Manual for Refrigeration Servicing Technicians - UNEP - Division of ...
Manual for Refrigeration Servicing Technicians - UNEP - Division of ...
Manual for Refrigeration Servicing Technicians - UNEP - Division of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2<br />
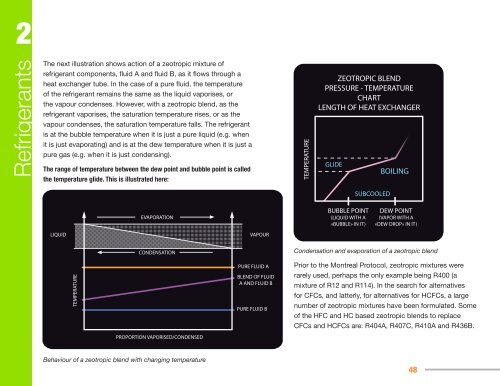
CHAPITRE The 2 next illustration shows action <strong>of</strong> a zeotropic mixture <strong>of</strong><br />
PAGE 16<br />
refrigerant components, fluid A and fluid B, as it flows through a<br />
heat exchanger tube. In the case <strong>of</strong> a pure fluid, the temperature<br />
<strong>of</strong> the refrigerant remains the same as the liquid vaporises, or<br />
the vapour condenses. However, with a zeotropic blend, as the<br />
refrigerant vaporises, the saturation temperature rises, or as the<br />
vapour condenses, the saturation temperature falls. The refrigerant<br />
is at the bubble temperature when it is just a pure liquid (e.g. when<br />
it is just evaporating) and is at the dew temperature when it is just a<br />
pure gas (e.g. when it is just condensing).<br />
Refrigerants<br />
The range <strong>of</strong> temperature between the dew point and bubble point is called<br />
the temperature glide. This is illustrated here:<br />
TEMPERATURE<br />
EVAPORATION<br />
LIQUID VAPOUR<br />
CONDENSATION<br />
PROPORTION VAPORISED/CONDENSED<br />
Behaviour <strong>of</strong> a zeotropic blend with changing temperature<br />
PURE FLUID A<br />
BLEND OF FLUID<br />
A AND FLUID B<br />
PURE FLUID B<br />
DONE<br />
TEMPERATURE<br />
ZEOTROPIC BLEND<br />
PRESSURE - TEMPERATURE<br />
CHART<br />
LENGTH OF HEAT EXCHANGER<br />
GLIDE<br />
BUBBLE POINT<br />
(LIQUID WITH A<br />
«BUBBLE» IN IT)<br />
SUBCOOLED<br />
BOILING<br />
DEW POINT<br />
(VAPOR WITH A<br />
«DEW DROP» IN IT)<br />
Condensation and evaporation <strong>of</strong> a zeotropic blend<br />
Prior to the Montreal Protocol, zeotropic mixtures were<br />
rarely used, perhaps the only example being R400 (a<br />
mixture <strong>of</strong> R12 and R114). In the search <strong>for</strong> alternatives<br />
<strong>for</strong> CFCs, and latterly, <strong>for</strong> alternatives <strong>for</strong> HCFCs, a large<br />
number <strong>of</strong> zeotropic mixtures have been <strong>for</strong>mulated. Some<br />
<strong>of</strong> the HFC and HC based zeotropic blends to replace<br />
CFCs and HCFCs are: R404A, R407C, R410A and R436B.<br />
48