Gene-Spin™ MiniPrep Plasmid Purification Kit
Gene-Spin™ MiniPrep Plasmid Purification Kit
Gene-Spin™ MiniPrep Plasmid Purification Kit
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
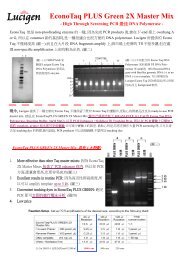
KIT CONTENTS :<strong>Gene</strong>-Spin kit 50 reactions 250 reactionsCat No. MP530 MP530XLSolution I 12ml*260ml*2Solution II 12ml*360ml*3Solution III 18 ml 90mlWashing Solution 16 ml *1 40 ml X 2 *1Elution Solution 10 ml 50ml<strong>Gene</strong>-Spin spin Column 50 pcs 250 pcsCollection tubes 50 pcs 250 pcsREMARKS BEFORE YOU START :1. Before Using Washing Buffer, add 64 ml (for 50reactions) or 160 ml (for 250 reactions) 95~100% ethanol and mix well.2. Please store Solution I at 4 °C for longer storage.3. The SDS in Solution II will precipitate attemperature below 20 °C. If this is the case,store the Solution II at 30 to 40 °C and mix well.2
10Un certain nombre d'ingénieries ont été élaborées et expérimentées suivant ceschéma. Nous avons en particulier mis au point, pour des élèves de cours moyen, unprocessus d'enseignement des angles, décrit dans Grand N nO 56, dont l'élément centralest une situation de communication.b. Un exemple de processus didactique construit sur ce modèleLe milieu matériel est constitué de pièces découpées dans du carton, de formepolygonale, convexes ou non, dont les mesures des angles sont des multiples de 30degrés; elles sont conçues de telle manière qu'il existe au moins une solution au problèmeposé par leur assemblage, en utilisant la règle suivante : Deux côtés de la énième pièce àposer doivent toucher 2 côtés du polygone formé avec les n-1 pièces déjà posées (annexe2).• Le jeu du géométriscrabbleUn jeu de n pièces polygonales est commun à p joueurs. Deux des pièces sontposées sur la table, et deux de leurs côtés ont une partie accolée, suivant uneconfiguration déterminée à l'avance; les autres pièces sont distribuées aux joueurs. Àtour de rôle, chacun se procure une pièce de son lot et peut la poser si elle s'accole; sanschevauchement, le long de deux de ses côtés, à deux côtés du polygone formé par lespièces déjà assemblées. Sinon le tour passe au joueur suivant. Le premier qui s'estdébarrassé de ses pièces a gagné.Les contraintes d'assemblage pièce-emplacement constituent unevariabledidactique prenant des valeurs différentes au cours de jeux successifs que réalisent lesélèves:*pas de contraintesChaque joueur tirant au hasard une pièce, il essaie de l'encastrer convenablementpar essais-erreurs. Dans ces conditions, la réussite finale est liée à la qualité del'exploration; les joueurs doivent seulement être capables de déterminer si une pièces'encastre bien ou non sur l'un de ses angles et sinon d'organiser de manière efficace,plus ou moins systématique, une recherche des emplacements ou des autres angles de lapièce possibles. La comparaison des angles est prise en charge par le matériel, elle n'apas à être anticipée.* avec anticipationChaque joueur tire une pièce au hasard et doit prévoir à voix haute quelle partie dela pièce il va pouvoir encastrer et à quel endroit du puzzle elle se place. L'anticipationporte donc sur la reconnaissance par comparaison visuelle à distance d'une proximité devaleur entre un angle de la pièce polygonale et un angle extérieur du polygone constituépar l'assemblage.* par communication graphiqueCeci est réalisé lorsque le stock des pièces n'est plus à la disposition du joueur E(Emetteur) qui va les placer, mais d'un autre R (Récepteur). E (qui ne connaît pas lesformes et dimensions précises des pièces du stock) doit donc fournir à R uneinformation lui permettant de trouver une pièce convenable. Pour cela il dispose d'un
The procedure consists of three basic steps:Preparation and clearing of the bacterial lysateBinding of plasmid DNA onto the <strong>Gene</strong>-Spin<strong>MiniPrep</strong> ColumnWashing and elution of plasmid DNA5
<strong>Gene</strong>Spin <strong>Plasmid</strong> <strong>MiniPrep</strong> Flow Chart1~5 ml E. coli LB Culture12,000 - 14, 000 g , 1 min+ 200 ul Solution I200 ul Solution II300 ul Solution III12,000 - 14, 000 g , 5 minLoad Supernatant ~ 700 ul12,000 - 14, 000 g 1 min+ 700 ul Washing 12,000 - 14, 000 g , 1 min12,000 - 14, 000 g , 3 min60 o C oven for 5-10 min toevaporate all the ethanol + 50 ul Elution Buffer / ddH 2 O12,000 - 14, 000 g , 2 min6
GENERAL PROTOCOL :1. Transfer an overnight 1-5 ml culture to a microcentrifugetube. Spin down the cells for 30s-1minat top speed (12,000-14,000 x g). Discard thesupernatant.2. Add 200 l Solution I and pipette up and down(or vortex) until the cells are completelyresuspended.3. Add 200 l Solution II and mix by gentlyinverting the capped tube 5-6 times. Do notvortex. Incubate at room temperature for amaximum of 5 min.4. Add 300 l Solution III and mix by gentlyinverting the capped tube 5-6 times. Do notvortex.5. Pellet the precipitate for 5 mins at top speed(12,000-14,000 x g). A compact white pellet willform along the side or at the bottom of the tube.6. Insert the spin column into a collection tube,load the supernatant from step 5 directly to spin7
column, spin for 30 s.7. Remove the spin column from the collectiontube, discard the flowthrough and add 700 lWashing Solution and spin for 1 min. Forfluorescent sequencing repeat this step for onemore time is recommended.8. Discard the filtrate then centrifuge for 3 min at topspeed to remove any residual trace of ethanol (seeNote 2). Spin column incubate at 60 o C oven for 5-10 min.9. Remove the spin column and place the column ina new microcentrifuge tube. Add 50-100 l H 2 O orElution Buffer into the column. For plasmid largerthan 7kb, use preheated 60-70 0 C H 2 O or TE toelute.10. Elute the DNA by centrifugation for 1min andstore the eluted DNA at -20 0 C.Repeat step 9-10 may give 10-15% more DNA,but DNA concentration will be diluted.8
Note:1. Use an endA - E.coli strain for plasmid purification.The instability of plasmids isolated from endA +strains has been reported.2. To remove residual trace of ethanol at step 8 isvery important, if some trace ethanol still remainsin binding resin, the eluted DNA may interfere withfurther application. If necessary, after 3 mincentrifugation at step 8, incubate the spin columnat 60 0 C oven for 5-10 min to evaporate all theethanol before elute the DNA.3. Depending on the E. coli strain, plasmid copynumbers and medium, the yield of plasmid DNA isaround 2-15 ug per ml E.coli culture at a purity of1.8 (260/280).9
TROUBLESHOOTINGQ: Incomplete lysis of bacterial cellsSDS in Solution II precipitated - SDS in SolutionII may precipitate upon storage. If this happens,incubate Solution II at 30-40ºC for 5 min and mixwell.Too many bacterial cells used - We recommendLB as the optimal growth medium. When usingvery rich media like TB, the cell density of thecultures may become to high.Q: Poor <strong>Plasmid</strong> YieldIn complete lysis of bacterial cells - See “Possiblecause and suggestions” above.Suboptimal precipitation of SDS and cell debris -Precipitation of SDS and cell debris will be slightlymore effective when centrifuging at 4ºC insteadof room temperature (step 5).10
Suboptimal elution conditions - If possible, usinga slightly alkaline elution buffer like elution solution(10mM Tris-HCl, pH8.5). If using nucleasefreewater, check the pH of the water. Q: No <strong>Plasmid</strong> YieldReagent not applied properly - Add indicatedvolume of 96-100% ethanol to buffer concentratewashing solution and mix well.Nuclease-rich host strains used - If using nuclease-richstrains like E.coli HB101 or strains of theJM series, be sure to perform the optimal washingsolution step. Q: Poor <strong>Plasmid</strong> Quality Genomic DNA contamination - Cell lysate wasvortexed or mixed too vigorously after addition ofsolution II. Genomic DNA was sheared and thus11
liberated.Smeared plasmid bands on agarose gel - Ifusing nuclease-rich strains like E.coli HB101 orstrains of the JM series, be sure to perform theoptimal washing solution step. When working withnuclease-rich strains, keep plasmid preparationson ice or frozen in order to avoid plasmid DNAdegradation.12
Manufactured for and distributed byProtech Technology Enterprise Co., LtdTEL: 886-2-2655-7677 FAX: 886-2-2655-7601E-mail: tech@bio-protech.com.twWeb Site: http://www.bio-protech.com.tw