VIRAL INFECTION - Faculty of Medicine
VIRAL INFECTION - Faculty of Medicine VIRAL INFECTION - Faculty of Medicine
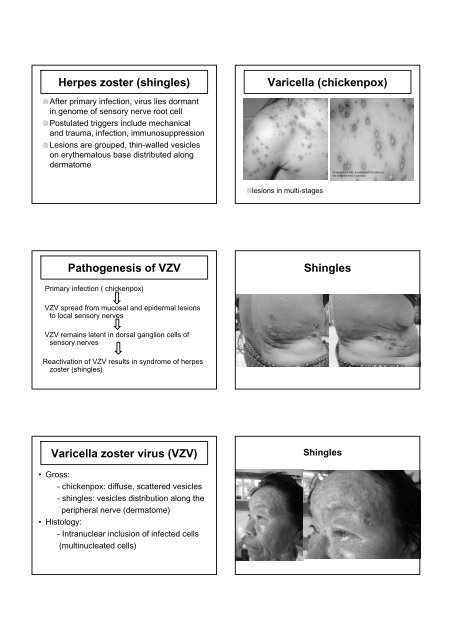
Herpes zoster (shingles)Varicella (chickenpox)After primary infection, virus lies dormantin genome of sensory nerve root cellPostulated triggers include mechanicaland trauma, infection, immunosuppressionLesions are grouped, thin-walled vesicleson erythematous base distributed alongdermatomelesions in multi-stagesPathogenesis of VZVShinglesPrimary infection ( chickenpox)VZV spread from mucosal and epidermal lesionsto local sensory nervesVZV remains latent in dorsal ganglion cells ofsensory nervesReactivation of VZV results in syndrome of herpeszoster (shingles)Varicella zoster virus (VZV)Shingles• Gross:- chickenpox: diffuse, scattered vesicles- shingles: vesicles distribution along theperipheral nerve (dermatome)• Histology:- Intranuclear inclusion of infected cells(multinucleated cells)
VZVHand-foot-and-mouth diseaseIntranuclear inclusionCoxsackie Virus• Type A– Causes herpangina and hand- foot-and mouthdisease• Type B– Causes Pluerodynia• Both– Causes meningitis, myocarditis andpericarditis, also can cause juvenile diabetes• Coxsackie Virus A• Common in child• Infection of the throat• Causes red-ringedblisters or ulcers ontonsils, roof of mouthand tongueHerpanginaHand-Foot-and Mouth diseaseCoxsackie Virus A, B or Enterovirus71Common in childProdome : low-grade fever, malaise, soremouth, anorexia1-2 days later :- oral lesions (tongue, throat, gum) : shallow,yellow ulcers surrounded by red halos- painful red blister on hand and footRx : supportive treatmentSystemic withhematopoietic disorder
- Page 3: Influenza Antigenic Changes• Anti
- Page 10 and 11: Measles virus• Clinical:- conjunc
- Page 12 and 13: Recurrent herpes simplex infectionH
- Page 16 and 17: Cytomegalovirus (CMV)• Produce a
- Page 18 and 19: Human Immunodeficiency Virus(HIV)
- Page 20 and 21: Human papilloma virus (HPV)• Most
- Page 22 and 23: Intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies(m
Herpes zoster (shingles)Varicella (chickenpox)After primary infection, virus lies dormantin genome <strong>of</strong> sensory nerve root cellPostulated triggers include mechanicaland trauma, infection, immunosuppressionLesions are grouped, thin-walled vesicleson erythematous base distributed alongdermatomelesions in multi-stagesPathogenesis <strong>of</strong> VZVShinglesPrimary infection ( chickenpox)VZV spread from mucosal and epidermal lesionsto local sensory nervesVZV remains latent in dorsal ganglion cells <strong>of</strong>sensory nervesReactivation <strong>of</strong> VZV results in syndrome <strong>of</strong> herpeszoster (shingles)Varicella zoster virus (VZV)Shingles• Gross:- chickenpox: diffuse, scattered vesicles- shingles: vesicles distribution along theperipheral nerve (dermatome)• Histology:- Intranuclear inclusion <strong>of</strong> infected cells(multinucleated cells)