Sepax Proteomix Brochure - Winlab.com.au
Sepax Proteomix Brochure - Winlab.com.au
Sepax Proteomix Brochure - Winlab.com.au
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
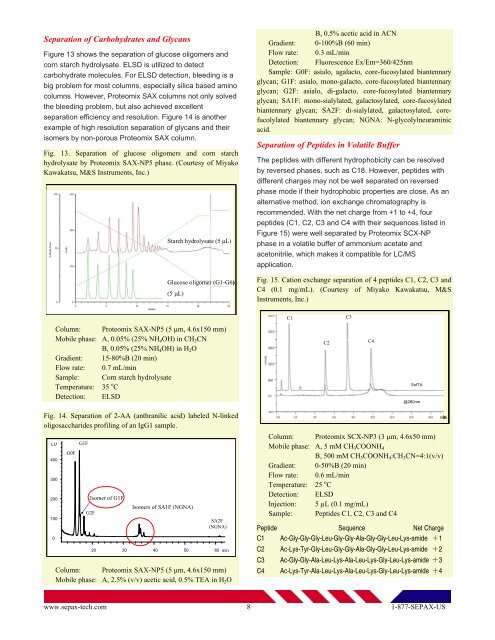
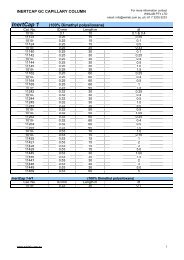
Separation of Carbohydrates and GlycansFigure 13 shows the separation of glucose oligomers andcorn starch hydrolysate. ELSD is utilized to detectcarbohydrate molecules. For ELSD detection, bleeding is abig problem for most columns, especially silica based aminocolumns. However, <strong>Proteomix</strong> SAX columns not only solvedthe bleeding problem, but also achieved excellentseparation efficiency and resolution. Figure 14 is anotherexample of high resolution separation of glycans and theirisomers by non-porous <strong>Proteomix</strong> SAX column.Fig. 13. Separation of glucose oligomers and corn starchhydrolysate by <strong>Proteomix</strong> SAX-NP5 phase. (Courtesy of MiyakoKawakatsu, M&S Instruments, Inc.)Starch hydrolysate (5 µL)Glucose oligomer (G1-G6)(5 µL)B, 0.5% acetic acid in ACNGradient: 0-100%B (60 min)Flow rate: 0.3 mL/minDetection: Fluorescence Ex/Em=360/425nmSample: G0F: asialo, agalacto, core-fucosylated biantennaryglycan; G1F: asialo, mono-galacto, core-fucosylated biantennaryglycan; G2F: asialo, di-galacto, core-fucosylated biantennaryglycan; SA1F: mono-sialylated, galactosylated, core-fucosylatedbiantennary glycan; SA2F: di-sialylated, galactosylated, corefucolylatedbiantennary glycan; NGNA: N-glycolylneuraminicacid.Separation of Peptides in Volatile BufferThe peptides with different hydrophobicity can be resolvedby reversed phases, such as C18. However, peptides withdifferent charges may not be well separated on reversedphase mode if their hydrophobic properties are close. As analternative method, ion exchange chromatography isre<strong>com</strong>mended. With the net charge from +1 to +4, fourpeptides (C1, C2, C3 and C4 with their sequences listed inFigure 15) were well separated by <strong>Proteomix</strong> SCX-NPphase in a volatile buffer of ammonium acetate andacetonitrile, which makes it <strong>com</strong>patible for LC/MSapplication.Fig. 15. Cation exchange separation of 4 peptides C1, C2, C3 andC4 (0.1 mg/mL). (Courtesy of Miyako Kawakatsu, M&SInstruments, Inc.)C1C3Column: <strong>Proteomix</strong> SAX-NP5 (5 µm, 4.6x150 mm)Mobile phase: A, 0.05% (25% NH 4 OH) in CH 3 CNB, 0.05% (25% NH 4 OH) in H 2 OGradient: 15-80%B (20 min)Flow rate: 0.7 mL/minSample: Corn starch hydrolysateTemperature: 35 o CDetection: ELSDC2C4SofTA@280nmFig. 14. Separation of 2-AA (anthranilic acid) labeled N-linkedoligosaccharides profiling of an IgG1 sample.LU4003002001000G0FG1FIsomer of G1FG2FIsomers of SA1F (NGNA)SA2F(NGNA)20 30 40 50 60minColumn: <strong>Proteomix</strong> SAX-NP5 (5 µm, 4.6x150 mm)Mobile phase: A, 2.5% (v/v) acetic acid, 0.5% TEA in H 2 OColumn: <strong>Proteomix</strong> SCX-NP3 (3 µm, 4.6x50 mm)Mobile phase: A, 5 mM CH 3 COONH 4B, 500 mM CH 3 COONH 4 :CH 3 CN=4:1(v/v)Gradient: 0-50%B (20 min)Flow rate: 0.6 mL/minTemperature: 25 o CDetection: ELSDInjection: 5 µL (0.1 mg/mL)Sample: Peptides C1, C2, C3 and C4Peptide Sequence Net ChargeC1 Ac-Gly-Gly-Gly-Leu-Gly-Gly-Ala-Gly-Gly-Leu-Lys-amide +1C2C3C4Ac-Lys-Tyr-Gly-Leu-Gly-Gly-Ala-Gly-Gly-Leu-Lys-amide +2Ac-Gly-Gly-Ala-Leu-Lys-Ala-Leu-Lys-Gly-Leu-Lys-amide +3Ac-Lys-Tyr-Ala-Leu-Lys-Ala-Leu-Lys-Gly-Leu-Lys-amide +4minwww.sepax-tech.<strong>com</strong> 8 1-877-SEPAX-US