Smart Grids Roadmap - Smart Grid Sherpa
Smart Grids Roadmap - Smart Grid Sherpa
Smart Grids Roadmap - Smart Grid Sherpa
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
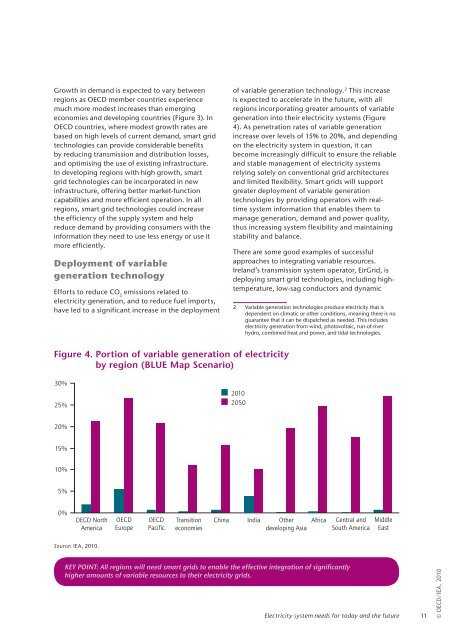
Growth in demand is expected to vary betweenregions as OECD member countries experiencemuch more modest increases than emergingeconomies and developing countries (Figure 3). InOECD countries, where modest growth rates arebased on high levels of current demand, smart gridtechnologies can provide considerable benefitsby reducing transmission and distribution losses,and optimising the use of existing infrastructure.In developing regions with high growth, smartgrid technologies can be incorporated in newinfrastructure, offering better market-functioncapabilities and more efficient operation. In allregions, smart grid technologies could increasethe efficiency of the supply system and helpreduce demand by providing consumers with theinformation they need to use less energy or use itmore efficiently.Deployment of variablegeneration technologyEfforts to reduce CO 2emissions related toelectricity generation, and to reduce fuel imports,have led to a significant increase in the deploymentof variable generation technology. 2 This increaseis expected to accelerate in the future, with allregions incorporating greater amounts of variablegeneration into their electricity systems (Figure4). As penetration rates of variable generationincrease over levels of 15% to 20%, and dependingon the electricity system in question, it canbecome increasingly difficult to ensure the reliableand stable management of electricity systemsrelying solely on conventional grid architecturesand limited flexibility. <strong>Smart</strong> grids will supportgreater deployment of variable generationtechnologies by providing operators with realtimesystem information that enables them tomanage generation, demand and power quality,thus increasing system flexibility and maintainingstability and balance.There are some good examples of successfulapproaches to integrating variable resources.Ireland’s transmission system operator, Eir<strong>Grid</strong>, isdeploying smart grid technologies, including hightemperature,low-sag conductors and dynamic2 Variable generation technologies produce electricity that isdependent on climatic or other conditions, meaning there is noguarantee that it can be dispatched as needed. This includeselectricity generation from wind, photovoltaic, run-of-riverhydro, combined heat and power, and tidal technologies.Figure 4. Portion of variable generation of electricityby region (BLUE Map Scenario)30%25%2010205020%15%10%5%0%OECD NorthAmericaOECDEuropeOECDPacificTransitioneconomiesChina India Otherdeveloping AsiaAfricaCentral andSouth AmericaMiddleEastSource: IEA, 2010.KEY POINT: All regions will need smart grids to enable the effective integration of significantlyhigher amounts of variable resources to their electricity grids.Electricity system needs for today and the future11© OECD/IEA, 2010