Letterland Common Core State Standards Correlation
Letterland Common Core State Standards Correlation
Letterland Common Core State Standards Correlation
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
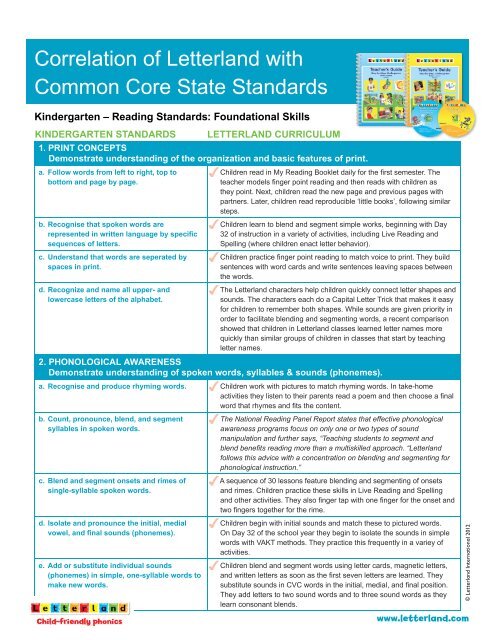
<strong>Correlation</strong> of <strong>Letterland</strong> with<strong>Common</strong> <strong>Core</strong> <strong>State</strong> <strong>Standards</strong>Kindergarten – Reading <strong>Standards</strong>: Foundational SkillsKINDERGARTEN STANDARDSLETTERLAND CURRICULUM1. PRINT CONCEPTSDemonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print.a. Follow words from left to right, top tobottom and page by page.b. Recognise that spoken words arerepresented in written language by specificsequences of letters.c. Understand that words are seperated byspaces in print.d. Recognize and name all upper- andlowercase letters of the alphabet.Children read in My Reading Booklet daily for the fi rst semester. Theteacher models fi nger point reading and then reads with children asthey point. Next, children read the new page and previous pages withpartners. Later, children read reproducible ‘little books’, following similarsteps.Children learn to blend and segment simple works, beginning with Day32 of instruction in a variety of activities, including Live Reading andSpelling (where children enact letter behavior).Children practice fi nger point reading to match voice to print. They buildsentences with word cards and write sentences leaving spaces betweenthe words.The <strong>Letterland</strong> characters help children quickly connect letter shapes andsounds. The characters each do a Capital Letter Trick that makes it easyfor children to remember both shapes. While sounds are given priority inorder to facilitate blending and segmenting words, a recent comparisonshowed that children in <strong>Letterland</strong> classes learned letter names morequickly than similar groups of children in classes that start by teachingletter names.2. PHONOLOGICAL AWARENESSDemonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables & sounds (phonemes).a. Recognise and produce rhyming words. Children work with pictures to match rhyming words. In take-homeactivities they listen to their parents read a poem and then choose a fi nalword that rhymes and fi ts the content.b. Count, pronounce, blend, and segmentsyllables in spoken words.c. Blend and segment onsets and rimes ofsingle-syllable spoken words.d. Isolate and pronounce the initial, medialvowel, and final sounds (phonemes).e. Add or substitute individual sounds(phonemes) in simple, one-syllable words tomake new words.The National Reading Panel Report states that effective phonologicalawareness programs focus on only one or two types of soundmanipulation and further says, “Teaching students to segment andblend benefi ts reading more than a multiskilled approach. “<strong>Letterland</strong>follows this advice with a concentration on blending and segmenting forphonological instruction.”A sequence of 30 lessons feature blending and segmenting of onsetsand rimes. Children practice these skills in Live Reading and Spellingand other activities. They also fi nger tap with one fi nger for the onset andtwo fi ngers together for the rime.Children begin with initial sounds and match these to pictured words.On Day 32 of the school year they begin to isolate the sounds in simplewords with VAKT methods. They practice this frequently in a variey ofactivities.Children blend and segment words using letter cards, magnetic letters,and written letters as soon as the fi rst seven letters are learned. Theysubstitute sounds in CVC words in the initial, medial, and fi nal position.They add letters to two sound words and to three sound words as theylearn consonant blends.© <strong>Letterland</strong> International 2012www.letterland.com
<strong>Correlation</strong> of <strong>Letterland</strong> with<strong>Common</strong> <strong>Core</strong> <strong>State</strong> <strong>Standards</strong>Kindergarten – Reading <strong>Standards</strong>: Foundational SkillsKINDERGARTEN STANDARDSLETTERLAND CURRICULUM3. PHONICS AND WORD RECOGNITIONKnow and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.a. Demonstrate basic knowledge of one-to-oneletter-sound correspondences by producingthe primary or many of the most frequentsound for each consonant.b. Associate the long and short sounds withcommon spellings (graphemes) for the fivemajor vowels.c. Read common high-frequency words bysight (e.g., the, of, to, you, she)d. Distinguish between similarly spelled wordsby identifying the sounds of the letters thatdiffer.4. FLUENCYRead emergent-reader texts with purpose andunderstanding.Children learn the most common sounds of all 26 letters within the fi rstfour weeks of school. They review these sounds, a few common variantsounds and high frequency digraphs daily. They also use these sounds inreading and spelling words.The short vowels are emphasized in blending and segmenting in earlylessons (e.g. cap, bed, hug) but long vowels are briefl y introduced aswell. Long Vowel spellings are learned later in the year including opensyllables (we, go), Magic e (cake, hide), and Vowel Men Out Walking(tree, boat).Twenty fi ve high-frequency words are learned by tracing the letters whilespelling aloud and by frequent use in context.Children sound out words that other children form with Live Reading orthat the teacher forms with letters. Frequently words are changed byone letter for children to sound out again. Spelling is handled in similaractivities.Children read and reread brief emergent reader text daily in fi rstsemester in My <strong>Letterland</strong> Reading Booklet. In second semester thereare copy masters for 12 booklets with predictable/decodable text andtwo plays. Children learn the words and build sentences that culminatein reading these booklets. They also practice reading word cards withincreasing fl uency in an activity called Tractors, Trains, Plains, andHelicopters.As of April 2011 the <strong>Common</strong> <strong>Core</strong> <strong>Standards</strong> for English Language Arts have been adopted by 42 of the 50 United <strong>State</strong>s. Thefull listing of the standards and more information can be found at www.corestandards.org/. <strong>Letterland</strong> is designed primarily for theteaching of Foundational Skills as described in the section of the standards listed above. In addition much of the literature thataccompanies the <strong>Letterland</strong> program is suitable as a part of the teaching and practice of the standards for comprehension entitled,“Reading <strong>Standards</strong> Literature K-5.”Building Sentences Long Vowels/Magic e High FrequencyWordsMy <strong>Letterland</strong>Reading BookletTractors, Trains,Planes & Helicopters© <strong>Letterland</strong> International 2012www.letterland.com
<strong>Correlation</strong> of <strong>Letterland</strong> with<strong>Common</strong> <strong>Core</strong> <strong>State</strong> <strong>Standards</strong>Grade One – Reading <strong>Standards</strong>: Foundational SkillsGRADE ONE STANDARDSLETTERLAND CURRICULUM1. PRINT CONCEPTSDemonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print.a. Recognize the distinguishing features ofa sentence (e.g., first word, capitalization,ending punctuation).Children write dictated sentences and original sentences with words fromeach Unit. They receive feedback on conventions from peers and theteacher, and they correct as needed.2. PHONOLOGICAL AWARENESSDemonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables & sounds (phonemes).a. Distinguish long from short vowel sounds inspoken single-syllable words.b. Orally produce single-syllable words byblending sounds (phonemes), includingconsonant blends.c. Isolate and pronounce initial, medial vowel,and final sounds (phonemes) in spokensingle syllable words.Children segment words to identify vowel sounds and match them toshort vowel <strong>Letterland</strong>ers or to long vowels, represented by fi ve VowelMen.Children blend sounds in Pocket Chart Reading activities and in LiveReading. They use multi-sensory ‘fi nger-sounding’ in these exercises andwhen they encounter an unknown word.Children use multi-sensory fi nger sounding to segment words intophonemes in various word building reading and spelling activities daily.d. Segment spoken single-syllable wordsIn Live Spelling, individual word building and various spelling activities,into their complete sequence of individual children segment words of two to fi ve sounds every day.sounds (phonemes).3. PHONICS AND WORD RECOGNITIONKnow and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.a. Know the spelling-sound correspondencesfor common consonant digraphs.b. Decode regularly spelled one-syllablewords.c. Know final -e and common vowel teamconventions for representing long vowelsounds.Children learn the sounds and spellings of consonant digraphs with<strong>Letterland</strong> story logic, songs and pictograms. To ensure mastery theypractice the sounds in isolation and in words.Children learn to decode regular one-syllable words in a systematicsequence supported by assessments that help teachers pace instructionfor maximum success.Appealing and memorable stories, songs, and pictograms engagechildren in active involvement in learning these vowel patterns. Variedpractice activities ensure retention and application in reading andspelling.Nate said,“Where didyou go?”Writing Sentences Identifying Vowel Sounds Finger SoundingLive Spelling Consonant Digraphs© <strong>Letterland</strong> International 2012www.letterland.com
<strong>Correlation</strong> of <strong>Letterland</strong> with<strong>Common</strong> <strong>Core</strong> <strong>State</strong> <strong>Standards</strong>Grade One – Reading <strong>Standards</strong>: Foundational SkillsGRADE ONE STANDARDSLETTERLAND CURRICULUM3. PHONICS AND WORD RECOGNITIONKnow and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.a. Use knowledge that every syllable musthave a vowel sound to determine thenumber of syllables in a printed word.b. Decode two-syllable words followingbasic patterns by breaking the words intosyllables.Limited practice with two syllable words is begun in Grade One andexpanded in Grade Two.<strong>Common</strong> two syllable patterns such as fi nal er and fi nal y with the long esound are taught in Grade One. For most two-syllable words, the teacherindicates the syllable division and children decode and combine thesyllables. Extensive study of multi-syllable words is continued throughoutGrade Two.c. Read words with inflectional endings. Infl exion endings (-s, -ing, -ed) are learned with <strong>Letterland</strong> story logicand engaging practice activities for reading and spelling. Children learnto read and spell the words by recognizing the base word and adding thesuffi x.d. Recognize and read grade-appropriateirregularly spelled wordsEach weekly Unit introduces 2-4 irregular, high-frequency words alongwith 20-30 decodable words. These words are learned with the multisensory‘3-by-3 Strategy.’3. PHONICS AND WORD RECOGNITIONKnow and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.a. Read on-level text with purpose andunderstandingb. Read on-level text orally with accuracy,appropriate rate, and expression onsuccessive readings.c. Use context to confirm or self-correct wordrecognition and understanding, rereading asnecessary.Each of the 45 Units includes an engaging decodable story that canby copied for each student. Teachers guide children in comprehensionactivities with each story.Children reread the stories with choral reading and partner reading,building rate, accuracy and expression. They also build automatic wordrecognition through varied activities including charting their rate onreading weekly word lists.Unit stories provide a rich context for coaching word recognitionstrategies and for practicing self-correction and reading for meaning.As of April 2011 the <strong>Common</strong> <strong>Core</strong> <strong>Standards</strong> for English Language Arts have been adopted by 42 of the 50 United <strong>State</strong>s. Thefull listing of the standards and more information can be found at www.corestandards.org/. <strong>Letterland</strong> is designed primarily for theteaching of Foundational Skills as described in the section of the standards listed above. In addition much of the literature thataccompanies the <strong>Letterland</strong> program is suitable as a part of the teaching and practice of the standards for comprehension entitled,“Reading <strong>Standards</strong> Literature K-5.”Two-syllable Words High-frequencyInflexion Endings DecodableWordsStoriesWeeklyWord Lists© <strong>Letterland</strong> International 2012www.letterland.com