Grade 2 - Coppell Independent School District
Grade 2 - Coppell Independent School District
Grade 2 - Coppell Independent School District
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
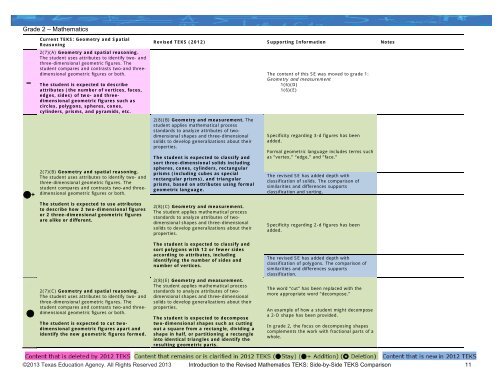
<strong>Grade</strong> 2 – Mathematics–+Current TEKS: Geometry and SpatialReasoning2(7)(A) Geometry and spatial reasoning.The student uses attributes to identify two- andthree-dimensional geometric figures. Thestudent compares and contrasts two-and threedimensionalgeometric figures or both.The student is expected to describeattributes (the number of vertices, faces,edges, sides) of two- and threedimensionalgeometric figures such ascircles, polygons, spheres, cones,cylinders, prisms, and pyramids, etc.2(7)(B) Geometry and spatial reasoning.The student uses attributes to identify two- andthree-dimensional geometric figures. Thestudent compares and contrasts two-and threedimensionalgeometric figures or both.The student is expected to use attributesto describe how 2 two-dimensional figuresor 2 three-dimensional geometric figuresare alike or different.Revised TEKS (2012) Supporting Information Notes2(8)(B) Geometry and measurement. Thestudent applies mathematical processstandards to analyze attributes of twodimensionalshapes and three-dimensionalsolids to develop generalizations about theirproperties.The student is expected to classify andsort three-dimensional solids includingspheres, cones, cylinders, rectangularprisms (including cubes as specialrectangular prisms), and triangularprisms, based on attributes using formalgeometric language.2(8)(C) Geometry and measurement.The student applies mathematical processstandards to analyze attributes of twodimensionalshapes and three-dimensionalsolids to develop generalizations about theirproperties.The content of this SE was moved to grade 1:Geometry and measurement1(6)(D)1(6)(E)Specificity regarding 3-d figures has beenadded.Formal geometric language includes terms suchas “vertex,” “edge,” and “face.”The revised SE has added depth withclassification of solids. The comparison ofsimilarities and differences supportsclassification and sorting.Specificity regarding 2-d figures has beenadded.2(7)(C) Geometry and spatial reasoning.The student uses attributes to identify two- andthree-dimensional geometric figures. Thestudent compares and contrasts two-and threedimensionalgeometric figures or both.The student is expected to cut twodimensionalgeometric figures apart andidentify the new geometric figures formed.The student is expected to classify andsort polygons with 12 or fewer sidesaccording to attributes, includingidentifying the number of sides andnumber of vertices.2(8)(E) Geometry and measurement.The student applies mathematical processstandards to analyze attributes of twodimensionalshapes and three-dimensionalsolids to develop generalizations about theirproperties.The student is expected to decomposetwo-dimensional shapes such as cuttingout a square from a rectangle, dividing ashape in half, or partitioning a rectangleinto identical triangles and identify theresulting geometric parts.The revised SE has added depth withclassification of polygons. The comparison ofsimilarities and differences supportsclassification.The word “cut” has been replaced with themore appropriate word “decompose.”An example of how a student might decomposea 2-D shape has been provided.In grade 2, the focus on decomposing shapescomplements the work with fractional parts of awhole.©2013 Texas Education Agency. All Rights Reserved 2013 Introduction to the Revised Mathematics TEKS: Side-by-Side TEKS Comparison 11