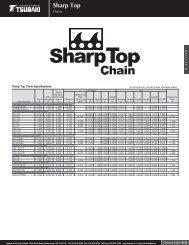
Roller Chain - Tsubaki
Roller Chain - Tsubaki
Roller Chain - Tsubaki
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Drive <strong>Chain</strong> SelectionData required for roller chain selection1) Driven machine2) Load classification3) Source of power4) HP to be transmitted5) Diameter and RPM of driving shaft6) Diameter and RPM of driven shaft7) Center distance between shaftsNecessary power (motor) characteristics for thespecial method of chain selection1) Moment of inertia2) Rated torque3) Starting torque4) Stalling torque2. Service Factors<strong>Tsubaki</strong> offers simplex, duplex and triplex chains in RF06B toRS40B of BS/DIN European standard. In ANSI standard, up to6 strands are available as standard items from RS40 to RS240and up to triplex for RS25 and RS35. In multiple strand chaindrives, the load is unequal across the width of the chain, so thetransmission capability of multiple strand chain is calculatedusing multiple strand factors shown in the table below.Table 1 : Multi-strand factorNo. of strands2 strands3 strands4 strands5 strands6 strandsService factor K sThe chain’s transmission capacity is affected if there is frequentload fluctuation. The appropriate service factor K s must beapplied based on the source of power and type of machine asshown in the table below. Please note that the service factor isnever smaller than 1.0.Table 2 : Service factor KsType ofImpactSmoothSome impactLarge impactMulti-strand factor1.72.53.33.94.6MachinesBelt Conveyors with smallload fluctuation, chainconveyors, centrifugalblowers, ordinary textilemachines, ordinary machineswith small load fluctuation.Centrifugal compressors,marine engines, conveyorswith some load fluctuation,automatic furnaces, dryers,pulverizers, general machinetools, compressors, generalwork machines, generalpaper mills.Press, construction or miningmachines, vibration machines,oil well rigs rubber mixers,rolls, roll gangs, generalmachines with reverse orlarge impact loads.ElectricMotororTurbine1.01.31.5Source of PowerInternal Combustion EngineWith hydraulicdrive1.01.21.4Withouthydraulic drive1.21.41.7Speed factor K v and sprocket teeth factor K CTable 3 : Speed factor, K v and sprocket teeth factor K CKv·Kc1.41.31.21.11.033Speed factor K vShock factor KThis coefficient is determined by the rate of inertia between thepower source (eg. motor or engine) and the driven machinery(rate of I, GD 2 ) as well as the amount of backlash in thetransmission equipment.When rate of inertia R > 10, R = 10When rate of inertia R < 0.2, R = 0.2When I or GD 2 for either the motor/power source or drivenmachinery is unknown, use the value of R on table 4.Table 4 : Shock factor KShock factor3.02.52.01.51.00.80.60.5k 0.40.30.2Sprocket teeth factor K c49 66 82 98 115 131 164<strong>Chain</strong> speed (ft/min)10 15 20 25 30 35 40 50 60Small sprocket teeth0For backlash in transmission equipmentR=Motor shaft converted inertia of loadInertia of motorFor NO backlash in transmission equipment, etc.0.2 0.3 0.5 0.8 1 2 3 5 8 10Hoist work ConveyorMillHoistgang rollcrane travel and shuffleInertia ratio RflywheelImbalance load factor K uWhen carrying out shuttle traction and lifting with two chains, orfour chains for shuttle drive and lifting, the chain tension is notuniform. This must be accounted for by multiplying the followingimbalance load coefficient K u to adjust the left-and-right loadimbalance.Example : For four lifting strands, the imbalance load factor forone strand K u = 0.6 × 0.6 = 0.36Table 5 : Imbalance load factor Ku2 lifting strands0.64 lifting strands0.36Drive <strong>Chain</strong>A-91