II.1 Programming in MATLAB Getting Started Graphing
II.1 Programming in MATLAB Getting Started Graphing
II.1 Programming in MATLAB Getting Started Graphing
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
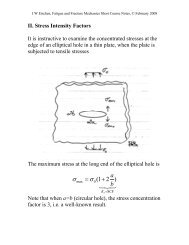
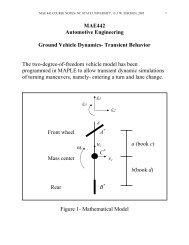
ArraysNext, look over the second template shown <strong>in</strong> Table 2.This program determ<strong>in</strong>es the force reactions act<strong>in</strong>g on the barshown <strong>in</strong> Fig. A2 – 2. The reactions are found by solv<strong>in</strong>g a setof three l<strong>in</strong>ear algebraic equations. The unknowns <strong>in</strong> thisproblem are⎛ F ⎞⎜ ⎟x =⎜N A⎟,⎝ N B ⎠where F is the friction force at A, N A is the normal force at A,and N B is the normal force at B. Create the M-file namedtarray.m and type <strong>in</strong> Table 2. Notice how the program def<strong>in</strong>eselements of vectors and matrices (arrays). Also notice howthese arrays are manipulated us<strong>in</strong>g vector algebra. In thisprogram, a set of l<strong>in</strong>ear algebraic equations of the form Ax = bis solved by first calculat<strong>in</strong>g A -1 and then by calculat<strong>in</strong>g thesolution x = A -1 b.Next, save and close tarray.m, go to the commandw<strong>in</strong>dow, typetarrayand hit return. The command w<strong>in</strong>dow diplays b, A, and thesolution x. You’ll see that F = 31.6987 lb, N A = 68.3013 lb, andN B = 44.8288 lb.4