chap06 - Learning Services Home
chap06 - Learning Services Home
chap06 - Learning Services Home
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
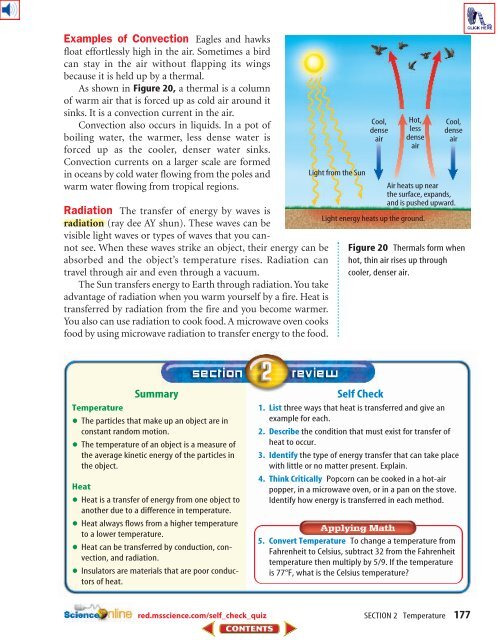
Examples of Convection Eagles and hawksfloat effortlessly high in the air. Sometimes a birdcan stay in the air without flapping its wingsbecause it is held up by a thermal.As shown in Figure 20, a thermal is a columnof warm air that is forced up as cold air around itsinks. It is a convection current in the air.Convection also occurs in liquids. In a pot ofboiling water, the warmer, less dense water isforced up as the cooler, denser water sinks.Convection currents on a larger scale are formedin oceans by cold water flowing from the poles andwarm water flowing from tropical regions.Radiation The transfer of energy by waves isradiation (ray dee AY shun). These waves can bevisible light waves or types of waves that you cannotsee. When these waves strike an object, their energy can beabsorbed and the object’s temperature rises. Radiation cantravel through air and even through a vacuum.The Sun transfers energy to Earth through radiation. You takeadvantage of radiation when you warm yourself by a fire. Heat istransferred by radiation from the fire and you become warmer.You also can use radiation to cook food. A microwave oven cooksfood by using microwave radiation to transfer energy to the food.Light from the SunCool,denseairHot,lessdenseairLight energy heats up the ground.Cool,denseairAir heats up nearthe surface, expands,and is pushed upward.Figure 20 Thermals form whenhot, thin air rises up throughcooler, denser air.SummaryTemperature•The particles that make up an object are in•constant random motion.The temperature of an object is a measure ofthe average kinetic energy of the particles inthe object.•HeatHeat is a transfer of energy from one object to•another due to a difference in temperature.Heat always flows from a higher temperature•to a lower temperature.Heat can be transferred by conduction, convection,and radiation.•Insulators are materials that are poor conductorsof heat.Self Check1. List three ways that heat is transferred and give anexample for each.2. Describe the condition that must exist for transfer ofheat to occur.3. Identify the type of energy transfer that can take placewith little or no matter present. Explain.4. Think Critically Popcorn can be cooked in a hot-airpopper, in a microwave oven, or in a pan on the stove.Identify how energy is transferred in each method.5. Convert Temperature To change a temperature fromFahrenheit to Celsius, subtract 32 from the Fahrenheittemperature then multiply by 5/9. If the temperatureis 77°F, what is the Celsius temperature?red.msscience.com/self_check_quizSECTION 2 Temperature 177