Modelling reactive distillation
Modelling reactive distillation
Modelling reactive distillation
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
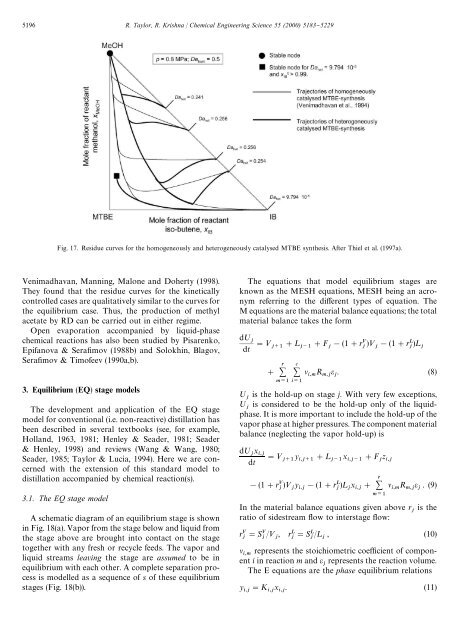
5196 R. Taylor, R. Krishna / Chemical Engineering Science 55 (2000) 5183}5229Fig. 17. Residue curves for the homogeneously and heterogeneously catalysed MTBE synthesis. After Thiel et al. (1997a).Venimadhavan, Manning, Malone and Doherty (1998).They found that the residue curves for the kineticallycontrolled cases are qualitatively similar to the curves forthe equilibrium case. Thus, the production of methylacetate by RD can be carried out in either regime.Open evaporation accompanied by liquid-phasechemical reactions has also been studied by Pisarenko,Epifanova & Sera"mov (1988b) and Solokhin, Blagov,Sera"mov & Timofeev (1990a,b).3. Equilibrium (EQ) stage modelsThe development and application of the EQ stagemodel for conventional (i.e. non-<strong>reactive</strong>) <strong>distillation</strong> hasbeen described in several textbooks (see, for example,Holland, 1963, 1981; Henley & Seader, 1981; Seader& Henley, 1998) and reviews (Wang & Wang, 1980;Seader, 1985; Taylor & Lucia, 1994). Here we are concernedwith the extension of this standard model to<strong>distillation</strong> accompanied by chemical reaction(s).3.1. The EQ stage modelA schematic diagram of an equilibrium stage is shownin Fig. 18(a). Vapor from the stage below and liquid fromthe stage above are brought into contact on the stagetogether with any fresh or recycle feeds. The vapor andliquid streams leaving the stage are assumed to be inequilibrium with each other. A complete separation processis modelled as a sequence of s of these equilibriumstages (Fig. 18(b)).The equations that model equilibrium stages areknown as the MESH equations, MESH being an acronymreferring to the di!erent types of equation. TheM equations are the material balance equations; the totalmaterial balance takes the formd; dt "< #¸ #F !(1#r )< !(1#r )¸# ν R ε . (8) ; is the hold-up on stage j. With very few exceptions,; is considered to be the hold-up only of the liquidphase.It is more important to include the hold-up of thevapor phase at higher pressures. The component materialbalance (neglecting the vapor hold-up) isd; x "< y x #F zdt #¸ !(1#r)< y !(1#r # )¸x ν R ε . (9) In the material balance equations given above r is the ratio of sidestream #ow to interstage #ow:r "S /< , r "S /¸, (10)ν represents the stoichiometric coe$cient of componenti in reaction m and ε represents the reaction volume.The E equations are the phase equilibrium relationsy "K x . (11)