Smart Grid Solutions Guide - Maxim
Smart Grid Solutions Guide - Maxim
Smart Grid Solutions Guide - Maxim
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
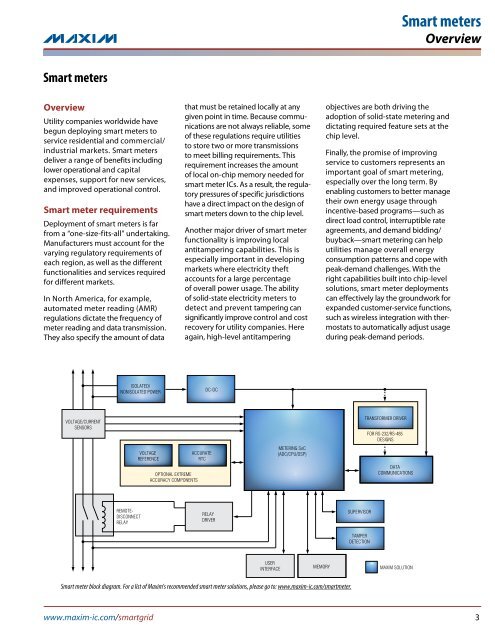
<strong>Smart</strong> metersOverview<strong>Smart</strong> metersOverviewUtility companies worldwide havebegun deploying smart meters toservice residential and commercial/industrial markets. <strong>Smart</strong> metersdeliver a range of benefits includinglower operational and capitalexpenses, support for new services,and improved operational control.<strong>Smart</strong> meter requirementsDeployment of smart meters is farfrom a “one-size-fits-all” undertaking.Manufacturers must account for thevarying regulatory requirements ofeach region, as well as the differentfunctionalities and services requiredfor different markets.In North America, for example,automated meter reading (AMR)regulations dictate the frequency ofmeter reading and data transmission.They also specify the amount of datathat must be retained locally at anygiven point in time. Because communicationsare not always reliable, someof these regulations require utilitiesto store two or more transmissionsto meet billing requirements. Thisrequirement increases the amountof local on-chip memory needed forsmart meter ICs. As a result, the regulatorypressures of specific jurisdictionshave a direct impact on the design ofsmart meters down to the chip level.Another major driver of smart meterfunctionality is improving localantitampering capabilities. This isespecially important in developingmarkets where electricity theftaccounts for a large percentageof overall power usage. The abilityof solid-state electricity meters todetect and prevent tampering cansignificantly improve control and costrecovery for utility companies. Hereagain, high-level antitamperingobjectives are both driving theadoption of solid-state metering anddictating required feature sets at thechip level.Finally, the promise of improvingservice to customers represents animportant goal of smart metering,especially over the long term. Byenabling customers to better managetheir own energy usage throughincentive-based programs—such asdirect load control, interruptible rateagreements, and demand bidding/buyback—smart metering can helputilities manage overall energyconsumption patterns and cope withpeak-demand challenges. With theright capabilities built into chip-levelsolutions, smart meter deploymentscan effectively lay the groundwork forexpanded customer-service functions,such as wireless integration with thermostatsto automatically adjust usageduring peak-demand periods.ISOLATED/NONISOLATED POWERDC-DCVOLTAGE/CURRENTSENSORSVOLTAGEREFERENCEOPTIONAL EXTREMEACCURACY COMPONENTSACCURATERTCMETERING SoC(ADC/CPU/DSP)TRANSFORMER DRIVERFOR RS-232/RS-485DESIGNSDATACOMMUNICATIONSREMOTE-DISCONNECTRELAYRELAYDRIVERSUPERVISORTAMPERDETECTIONUSERINTERFACEMEMORYMAXIM SOLUTION<strong>Smart</strong> meter block diagram. For a list of <strong>Maxim</strong>'s recommended smart meter solutions, please go to: www.maxim-ic.com/smartmeter.www.maxim-ic.com/smartgrid 3