Destination Math⢠Mastering Skills & Concepts (MSC)
Destination Math⢠Mastering Skills & Concepts (MSC)
Destination Math⢠Mastering Skills & Concepts (MSC)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
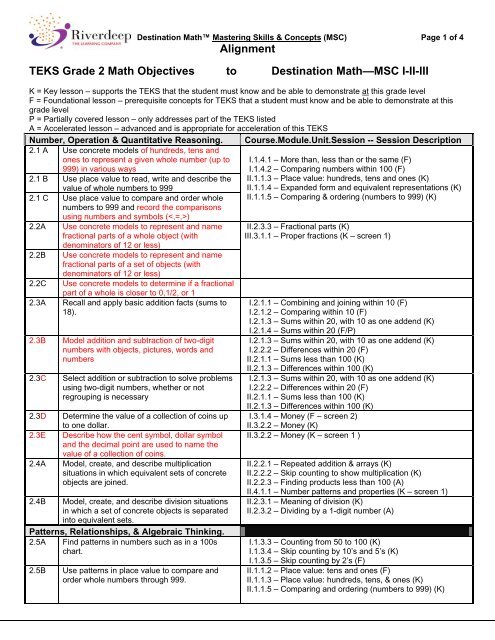
<strong>Destination</strong> Math <strong>Mastering</strong> <strong>Skills</strong> & <strong>Concepts</strong> (<strong>MSC</strong>) Page 1 of 4AlignmentTEKS Grade 2 Math Objectives to <strong>Destination</strong> Math—<strong>MSC</strong> I-II-IIIK = Key lesson – supports the TEKS that the student must know and be able to demonstrate at this grade levelF = Foundational lesson – prerequisite concepts for TEKS that a student must know and be able to demonstrate at thisgrade levelP = Partially covered lesson – only addresses part of the TEKS listedA = Accelerated lesson – advanced and is appropriate for acceleration of this TEKSNumber, Operation & Quantitative Reasoning. Course.Module.Unit.Session -- Session Description2.1 A Use concrete models of hundreds, tens andones to represent a given whole number (up to999) in various ways2.1 B Use place value to read, write and describe thevalue of whole numbers to 9992.1 C Use place value to compare and order wholenumbers to 999 and record the comparisonsusing numbers and symbols ()2.2A Use concrete models to represent and namefractional parts of a whole object (withdenominators of 12 or less)2.2B Use concrete models to represent and namefractional parts of a set of objects (withdenominators of 12 or less)2.2C Use concrete models to determine if a fractionalpart of a whole is closer to 0,1/2, or 12.3A Recall and apply basic addition facts (sums to18).2.3B Model addition and subtraction of two-digitnumbers with objects, pictures, words andnumbers2.3C Select addition or subtraction to solve problemsusing two-digit numbers, whether or notregrouping is necessary2.3D Determine the value of a collection of coins upto one dollar.2.3E Describe how the cent symbol, dollar symboland the decimal point are used to name thevalue of a collection of coins.2.4A Model, create, and describe multiplicationsituations in which equivalent sets of concreteobjects are joined.2.4B Model, create, and describe division situationsin which a set of concrete objects is separatedinto equivalent sets.Patterns, Relationships, & Algebraic Thinking.2.5A Find patterns in numbers such as in a 100schart.2.5B Use patterns in place value to compare andorder whole numbers through 999.I.1.4.1 – More than, less than or the same (F)I.1.4.2 – Comparing numbers within 100 (F)II.1.1.3 – Place value: hundreds, tens and ones (K)II.1.1.4 – Expanded form and equivalent representations (K)II.1.1.5 – Comparing & ordering (numbers to 999) (K)II.2.3.3 – Fractional parts (K)III.3.1.1 – Proper fractions (K – screen 1)I.2.1.1 – Combining and joining within 10 (F)I.2.1.2 – Comparing within 10 (F)I.2.1.3 – Sums within 20, with 10 as one addend (K)I.2.1.4 – Sums within 20 (F/P)I.2.1.3 – Sums within 20, with 10 as one addend (K)I.2.2.2 – Differences within 20 (F)II.2.1.1 – Sums less than 100 (K)II.2.1.3 – Differences within 100 (K)I.2.1.3 – Sums within 20, with 10 as one addend (K)I.2.2.2 – Differences within 20 (F)II.2.1.1 – Sums less than 100 (K)II.2.1.3 – Differences within 100 (K)I.3.1.4 – Money (F – screen 2)II.3.2.2 – Money (K)II.3.2.2 – Money (K – screen 1 )II.2.2.1 – Repeated addition & arrays (K)II.2.2.2 – Skip counting to show multiplication (K)II.2.2.3 – Finding products less than 100 (A)II.4.1.1 – Number patterns and properties (K – screen 1)II.2.3.1 – Meaning of division (K)II.2.3.2 – Dividing by a 1-digit number (A)I.1.3.3 – Counting from 50 to 100 (K)I.1.3.4 – Skip counting by 10’s and 5’s (K)I.1.3.5 – Skip counting by 2’s (F)II.1.1.2 – Place value: tens and ones (F)II.1.1.3 – Place value: hundreds, tens, & ones (K)II.1.1.5 – Comparing and ordering (numbers to 999) (K)
<strong>Destination</strong> Math <strong>Mastering</strong> <strong>Skills</strong> & <strong>Concepts</strong> (<strong>MSC</strong>) Page 2 of 4AlignmentTEKS Grade 2 Math Objectives to <strong>Destination</strong> Math—<strong>MSC</strong> I-II-IIIK = Key lesson – supports the TEKS that the student must know and be able to demonstrate at this grade levelF = Foundational lesson – prerequisite concepts for TEKS that a student must know and be able to demonstrate at thisgrade levelP = Partially covered lesson – only addresses part of the TEKS listedA = Accelerated lesson – advanced and is appropriate for acceleration of this TEKSPatterns, Relationships, & Algebraic Thinking.2.5C Use patterns and relationships to developstrategies to remember basic addition andsubtraction facts. Determine patterns in relatedaddition and subtraction number sentences(including fact families) such as 8 + 9 = 17, 9 +8 = 17, 17 - 8 = 9, and 17 - 9 = 8.2.6A Generate a list of paired numbers based on areal-life situation such as number of tricyclesrelated to number of wheels.2.6B Identify patterns in a list of related number pairsbased on a real-life situation and extend the list.2.6C Identify, describe, and extend repeating andadditive patterns to make predictions and solveproblems.Geometry and Spatial Reasoning.2.7A Describe attributes (the number of vertices,faces, edges, sides) of two- and threedimensionalgeometric figures such ascircles,polygons,spheres,cones, cylinders,prisms and pyramids2.7B Use attributes to describe how 2 twodimensionalgeometric figures are alike anddifferent2.7C Cut two-dimensional geometric figures apartand identify the new geometric figures formed.2.8 Use whole numbers to locate and name pointson a line.Measurement.2.9A Identify concrete models that approximatestandard units of length and use them tomeasure length.2.9B Select a non-standard unit of measure such assquare tiles to determine the area of a twodimensionalsurface2.9C Select a non-standard unit of measure such asa bathroom cup or a jar to determine thecapacity of a given container2.9D Select a non-standard unit of measure such asbeans and marbles to determine theweight/mass of a given object.Course.Module.Unit.Session -- Session DescriptionI.4.1.2 – Number Patterns (K)II.2.1.1 – Sums less than 100 (F)II.2.2.1 – Repeated addition and arrays (K – screen 1)III.2.1.1 – Whole Number Sums (A – uses four and five digitnumbers)II.4.1.1 – Number patterns & properties (A/screen2)II.4.1.1 – Number patterns & properties(A/screen2)I.4.1.2 – Number patterns (F)II.2.2.1 – Repeated addition & arrays (K)II.2.2.2 – Skip counting to show multiplication (K)II.4.1.1 – Number patterns and properties (A/ screen 2)I.3.2.1 – Triangles & rectangles (F –screen 2)I.3.2.2 – Three-dimensional shapes (F)I.4.1.1 – Shapes (F- screen 2)II.3.1.1 – Area (K)II.2.1.2 – Estimating & finding sums less than 1000 (A)II.2.1.4 – Estimating & finding differences within 1000 (A)II.2.2.2 – Skip counting to show multiplication (A) (All lessonsshould be whole group)I.3.1.1 – Length (K – screen 2 & practice questions 5 and 6)II.3.1.1 – Area (K)II.3.1.2 – Volume (A – uses standard units)I.3.1.2 – Weight (P – does not use mass)2.10A Read a thermometer to gather data. II.3.2.3 – Temperature (K)2.10B Read and write times shown on analog and II.3.2.1 – Time (K)digital clocks using five-minute increments
<strong>Destination</strong> Math <strong>Mastering</strong> <strong>Skills</strong> & <strong>Concepts</strong> (<strong>MSC</strong>) Page 3 of 4AlignmentTEKS Grade 2 Math Objectives to <strong>Destination</strong> Math—<strong>MSC</strong> I-II-IIIK = Key lesson – supports the TEKS that the student must know and be able to demonstrate at this grade levelF = Foundational lesson – prerequisite concepts for TEKS that a student must know and be able to demonstrate at thisgrade levelP = Partially covered lesson – only addresses part of the TEKS listedA = Accelerated lesson – advanced and is appropriate for acceleration of this TEKSProbability & Statistics.Course.Module.Unit.Session -- Session Description2.11A Construct picture graphs and bar-type graphs. I.4.1.3 – Tables & graphs (F with print activities)2.11B Draw conclusions and answer questions based I.4.1.3 – Tables & graphs (F with print activities)on picture graphs and bar-type graphs.2.11C Use data to describe events as more likely orless likely such as drawing a certain colorcrayon from a bag of seven red crayons andthree green crayonsThis language should be used as above lessons arecompleted.Underlying Processes & Mathematical Tools.2.12A Identify the mathematics in everyday situations. I.2.1.2 – Comparing within 10 (F)I.2.2.2 – Differences within 20 (F)I.3.1.1 – Length (K – screen 2)I.3.1.4 – Money (K – screen 2)II.2.3.3 – Fractional parts (K)II.3.1.1 – Area (K)II.3.1.2 – Volume (K)II.3.2.1 – Time (K)II.3.2.2 – Money (K)II.3.2.3 – Temperature (K)2.12B Solve problems with guidance that incorporatesthe processes of understanding the problem,making a plan, carrying out the plan, andevaluating the solution for reasonableness.2.12C Select or develop an appropriate problemsolvingstrategy including drawing a picture,looking for a pattern, systematic guessing andchecking, or acting it out in order to solve aproblem.2.12D Use tools such as real objects, manipulatives,and technology to solve problems.2.13A Explain and record observations using objects,words, pictures, numbers, and technology.All sessions align if the PACE chart and print activities areused consistently.All sessions align if the PACE chart and print activities areused consistently.I.2.1.1 – Combining & joining within 10 (F)I.2.1.2 – Comparing within 10 (F)I.2.1.3 – Sums within 20, with 10 as one addend (K)I.2.1.4 – Sums within 20 (P)I.2.2.2 – Differences within 20 (K)I.3.1.1 – Length (K – screen 2)I.3.1.2 – Weight (F)II.2.1.1 – Sums less than 100 (K)II.2.1.3 – Differences within 100 (K)I.2.1.1 – Combining & joining within 10 (F)I.2.1.2 – Comparing within 10 (F)I.2.1.3 – Sums within 20, with 10 as one addend (K)I.2.1.4 – Sums within 20 (P)I.2.2.2 – Differences within 20 (K)I.3.1.1 – Length (K – screen 2)I.3.1.2 – Weight (F)I.3.1.4 – Money (K – screen 2)I.3.2.1 – Triangles and rectangles (F)
<strong>Destination</strong> Math <strong>Mastering</strong> <strong>Skills</strong> & <strong>Concepts</strong> (<strong>MSC</strong>) Page 4 of 4AlignmentTEKS Grade 2 Math Objectives to <strong>Destination</strong> Math—<strong>MSC</strong> I-II-IIIK = Key lesson – supports the TEKS that the student must know and be able to demonstrate at this grade levelF = Foundational lesson – prerequisite concepts for TEKS that a student must know and be able to demonstrate at thisgrade levelP = Partially covered lesson – only addresses part of the TEKS listedA = Accelerated lesson – advanced and is appropriate for acceleration of this TEKSUnderlying Processes & Mathematical Tools.2.13B Relate informal language to mathematicallanguage and symbols.2.14 Justify his or her thinking using objects, words,pictures, numbers and technology.Course.Module.Unit.Session -- Session DescriptionI.2.1.1 – Combining & joining within 10 (F)I.2.2.2 – Differences within 20 (F)I.3.1.4 – Money (K – screen 2)II.2.2.2 – Skip counting to show multiplication (K)II.2.3.1 – Meaning of division (K)II.3.2.2 – Money (K)II.3.2.3 – Temperature (K)All sessions meet TEKS.