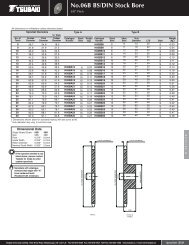
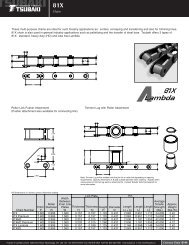
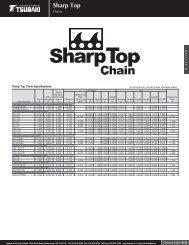
Roller Chain - Tsubaki
Roller Chain - Tsubaki
Roller Chain - Tsubaki
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Drive <strong>Chain</strong> Selection8. Selection Method for Lifting TransmissionsConsider the following procedures and points whenselecting roller chain for lifting transmissions:ProcedureConfirmation of data required for selectionBalancingEndFittings<strong>Roller</strong> <strong>Chain</strong>End FittingsProcedure 2Procedure 1 Confirmation of motor characteristicsCalculate chain tension from loadNStarting frequencyMore than 6 times/day (8hrs)YCalculate the chain tension from the motorEnd FittingsEnd bolts and exclusiveconnecting links for endbolts are stocked for RS<strong>Roller</strong> <strong>Chain</strong>.Drive <strong>Chain</strong>CounterweightSliderCompare the difference in massbetween the load and the counterweight, thencalculate the following using the greater massM {Weight W}Procedure 3From inertia ratio RProcedure 4From the acceleration, deceleration timeAscending/DescendingEquipment (1)CounterweightService factor: KsStarting torque: TsShock factor: KStalling torque: TbTime for acceleration: tsCalculate the chaintension FsTime for deceleration: tbCalculate the chaintension FbSpeed factor: KvEndFittings<strong>Roller</strong><strong>Chain</strong>EndFittingsReducer<strong>Roller</strong> <strong>Chain</strong>Sprocket tooth factor: KcCalculate the chaintension FmsCalculate the chaintension FmbChoose greater valueChoose greater valueSpeed factor: KvSprocket tooth factor: KcCalculate the designchain tension F’wCalculate the design chain tensionF’ms (or F’mb)Calculate the design chaintension F’s (or F’b)Ascending/DescendingEquipment (2)Reducer<strong>Roller</strong> <strong>Chain</strong>End Fittings(4 places)ForkAscending/DescendingEquipment (3)Reducer<strong>Roller</strong> <strong>Chain</strong>CounterweightEnd FittingsEnd FittingsExamples of Lifting TransmissionsChoose greater valueImbalance coefficient KuDetermine the chain size where a largetension for F’w, F’ms (or F’mb),F’s (or F’b) < = Max. Allowable LoadDetermine the sprocketConfirm that the sprockets fit the shafts.Determine the method of lubrication.EndSafety Precautions0Clear the area of allpersonnel whenlifting <strong>Roller</strong> <strong>Chain</strong>.0Install safety equipmentto preventinjuries and damageto equipment in theevent of <strong>Roller</strong><strong>Chain</strong> breakage.0Inspect and replaceworn <strong>Roller</strong> <strong>Chain</strong>periodically.0<strong>Roller</strong> <strong>Chain</strong> Selection for Lifting Applications(1) When making your selection, calculate the tension from the load and from the motor and apply the greater of the two. As arule of thumb, if the greater value is lower than the Max. Allowable Load of the chain you are thinking of choosing, then it maybe selected.(2) If there are any laws or guidelines for chain selection, check and calculate accordingly. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’sselections and select the safer of the two selections.(3) The chain speed should be less than 160 ft/min.(4) Use F-Type (Semi Press-fit) connecting links. Offset links cannot be used.(5) Lubricate the chain joints as much as possible after you reduce the loads. Sufficient lubrication is also required at end fittings(end bolts and connecting links, etc.) and connecting parts, etc.A-101