Chromosome Theory
Chromosome Theory Chromosome Theory
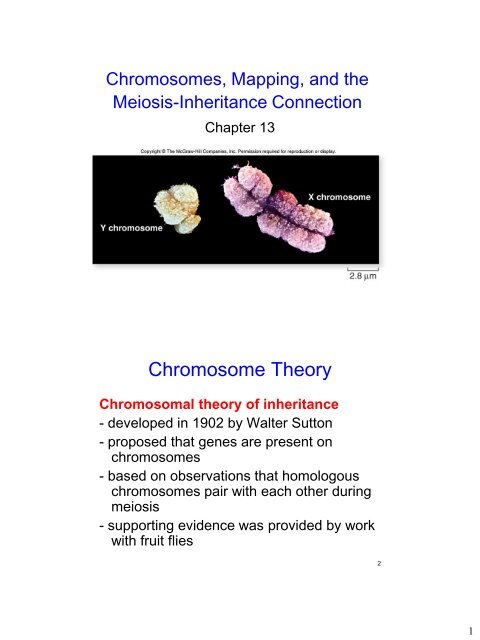
Chromosomes, Mapping, and theMeiosis-Inheritance ConnectionChapter 13Chromosome TheoryChromosomal theory of inheritance- developed in 1902 by Walter Sutton- proposed that genes are present onchromosomes- based on observations that homologouschromosomes pair with each other duringmeiosis- supporting evidence was provided by workwith fruit flies21
- Page 2 and 3: Chromosome TheoryT.H. Morgan isolat
- Page 4 and 5: Sex ChromosomesSex determination in
- Page 6 and 7: 11Chromosome Theory ExceptionsMitoc
- Page 8 and 9: 15168
- Page 10 and 11: 192010
- Page 12 and 13: Genetic MappingDetermining the orde
- Page 14 and 15: Human Genetic DisordersSome human g
- Page 16 and 17: 31Human Genetic DisordersNondisjunc
- Page 18 and 19: Human Genetic DisordersGenetic coun
<strong>Chromosome</strong>s, Mapping, and theMeiosis-Inheritance ConnectionChapter 13<strong>Chromosome</strong> <strong>Theory</strong>Chromosomal theory of inheritance- developed in 1902 by Walter Sutton- proposed that genes are present onchromosomes- based on observations that homologouschromosomes pair with each other duringmeiosis- supporting evidence was provided by workwith fruit flies21
<strong>Chromosome</strong> <strong>Theory</strong>T.H. Morgan isolated a mutant white-eyedDrosophilared-eyed female X white-eyed male gave aF 1 generation of all red eyesMorgan concluded that red eyes aredominant3<strong>Chromosome</strong> <strong>Theory</strong>Morgan crossed F 1 females X F 1 malesF 2 generation contained red and white- eyedflies but all white-eyed flies were maletestcross of a F 1 female with a white-eyedmale showed the viability of white-eyedfemalesMorgan concluded that the eye color gene islinked to the X chromosome42
563
Sex <strong>Chromosome</strong>sSex determination in Drosophila is based on thenumber of X chromosomes2 X chromosomes = female1 X and 1 Y chromosome = maleSex determination in humans is based on thepresence of a Y chromosome2 X chromosomes = femalehaving a Y chromosome (XY) = male7Sex <strong>Chromosome</strong>sIn many organisms, the Y chromosome isgreatly reduced or inactive.genes on the X chromosome are present inonly 1 copy in malessex-linked traits: controlled by genespresent on the X chromosomeSex-linked traits show inheritance patternsdifferent than those of genes onautosomes.84
9Sex <strong>Chromosome</strong>sDosage compensation ensures an equalexpression of genes from the sexchromosomes even though females have2 X chromosomes and males have only 1.In each female cell, 1 X chromosome isinactivated and is highly condensed into aBarr body.Females heterozygous for genes on the Xchromosome are genetic mosaics.105
11<strong>Chromosome</strong> <strong>Theory</strong> ExceptionsMitochondria and chloroplasts containgenes.traits controlled by these genes do not followthe chromosomal theory of inheritancegenes from mitochondria and chloroplastsare often passed to the offspring by onlyone parent126
<strong>Chromosome</strong> <strong>Theory</strong> ExceptionsMaternal inheritance: uniparental (oneparent)inheritance from the motherthe mitochondria in a zygote are from theegg cell; no mitochondria come from thesperm during fertilizationin plants, the chloroplasts are often inheritedfrom the mother, although this is speciesdependent13Genetic MappingEarly geneticists realized that they couldobtain information about the distancebetween genes on a chromosome.- this is genetic mappingThis type of mapping is based on geneticrecombination (crossing over) betweengenes.147
15168
Genetic MappingTo determine the distance between genes:- dihybrid organisms are testcrossed- offspring resembling the dihybrid parentresult from homologues that were notinvolved in the crossover- offspring resulting from a crossover arecalled recombinant progeny17Genetic MappingThe distance between genes is proportional tothe frequency of recombination events.recombinationfrequencyrecombinant progeny=total progeny1% recombination = 1 map unit (m.u.)1 map unit = 1 centimorgan (cM)189
192010
Genetic MappingMultiple crossovers between 2 genes canreduce the perceived genetic distanceprogeny resulting from an even number ofcrossovers look like parental offspring212211
Genetic MappingDetermining the order of genes can be donewith a three-point testcrossthe frequency of double crossovers is theproduct of the probabilities of eachindividual crossovertherefore, the classes of offspring with thelowest numbers represent the doublecrossovers and allow the gene order to bedetermined232412
Genetic MappingMapping genes in humans involvesdetermining the recombination frequencybetween a gene and an anonymousmarkerAnonymous markers such as singlenucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) canbe detected by molecular techniques.252613
Human Genetic DisordersSome human genetic disorders are causedby altered proteins.the altered protein is encoded by a mutatedDNA sequencethe altered protein does not functioncorrectly, causing a change to thephenotypethe protein can be altered at only a singleamino acid (e.g. sickle cell anemia)272814
29Human Genetic DisordersSome genetic disorders are caused by achange in the number of chromosomes.nondisjunction during meiosis can creategametes having one too many or one toofew chromosomesfertilization of these gametes createstrisomic or monosomic individualsDown syndrome is trisomy of chromosome213015
31Human Genetic DisordersNondisjunction of sex chromosomes canresult in:XXX triple-X femalesXXY males (Klinefelter syndrome)XO females (Turner syndrome)OY nonviable zygotesXYY males (Jacob syndrome)3216
33Human Genetic Disordersgenomic imprinting occurs when thephenotype exhibited by a particular alleledepends on which parent contributed theallele to the offspringa specific partial deletion of chromosome 15results in:Prader-Willi syndrome if the chromosome isfrom the fatherAngelman syndrome if it’s from the mother3417
Human Genetic DisordersGenetic counseling can use pedigreeanalysis to determine the probability ofgenetic disorders in the offspring.Some genetic disorders can be diagnosedduring pregnancy.amniocentesis collects fetal cells from theamniotic fluid for examinationchorionic villi sampling collects cells fromthe placenta for examination353618
3719