Geometry and Thermodynamics of Black Holes in Magnetic Fields ...
Geometry and Thermodynamics of Black Holes in Magnetic Fields ...
Geometry and Thermodynamics of Black Holes in Magnetic Fields ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
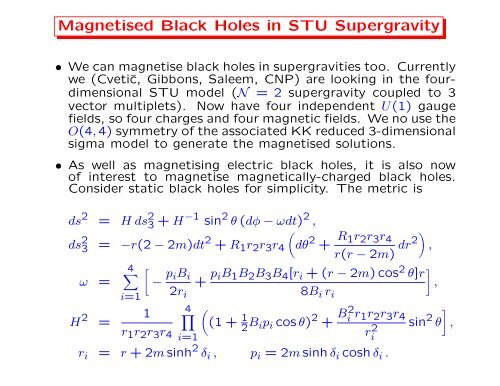
Magnetised <strong>Black</strong> <strong>Holes</strong> <strong>in</strong> STU Supergravity• We can magnetise black holes <strong>in</strong> supergravities too. Currentlywe (Cvetič, Gibbons, Saleem, CNP) are look<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the fourdimensionalSTU model (N = 2 supergravity coupled to 3vector multiplets). Now have four <strong>in</strong>dependent U(1) gaugefields, so four charges <strong>and</strong> four magnetic fields. We no use theO(4, 4) symmetry <strong>of</strong> the associated KK reduced 3-dimensionalsigma model to generate the magnetised solutions.• As well as magnetis<strong>in</strong>g electric black holes, it is also now<strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>terest to magnetise magnetically-charged black holes.Consider static black holes for simplicity. The metric isds 2 = H ds 2 3 + H−1 s<strong>in</strong> 2 θ (dφ − ωdt) 2 ,(ds 2 3 = −r(2 − 2m)dt2 + R 1 r 2 r 3 r 4 dθ 2 + R )1r 2 r 3 r 4r(r − 2m) dr2ω =4∑i=1[− p iB i+ p iB 1 B 2 B 3 B 4 [r i + (r − 2m) cos 2 ]θ]r,2r i 8B i r iH 2 1 ∏ 4 (=(1 + 1r 1 r 2 r 3 r2 B ip i cos θ) 2 + B2 i r 1r 2 r 3 r 44 i=1ri2r i = r + 2m s<strong>in</strong>h 2 δ i , p i = 2m s<strong>in</strong>h δ i cosh δ i .,]s<strong>in</strong> 2 θ ,