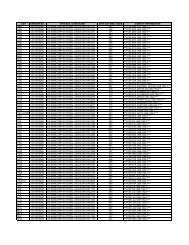
Chart of Accounts - 07/01/13 and Later - General Accounting Office
Chart of Accounts - 07/01/13 and Later - General Accounting Office
Chart of Accounts - 07/01/13 and Later - General Accounting Office
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PARTARIZONA ACCOUNTING MANUALAND SECTIONIV-A-1PAGE2DATE<strong>07</strong>/<strong>01</strong>/<strong>13</strong>SUBJECTCOMPTROLLER GENERAL LEDGERFY 14 CHART OF ACCOUNTSDefinitions (Cont’d)Contra accounts cause a reduction in the amounts that would be otherwise reported. For example,net revenue is gross revenue minus returns, allowances, <strong>and</strong> discounts. The net realizable value <strong>of</strong>accounts receivable is the accounts receivable balance minus the allowance for doubtful accounts.Control Account: A control account is a summary account in the general ledger. The details thatsupport the balance in the summary account are contained in a subsidiary ledger or table (ledgeroutside <strong>of</strong> the general ledger).The purpose <strong>of</strong> the control account is to keep the general ledger free <strong>of</strong> details, yet have the correctbalance for the financial statements. For example, the <strong>Accounts</strong> Receivable account in the generalledger could be a control account. If it were a control account, the company would merely update theaccount with a few amounts, such as total collections for the day, total sales on account for the day,total returns <strong>and</strong> allowances for the day, etc. The details on each customer <strong>and</strong> each transactionwould not be recorded in the <strong>Accounts</strong> Receivable control account in the general ledger. Rather,these details <strong>of</strong> the accounts receivable activity will be in the <strong>Accounts</strong> Receivable Subsidiary Ledger.GAAP <strong>General</strong> Ledger Account Class: These are used to group <strong>General</strong> Ledger <strong>Accounts</strong>. <strong>General</strong>Ledger Account Classes will appear as line items on the GAAP basis financial statements. Examplesinclude Fund Cash Account, <strong>Accounts</strong> Receivable, Warrants Payable <strong>and</strong> Other.GAAP <strong>General</strong> Ledger Account Category: These are used to group GAAP <strong>General</strong> Ledger AccountClasses. These categories are the highest level <strong>of</strong> general ledger account structure required forstatewide GAAP reporting. Refer to the list below.GAAP <strong>General</strong> Ledger Account Category1 Cash2 Current Receivables Treasurer3 Short-term Investments Treasurer4 Current Receivables6 Other Current Receivables8 Fixed Assets9 Other Assets12 Current Payables<strong>13</strong> Accrued Wages & Related Liabilities16 Other Current Liabilities17 Long-term Liabilities20 Treasurer Liabilities30 Fund Balance<strong>General</strong> Ledger Account: A general ledger account identifies the nature <strong>of</strong> financial activities <strong>and</strong>balances. The general ledger includes both balance sheet <strong>and</strong> operating accounts (Comptroller<strong>General</strong> Ledger <strong>Accounts</strong>) <strong>and</strong> operating accounts (Comptroller Object <strong>Accounts</strong>).