LM Guide THK - Industrial Technologies
LM Guide THK - Industrial Technologies
LM Guide THK - Industrial Technologies
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
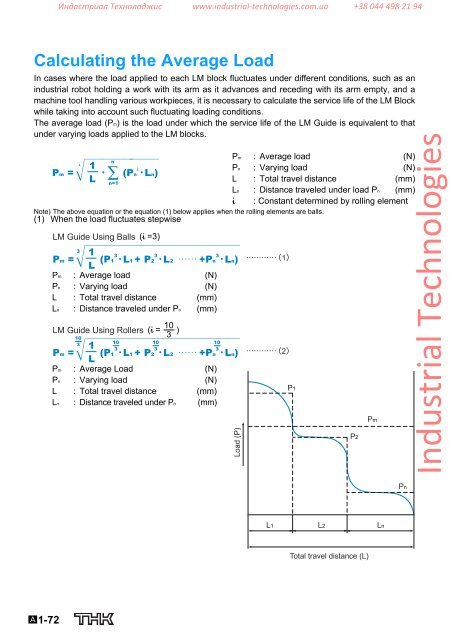
Индастриал Технолоджис www.industrial‐technologies.com.ua +38 044 498 21 94Calculating the Average LoadIn cases where the load applied to each <strong>LM</strong> block fluctuates under different conditions, such as anindustrial robot holding a work with its arm as it advances and receding with its arm empty, and amachine tool handling various workpieces, it is necessary to calculate the service life of the <strong>LM</strong> Blockwhile taking into account such fluctuating loading conditions.The average load (Pm) is the load under which the service life of the <strong>LM</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> is equivalent to thatunder varying loads applied to the <strong>LM</strong> blocks.Pm : Average load (N)ni 1Pn : Varying load (N)Pm = • ∑ (Pni •Ln)LL : Total travel distance (mm)n=1Ln : Distance traveled under load Pn (mm)i : Constant determined by rolling elementNote) The above equation or the equation (1) below applies when the rolling elements are balls.(1) When the load fluctuates stepwise<strong>LM</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> Using Balls (i =3)31 333Pm = (P1 •L1 + P2 •L2 ······ +Pn •Ln) 1LPm : Average load (N)Pn : Varying load (N)L : Total travel distance (mm)Ln : Distance traveled under Pn (mm)<strong>LM</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> Using RollersPm =1031L1010(i = )3333(P1 •L1 + P2 •L2 ······ +Pn •Ln)Pm : Average Load (N)Pn : Varying load (N)L : Total travel distance (mm)Ln : Distance traveled under Pn (mm)1010Load (P)2P1P2Pm<strong>Industrial</strong> <strong>Technologies</strong>PnL1 L2 LnTotal travel distance (L)A1-72