NEUTRALIZATION PROCESS OF ACID WELLS ... - Orkustofnun
NEUTRALIZATION PROCESS OF ACID WELLS ... - Orkustofnun
NEUTRALIZATION PROCESS OF ACID WELLS ... - Orkustofnun
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
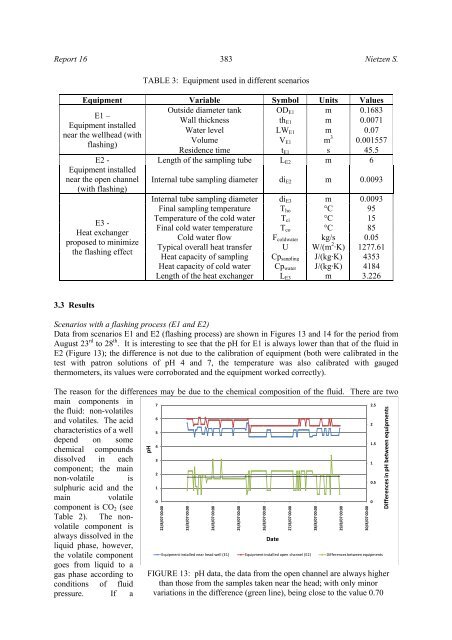
Report 16 383 Nietzen S.TABLE 3: Equipment used in different scenariosEquipment Variable Symbol Units ValuesOutside diameter tank OD E1 m 0.1683E1 –Wall thickness thEquipment installedE1 m 0.0071Water level LWnear the wellhead (withE1 m 0.07Volume Vflashing)E1 m 3 0.001557Residence time t E1 s 45.5E2 -Equipment installednear the open channel(with flashing)E3 -Heat exchangerproposed to minimizethe flashing effectLength of the sampling tube L E2 m 6Internal tube sampling diameter di E2 m 0.0093Internal tube sampling diameter di E3 m 0.0093Final sampling temperature T ho °C 95Temperature of the cold water T ci °C 15Final cold water temperature T co °C 85Cold water flow F coldwater kg/s 0.05Typical overall heat transfer U W/(m 2·K) 1277.61Heat capacity of sampling Cp sanpling J/(kg·K) 4353Heat capacity of cold water Cp water J/(kg·K) 4184Length of the heat exchanger L E3 m 3.2263.3 ResultsScenarios with a flashing process (E1 and E2)Data from scenarios E1 and E2 (flashing process) are shown in Figures 13 and 14 for the period fromAugust 23 rd to 28 th . It is interesting to see that the pH for E1 is always lower than that of the fluid inE2 (Figure 13); the difference is not due to the calibration of equipment (both were calibrated in thetest with patron solutions of pH 4 and 7, the temperature was also calibrated with gaugedthermometers, its values were corroborated and the equipment worked correctly).The reason for the differences may be due to the chemical composition of the fluid. There are twomain components inthe fluid: non-volatiles72.56and volatiles. The acidcharacteristics of a well5depend on some4chemical compoundsdissolved in each3component; the main2non-volatile issulphuric acid and the121.510.5main volatilecomponent is CO 2 (seeTable 2). The nonvolatilecomponent is00always dissolved in theliquid phase, however,the volatile componentgoes from liquid to aEquipment installed near head well (E1)DateEquipment installed open channel (E2) Differences between equipmentsgas phase according to FIGURE 13: pH data, the data from the open channel are always higherconditions of fluid than those from the samples taken near the head; with only minorpressure. If a variations in the difference (green line), being close to the value 0.70pH22/8/07 00:0023/8/07 00:0024/8/07 00:0025/8/07 00:0026/8/07 00:0027/8/07 00:0028/8/07 00:0029/8/07 00:0030/8/07 00:00Differences in pH between equipments