Chapter 7.3 & 7.4 Study Guide Answers
Chapter 7.3 & 7.4 Study Guide Answers
Chapter 7.3 & 7.4 Study Guide Answers
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
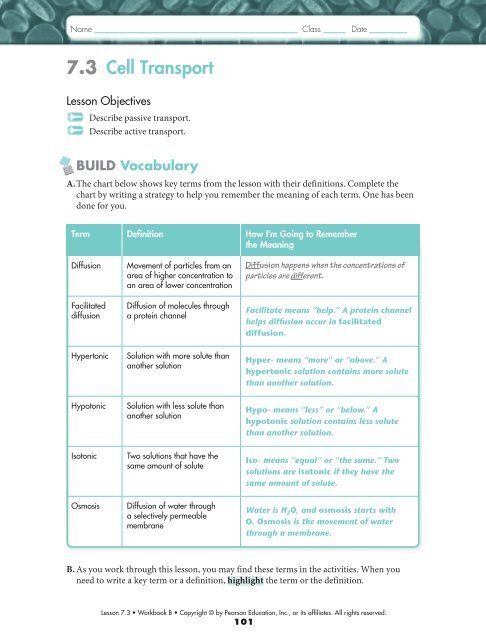
Name Class Date<strong>7.3</strong> Cell TransportLesson ObjectivesDescribe passive transport.Describe active transport.BUILD VocabularyA. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions. Complete thechart by writing a strategy to help you remember the meaning of each term. One has beendone for you.Term Definition How I’m Going to Rememberthe MeaningDiffusionFacilitateddiffusionMovement of particles from anarea of higher concentration toan area of lower concentrationDiffusion of molecules througha protein channelDiffusion happens when the concentrations ofparticles are different.Facilitate means “help.” A protein channelhelps diffusion occur in facilitateddiffusion.HypertonicSolution with more solute thananother solutionHyper- means “more” or “above.” Ahypertonic solution contains more solutethan another solution.HypotonicSolution with less solute thananother solutionHypo- means “less” or “below.” Ahypotonic solution contains less solutethan another solution.IsotonicTwo solutions that have thesame amount of soluteIso- means “equal” or “the same.” Twosolutions are isotonic if they have thesame amount of solute.OsmosisDiffusion of water througha selectively permeablemembraneWater is H 2 O, and osmosis starts withO. Osmosis is the movement of waterthrough a membrane.B. As you work through this lesson, you may find these terms in the activities. When youneed to write a key term or a definition, highlight the term or the definition.Lesson <strong>7.3</strong> • Workbook B • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.101
Name Class DateBUILD UnderstandingCompare/Contrast Table Use a compare/contrast table when you want to see thesimilarities and differences between two or more objects or processes. Select words or phrasesfrom the box to complete the table comparing passive and active transport.diffusion energy required exocytosis osmosisendocytosis energy not required facilitated diffusion protein pumpsPassive Transportdiffusionenergy not requiredfacilitated diffusionosmosisActive Transportendocytosisenergy requiredexocytosisprotein pumpsPassive TransportDiffusion is the movement of particlesfrom an area of high concentration toan area of low concentration. Osmosisis the diffusion of water through aselectively permeable membrane.<strong>Study</strong> the beakers at the right. Thearrows between beakers tell youwhat process is occurring.1. In the beakers on the right,draw the result of the describedprocess. Draw changes in waterlevels. Draw changes in the numberof solute particles. Remember todraw on both sides of themembrane.2. Look at the top left beaker. Whatwould happen if the membrane didnot allow water or solute particlesto pass through it?watersoluteparticlesmembraneDiffusionofSoluteParticlesnumber of solute particlesshould be the same on bothsides of the membraneOsmosisnumber of solute particles doesnot change, just level of watersolute particle movementwater movementThe solutions would stay the same. Neither water nor solute particles would movethrough the membrane.Lesson <strong>7.3</strong> • Workbook B • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.102
Name Class DateActive TransportFacilitated diffusion takes place when a substance diffuses across the cell membrane througha protein channel. Active transport takes place when the cell uses energy to carry a substanceacross the cell membrane against a concentration difference.Follow the directions.1. Label each diagram as either facilitated diffusion or active transport.facilitated diffusionGlucose moleculesactive transportMolecule tobe carriedEnergyMoleculebeing carriedAnswer the questions. Circle the correct answer.2. Which process can move molecules from a lower concentration solution on one side ofthe membrane to a higher concentration solution on the other side?active transportfacilitated diffusion3. Which process does not require energy?active transportfacilitated diffusion4. What does the word facilitated mean in facilitated diffusion ?hinderedhelpedLesson <strong>7.3</strong> • Workbook B • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.103
Name Class Date<strong>7.4</strong> Homeostasis and CellsLesson ObjectivesExplain how unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis.Explain how multicellular organisms maintain homeostasis.Lesson SummaryThe Cell as an Organism Sometimes a single cell is an organism. Single-celledorganisms must be able to carry out all the functions necessary for life.▶ Unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis, relatively constant internal conditions, bygrowing, responding to the environment, transforming energy, and reproducing.▶ Unicellular organisms include both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.▶ Unicellular organisms play many important roles in their environments.Multicellular Life Cells of multicellular organisms are interdependent and specialized.▶ The cells of multicellular organisms become specialized for particular tasks andcommunicate with one another to maintain homeostasis.▶ Specialized cells in multicellular organisms are organized into groups.• A tissue is a group of similar cells that performs a particular function.• An organ is a group of tissues working together to perform an essential task.• An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function.▶ The cells of multicellular organisms communicate with one another by means of chemicalsignals that are passed from one cell to another.• Certain cells form connections, or cellular junctions, to neighboring cells. Some of thesejunctions hold cells together firmly.• Other cells allow small molecules carrying chemical signals to pass directly from one cellto the next.• To respond to a chemical signal, a cell must have a receptor to which the signalingmolecule can bind.The Cell as an OrganismFor Questions 1–5, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words.1. The term homeostasis refers to the relatively constant internal physical and chemicalstate of a living cell.2. Unicellular prokaryotes, called bacteria , are adapted to living in a remarkablenumber of different places.3. Some unicellular eukaryotes, called algae , contain chloroplasts.4. Yeasts are unicellular fungi , which are eukaryotes.5. Other unicellular eukaryotes include protozoans and algae.Lesson <strong>7.4</strong> • Workbook A • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.109
Name Class Date11. The Venn diagram below consists of four concentric circles. Complete the diagram toshow the relationships among four levels of organization of life. Use the terms cells, organ,organ system, and tissue.CellsTissueOrganOrgan system12. Starting with the outermost circle of the diagram, explain how each level is related to thenext level within each circle.Organ systems are made of one or more organs. Organs are made up of one or moretissues. Tissues are made up of many cells with similar shapes and functions.13. What is the name of the areas that hold adjacent cells together and enable them tocommunicate?Cellular junctions14. On the Venn diagram above, where would you add a circle that represents the organismlevel of life? Where would you add a circle that represents another organ of the sameorgan system?A circle that represents the organism level of life should be drawn outside of theoutermost circle for an organ system. A circle that represents another organ of thesame organ system would be drawn within the organ system circle but would beseparate from the series of circles that represent the organs already shown in theVenn diagram.Lesson <strong>7.4</strong> • Workbook A • Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.111








![8.3 Rational Functions and Their Graphs - [x] Remove frame](https://img.yumpu.com/46677280/1/190x146/83-rational-functions-and-their-graphs-x-remove-frame.jpg?quality=85)