CHAPTER 17 Vehicle Systems and Maintenance - Delsea
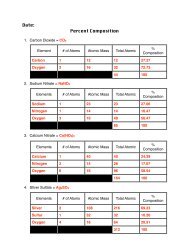
CHAPTER 17 Vehicle Systems and Maintenance - Delsea
CHAPTER 17 Vehicle Systems and Maintenance - Delsea
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Vehicle</strong><strong>Systems</strong> <strong>and</strong><strong>Maintenance</strong>Good drivers make sure that their vehicles are safeto drive. Good drivers underst<strong>and</strong> their vehicles'different systems <strong>and</strong> make sure that those systems areproperly maintained.LESSO(IIOlYEChecking Your <strong>Vehicle</strong> Before <strong>and</strong>After You Start the EngineLEfUmnm,Becoming Familiar with the Engine <strong>and</strong>Power TrainLESSOIIITHREEUnderst<strong>and</strong>ing <strong>and</strong> Maintaining <strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong>ussm FOURSuspension, Steering, Brakes, <strong>and</strong> Tires<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Maintenance</strong>
LESSON ONE~hecking Your Len~c~e:+ ; Before <strong>and</strong> After Youstarting the engine. I Start the Engine11. List several things onyour vehicle that you caninspeabeforeentering11.2. List what to check after1. Explain when to haveyour vehicle serviced.+ Before you enter your vehicle,check under the hood for itemssuch as the coolant level.You've probably heard the old saying that an ounce of prevention isworth a pound of cure. That maxim is especially important for drivers.Inspecting <strong>and</strong> caring for your vehicle before something goes wrongcan save you both money <strong>and</strong> aggravation. More important, maintainingyour vehicle can save your life.Different makes <strong>and</strong> models are alike in some ways, different in others.To be able to check your particular model properly, you should referto the owner's manual. If you don't have the manual for your vehicle, obtaina copy from a dealer or order one from the manufacturer. Manualsare also available in many bookstores. Keep the manual in your glovecompartment so you11 have it h<strong>and</strong>y when you need it.IWhat Can You InspectBefore Entering Your<strong>Vehicle</strong>?You don't need to be a mechanic to inspect your vehicle.You can check many items quickly <strong>and</strong> easily beforedriving. Make these checks at least once a month <strong>and</strong> beforelong drives.In addition to the guidelines below, refer to Chapter7 for other important predriving checks <strong>and</strong> procedures.Fluid LevelsYou can inspect the different fluid levels. Check:the engine oil (when the engine is cool <strong>and</strong> not running).the level of coolant in the radiator overflow tank orradiator.the transmission fluid <strong>and</strong> the fluid level in the powersteering<strong>and</strong> master-brake-cylinder reservoirs.the battery fluid (if necessary for your battery).the windshield-washer fluid.UNIT 4Plonning for Your Future
Belts, Hoses, <strong>and</strong> WiresBefore you enter your vehicle, inspect belts, hoses,<strong>and</strong> wires.Check the fan belt <strong>and</strong> the belts that run the powersteering<strong>and</strong> air-conditioning units. Many new vehicleshave only one belt that drives these units. Beltsmay need tightening or adjustment. Replace frayedor cracked belts as soon as possible.Check all hoses <strong>and</strong> hose connections for leaks.Look for loose, broken, or disconnected wires. Alsocheck for cracked insulation on wires.Make sure the battery cables are tightly connected<strong>and</strong> the terminals are free of corrosion.What Can You Check AfterStarting the Engine?Once your engine is running, you should make several routinechecks to ensure that your vehicle is operating properly <strong>and</strong> safely.+ Learning how to do your ownmaintenance can save you thecost <strong>and</strong> inconvenience of repairs.Gauges <strong>and</strong> Warning LightsYou have already read about the various gauges <strong>and</strong> warning lightsthat provide information about your vehicle. Check these gauges <strong>and</strong>lights regularly as you drive. They will warn you of a wide range of problems,such as low oil pressure or fuel level, engine overheating, <strong>and</strong> alternatormalfunction.BrakesYour vehicle's brake-warninglight will make you aware of somebutnot all-problems with yourbrake system.For this reason, always test yourbrakes as soon as you begin driving.When you step on the brake pedal,you should feel firm resistance,<strong>and</strong> your vehicle should come to asmooth, straight stop. The pedalshould stay well above the floor.Specific warning signs of abrake system malfunction are discussedlater in this chapter.rnHaving Your <strong>Vehicle</strong> Servicedor RepairedTo find a reliable mechanic or garage, ask friends <strong>and</strong> relativesfor their recommendations. You can also call yourlocal American Automobile Association.Ask the mechanic for a cost estimate of the work to be done.Find out for how long the mechanic will guarantee anywork done. Save your bill or receipt.Know what you're paying for. If there's something youdon't underst<strong>and</strong>, ask for an explanation.If the mechanic replaces a part, ask to see the old part.Warranties may cover many repairs. Know what your warrantydoes <strong>and</strong> does not cover.<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> und Muintenonce
ETY TAlways check radiatorcoolant level by lookingat the radiator overflowtank. If additional coolantis needed, add it to theoverflow tank, not to theradiator. Rarely should itbe necessary to removethe radiator cap. If you dohave to remove the radiatorcap, do so only whenthe radiator is cool. If youremove the cap when theradiator is hot, boilingwater could spurt out<strong>and</strong> scald you.-jD YOU ,HornPeriodically check to make sure your horn works. If you're driving anunfamiliar vehicle, always locate <strong>and</strong> try the horn before you begin driving.Horn position on the steering wheel varies from vehicle to vehicle.Lights <strong>and</strong> Turn Signals<strong>Vehicle</strong> safety checks find that nearly one out of four vehicles has atleast one lightbulb or headlight burned out. Check all exterior lights<strong>and</strong> turn signals before you drive. Periodically have a friend or familymember st<strong>and</strong> outside the vehicle <strong>and</strong> tell you if your brake lights workwhen you press the brake pedal.How Do You Know When Your<strong>Vehicle</strong> Should Be Serviced?Your owner's manual contains guidelines for servicing <strong>and</strong> maintainingyour vehicle. The guidelines vary, depending on the kind <strong>and</strong>amount of driving you do <strong>and</strong> on the manufacturer's recommendations.Some systems <strong>and</strong> parts require more frequent attention than others.Recommended intervals for servicing may be based either on time or onmiles driven. For example, your manual might recommend checlung tirepressure once a month, changing the oilevery few months, <strong>and</strong> having the suspen-Ision checked every 20,000 miles.Keeping complete records will help youmaintain a schedule of care. An easy wayto keep track of repairs <strong>and</strong> maintenance isto keep a small notebook in your vehicle.Each time you or a mechanic services orrepairs the vehicle, jot down exactly whatwas done <strong>and</strong> the date. Save your receiptsin an envelope in the glove compartment.Lesson 7 Review1. What kinds of problems might youspot as you check your vehicle beforeentering it?2. What can you check after you'start1the engine?A friend has agreed to let you use her car while she's onvacation. What checks will vou make before getting into her car? 3. What can help you determine when toWhat checks will you makeafter starting theengiie?Ihave your vehicle serviced?UNIT 4Planning for Your Future
Decoming Familiar withthe ~ngine <strong>and</strong> Power TrainMany parts work together to produce a vehicle's power <strong>and</strong> motion.By keeping these parts operating smoothly, you help your vehicle runsafely <strong>and</strong> fuel efficiently.How Does the Engine Work?Your vehicle's engine is known as an internal combustion engine.It is called that because the power it produces comes from burning amixture of fuel <strong>and</strong> air inside, rather than outside, the engine.When you start your vehicle's engine, you're setting off a chain ofevents.1. Turning the key in the ignition causes power to be drawn from thebattery to a small electric starter motor, commonly called the starter.2. The starter turns the flywheel of the engine. When the flywheelturns, it turns the crankshaft.3. A piston in each cylinder of the vehicle is attached to the crankshaft.Most vehicles have 4, 6, or 8 cylinders. The more cylinders ina vehicle, the more power the engine has, but also the more gasolinethe engine uses.OBJECTIVES1. Explain how a typicalvehicle engine works.2. Tell what the power trainis <strong>and</strong> what it does.3. Describe four guidelimfor maintaining the en- 'gine <strong>and</strong> power train.KEY TERMSinternal combustion engine jcylinderspark plugpistoncrankshaftpower traindrive wheel<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> <strong>and</strong><strong>Maintenance</strong>
4. In each cylinder, a spark plug produces a spark. This spark causesthe fuel-air mixture inside the cylinder to explode. The explosionpushes down the piston, which turns the crankshaft.5. The continuous up-<strong>and</strong>-down motion of 6epistons keeps thecrankshaft turning. Power sent from the crankshaft is transmittedto the wheels, making the vehicle move.+ Power is transmitted differentlyto vehicles with rear-wheel drive,front-wheel drive, <strong>and</strong> four-wheeldrive.Transmission\A-F ' Front axleI\ Front axleWhat Is the Power Train <strong>and</strong>What Does It Do?Several parts of your vehicle work together to transmit power fromthe engine to the wheels. These parts make up the power train.In most vehicles, the power train sends power from the engine toonly two of the four wheels. The wheels that receive the power arecalled the drive wheels. If the two front wheels are the drive wheels,the vehicle has front-wheel drive. If the two rear wheels receive thepower, the vehicle has rear-wheel drive. A vehicle has four-wheel driveif all four wheels receivepower.The transmission is partof the power train. Gears inthe transmission allow it totransfer power to the drivewheels. With a manual transmission,the driver uses theclutch pedal <strong>and</strong> the gearshiftlever to shift gears <strong>and</strong> changethe amount of power thatgoes to the drive wheels. With-4.an automatic transmission,the clutch works automatically,so the gears are shiftedautomatically too.In a vehicle with rearwheeldrive, the transmissionis connected by a driveshafttonIto the differential, rear axle,riveshaft Rear axle <strong>and</strong> rear wheels. The differentialallows the rear wheelsear arlvesnato turn at different speedswhen the vehicle turns.\- ,rnTransfer caseUNIT 4Planning for Your Future
In a vehicle with front-wheel drive, engine power is sent to a combinationtransmission <strong>and</strong> differential <strong>and</strong> then directly to the front wheels.How Can You Maintain theEngine <strong>and</strong> Power Train?<strong>Vehicle</strong>s that are well maintained perform better, are more fuel efficient,<strong>and</strong> last longer than vehicles that are neglected.Here are some basic guidelines for keeping your vehicle's engine<strong>and</strong> power train in top condition. Your owner's manual will give youadditional specific recommendations.Check <strong>and</strong> Change the Oil RegularlyCheck your vehicle's oil every second time you fill the fuel tank.Change the oil according to the recommendations in your owner's manual.Most manufacturers give two schedules for oil changes: one for normaluse <strong>and</strong> one for severe use. Severe use is often described as plenty ofshort trips, stop-<strong>and</strong>-go driving, or regular travel in dusty conditions.Failure to follow the recommended schedule can void your warranty.Have Regular Tune-UpsSome older vehicles require regular tune-ups, but most new ones donot have any need for such attention beyond regular checks <strong>and</strong> replacementof fluids <strong>and</strong> filters. Emission regulations require a vehicle's com-puter to make the necessary "tune-ups" as the vehicle ages to ensure themost complete combustion of fuel <strong>and</strong> to prevent pouring unburned hydrocarbonsinto the atmosphere. Consult yourvehicle manual to determine your recommendedtune-up intervals. Do a visual check ofbelts, hoses, <strong>and</strong> wires under the hood for anyobvious signs of wear or problems as you checkthe oil--every second time you fill the vehicle's,fuel tank.IAT3 YOULesson 4 Review1. What is an internal combustion engine,<strong>and</strong> how does it work?2. What parts make up the power train, <strong>and</strong>how do they supply power to the wheels?1is running beautifolly3. What are some of the tasks a mechanic might You'd like to keep it that wav. Describe the actions you willdo when giving your vehicle a tune-up? take to maintainyour car in top shape.I<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> <strong>and</strong> Maintenme
&g&sit;-bekOBJECTIVES<strong>and</strong> how to maintain3. Describe how the lucating <strong>and</strong> cooling stems work <strong>and</strong> howmaintain them.KEY TERMSToday it's easy to take motor vehicles for granted. But they are stillamong the most complicated machines ever invented. Every time youget behind the wheel, you take control of a network of many differentsystems that work together to make your vehicle work the way it does.yrrnoL-.-Fuel tank/How Do the Fuel <strong>and</strong>Exhaust <strong>Systems</strong> Work?The Fuel <strong>and</strong> exhaust systems in a vehicle must operate properly tomaximize engine efficiency <strong>and</strong> minimize pollution.The Fuel SystemYour vehicle's fuel system includes the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel+ ~h~ fuel system both stores fuel pump, fuel filter, electronic fuel-injection (EFI) system, <strong>and</strong> air fi1-<strong>and</strong> delivers the correct air-fuel ter. Fuel is stored in the tank, where in some cases the fuel pump remixtureto the engine.sides. The pump forces Fuelthrough the fuel lines <strong>and</strong>Ifilter. The air-Fuel mixtureforms a vapor that is injectedat a specific time intoeach cylinder, where it is ignitedby a spark plug.Most vehicles now haveelectronic multipoint fuel-injectionsystems. Multipointmeans that there is a separatenozzle or injector fed bya separate fuel line for eachcylinder.322 UNIT 4 hnning for Your Future
The Exhaust SystemThe exhaust system serves twomain purposes. First, it carries offcarbon monoxide <strong>and</strong> other harmfulgas by-products of combustion.Second, it muffles engine noise.The pipes that make up the exhaustmanifold collect unburnedgases from the engine <strong>and</strong> carrythem to the muffler. The muffler absorbsnoise created from the explosionsin the cylinders. Exhaust gasesexit through the tailpipe. Pollutioncontroldevices, such as the catalyticconverter, reduce the amount ofharmful gases coming from thetailpipe.- .. . MufflerPe /How Can You Maintainthe Fuel <strong>and</strong> Exhaust <strong>Systems</strong>?To maintain your vehicle's fuel system, replace the air <strong>and</strong> fuel filtersas needed.Most vehlcles today operate on lead-free gasoline. Using leaded gaso-line will destroy the catalytic converter.How much maintenance or re~air the exhaust svstem reauires varieswith the conditions under which you drive. Short trips, for example, areharder on a vehicle than long highway drives. Be on the lookout for loose,rusting, or damaged parts. Alwayshave your exhaust system thoroughlyinspected as part of a tune-up.How Do theElectrical <strong>and</strong>Light <strong>Systems</strong>Work?The electrical <strong>and</strong> light systemshelp keep your vehicle runningsmoothly <strong>and</strong> safely'.Ignition switchStarterExhaust pipeExha';The exhaust system carries offpoisonous gases <strong>and</strong> muffles enginenoise.~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~sends ele~rical current to thespark plugs.<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Maintenance</strong>
+ In order to keep your batteryin top working condition, keepterminals free of corrosion.If the "check engine"light comes on, makesure the gas cap or lids fully tightened tothe point of at leastme click or notch. The:mission control equipnentis so sensitive:hat it can detect if thecap is not correctlytightened <strong>and</strong> willcause the warning'ight to come on. Younay or may not need:o computer reset it.IIThe Electrical SystemThe heart of your vehicle's electrical systemis the battery. The battery provides thepower to start the engine. It also enablesyou to operate, for a short time, such equipmentas your radio <strong>and</strong> lights when the engineis not running.After you turn the ignition key <strong>and</strong> startthe vehicle, the battery supplies the electricityto fire the spark plugs, operate thestereo, air-conditioning, <strong>and</strong> other systems.The alternator, or generator, provides aconstant charge for the battery. The enginecontrol module (ECM) controls the electrical<strong>and</strong> other engine systems.To prevent electrical overloads <strong>and</strong>damage to delicate electronic components,the electrical system is equipped with fuses,usually located in a clearly labeled pod beneath the instrument panel orunder the hood.The Light SystemYour vehicle's light system enables you to see <strong>and</strong> be seen.Exterior lights include headlights, taillights, side-marker lights,brake lights, signal lights, parking lights, <strong>and</strong> emergency flashers.Interior lights include the dome light on the inside roof of the vehicle<strong>and</strong> the various dashboard lights that provide you with informationabout the vehicle or warn you of malfunctions.How Can You Maintain theElectrical <strong>and</strong> Light <strong>Systems</strong>?The first step in maintaining the electrical <strong>and</strong> light systems is tokeep your battery in top working condition. Keep the battery terminalsfree of corrosion <strong>and</strong> the battery cables firmly connected. Most currentbatteries are maintenance-free, but if you have an older one, check thefluid level at least once a month, <strong>and</strong> add water when needed.The electrical system is constantly monitored by the engine controlmodule or computer. If it detects a problem, the "check engine" lighton the instrument panel may come on.Keep headlights clean <strong>and</strong> properly aligned. Even a thin layer ofdirt can cut light output by as much as 90 percent. Misaligned lightsUNIT 4Plonning for Your Future
can reduce your ability to see the roadway <strong>and</strong> can momentarily blindoncoming drivers.Check exterior lights at least once a week, <strong>and</strong> promptly replace anyburned-out bulbs.How Do the Lubricating <strong>and</strong>Cooling <strong>Systems</strong> Work?As the parts of your vehicle's engine move rapidly <strong>and</strong> rub againsteach other, they produce friction <strong>and</strong> heat. At the same time, the fuelairexplosions in the cylinders create more heat. Small wonder thenthat the engine temperature may exceed 4,000°F.Too much heat can destroy your vehicle's engine. The lubricating<strong>and</strong> cooling systems are designed to keep that from happening.Te-LiibWicatlng System------------Oil is the key element in your vehicle's lubricating system. Coatingengine parts with oil reduces friction, heat, <strong>and</strong> wear. Oil also helpsclean internal engine surfaces <strong>and</strong> prevent rust <strong>and</strong> corrosion.An oil pump moves oil from the oil pan, where it is stored, to allmoving engine parts. The oil filter cleans the oil as it circulates.In addition to oil, grease is used to lubricate parts of the vehicle,such as the steering system. Like oil, grease reduces friction <strong>and</strong> helpsparts move smoothly.ule or computer in a modernvehicle automaticallyadjusts the engine's systemsfor whatever gradeof fuel you use. Some engineswill perform betterwith higher, more expensivegrades of fuel, butmost will not. See your Iowner's manual for the 1----------manufacturer's recommendations.1tach year, electrical;ystem failures disablemore vehicles than thecombined next twocauses of vehicle~rea kdowns.I-Oil filter ' \7-Oil pumpOil pan+ The lubricating system reducesheat by coating the parts of theengine with oil.<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> <strong>and</strong><strong>Maintenance</strong>
'The so-caNed water-c001ed engineactually uses a coolant in itscoolinq system.Hoses 7The Cooling SystemThe purpose of the cooling systemis to keep your vehicle's enginefrom overheating. To do this, thecooling system circulates coolantamixture of water <strong>and</strong> antifreezethroughthe engine by means of anetwork of pipes, channels, <strong>and</strong> connectinghoses.Antifreeze has a lower freezingpoint <strong>and</strong> higher boiling point thanpure water. Without it, the liquid inthe cooling system would freeze invery cold weather <strong>and</strong> could boilover in hot weather, especially in trafficjams <strong>and</strong> on long trips. Frozen orboiling coolant does not circulate,<strong>and</strong> this can cause the engine to overheat.Your vehicle's coolant is stored inthe radiator <strong>and</strong> in the radiator over-flow tank. A water pump pumps thecoolant through the radiator <strong>and</strong> the circulating network. A fan forcesthe air through the radiator to cool the liquid. A thermostat in the systemworks td control the flow of the coolant in order to maintain thebest operating temperature.Carbon monoxide is an odorless, colorless,<strong>and</strong> tasteless gas. Small amounts of carbonmonoxide can make you sleepy or nauseated orgive you a headache by interfering with the abilityof your red blood cells to carry oxygen. Largeamounts of carbon monoxide can kill you.Avoid driving a vehicle that has an exhaustleak or a broken tailpipe. Such defects allow carbonmonoxide <strong>and</strong> other harmful exhaust gasesto be trapped beneath the vehicle, even when it isTo guard against carbon monoxide poisoning,also avoid:running a vehicle's engine in a closed garage.sitting in a parked vehicle with the windowsclosed, the engine running, <strong>and</strong> the heater on.driving with the trunk lid up.driving with the rear window of a stationwagon open.stopping so close to the vehicle ahead that yourheater or air conditioner draws in exhaustgases from that vehicle's tailpipe.UNIT 4Planning for Your Future
How Can You Maintainthe Lubricating<strong>and</strong> Cooling <strong>Systems</strong>?Checking <strong>and</strong> changing the oil <strong>and</strong> oil filter regularlyis the key to maintaining your vehicle's lubricatingsystem. Low oil pressure allows the engine tobecome too hot, which may cause excessive wear ofmoving parts.Keep in mind that the oil-pressure gauge or warninglight does not indicate how much oil is in the engine,but it will signal a drop in oil pressure. To checkthe actual level of oil, use the oil dipstick. Never driveyour vehicle with insufficient oil: you could destroythe engine. The engine oil level can only be checkedafter the engine has been turned off for some periodof time, preferably an hour or more. This is necessaryto give the oil time to drain back into the oil pan Fromthroughout the engine. Checking it before that hashappened will give you a false low reading.Driving with an overheated engine can also damage your vehicle. Ifthe temperature gauge or warning light indicates overheating, stop drivingas soon as possible. Let the engine cool before you look for the causeof the problem.To maintain the cooling system,use the proper coolant, <strong>and</strong> check thefluid level whenever the vehicle is serviced.Also check the fan belt <strong>and</strong> connectinghoses. Have the coolingsystem completely drained, flushed,<strong>and</strong> refilled every two years.IC+ You can learn to use a dipstick~'?$~~~h~~~~.notyour ve-WOULD YOU LLesson 5 Review1. Why is it important to keep theFuel <strong>and</strong> exhaust systems of yourvehicle in good condition?2. Explain how your vehicle useselectricity, <strong>and</strong> name the source ofelectrical power in your vehicle.3. How do the lubricating <strong>and</strong> coolingsystems work?I 1You've been stuck in bumper-to-bumper traffic for nearly an hour on ahot summer day. The temperature warning light has just come on. Howwill you h<strong>and</strong>le this situation? What safety precautions will you take?<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Maintenance</strong>
LESSON FOUROBJECTIVESI1. Describe four vehicle systemsfor comfort that are <strong>and</strong> important safety. suspension, S!eering,Brakes, <strong>and</strong> Tires2. Describe warning signs ofpossible problems withthe suspension, steering,or tires.KEY TERMSstrutshock absorberhydraulic pressuredisc brakedrum braketreadYour comfort <strong>and</strong> safety in a vehicle depend not only on how wellyou drive but also on how your vehicle h<strong>and</strong>les. To protect yourself <strong>and</strong>others, make sure your vehicle's suspension, steering, <strong>and</strong> brake systernsas well as all four tires are in good operating condition.What <strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong>Are Important for Comfort<strong>and</strong> safety?The suspension, steering, <strong>and</strong> brake systems, <strong>and</strong> tires, work togetherto give you control over your vehicle <strong>and</strong> to provide a comfortable ride.The Suspension SystemThe suspension system supports your vehicle's weight, cushions theride, <strong>and</strong> helps keep the vehicle stable when you drive over bumps oruneven roadway surfaces.Most vehicles today use suspensions-especially in the front of the+ The suspension system cushions vehicle-where the spring <strong>and</strong> shock absorber are contained in onethe vehicle's frame against bumps unit called a strut.in the road.The springs soften the impact ofbumps in the roadway If your vehiclehad only springs, however, it wouldcontinue bouncing after hitting abump. This bouncing would reducethe contact between the tires <strong>and</strong> theroad <strong>and</strong> make it harder for you tocontrol the vehicle.The shock absorbers-or shocks,as they're commonly called-work tocontrol bouncing. By absorbing theshocks of driving, they make the ridesmoother <strong>and</strong> help you maintainsteering <strong>and</strong> braking control.UNIT 4Planning for Your Future
The Steering SystemThe steering system enables you to turn the front wheels. The steeringwheel is connected to the front wheels by a steering shaft <strong>and</strong> movablerods.The front wheels are designed to remain in an upright position <strong>and</strong>move up <strong>and</strong> down over bumps, even when they are turned.The Brake SystemBrakes slow or stop a vehicle by applying hydraulic pressure-pressurecreated by the force of a liquid-against the four wheels. Steppingon the brake pedal forces brake fluid from the master brake cylinderthrough the brake-fluid lines to the wheel cylinders. There are two typesof brakes: disc brakes <strong>and</strong> drum brakes.Disc brakes In a disc brake, pressure squeezes the brake pads againsta flat metal wheel disc, producing the fnction needed to stop the wheelfrom turning.All new vehlcles now have disc brakes on the front wheels. Many havethem on the rear wheels as well. All new vehicles now also have powerbrakes, which require less pressure on the brake pedal than older nonpowersystems. Power brakes do not, however, shorten a vehicle's stoppingdistance.Drum brakes In a drum brake, the fluid pressure causes the brakeshoes to push against the brake lining. The lining then presses againstthe round hollow metal drum inside the wheel. Friction slows <strong>and</strong> stopsthe wheel's turning motion.You can check for sufficienttread depth by inserting aquarter in the tread. Itshould at least come to thetop of Washington's head.If there is less tread thanthis, the tire will not func-tion safely in even a lightrain.+ A hydraulic brake system givesall four wheels stopping power.FDrum brakesA<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> und <strong>Maintenance</strong>
4 It is important for fuel efficiency<strong>and</strong>traction that a vehicle'stires be properly inflated.---------------------- ofTo minimize the risk of brake failure,brake systems are designed sothat front <strong>and</strong> rear brakes are controlledindependently. If one pair ofbrakes fails, the other air will stillwork to stop the vehicle.Antilock brakes Many newer vehicleshave an antilock brake system(ABS), which is designed to keep thewheels from locking when the driverpresses too hard on the brake pedalin an emergency. Since the wheelsdo not lock, the driver can continueto steer the vehicle. Antilock brakesdo not shorten the stopping distancea vehicle.Parking brake A parking brake is a mechanically operated brake thatis separate from the hydraulic brake system. Attached by cable to therear wheels, it is used to prevent a parked vehicle from rolling.4 The vehicle manufacturer oftenplaces maximum tire air pressureon the inside of the door.The TiresA driver's control of a vehicle depends largely on the condition ofthe tires. Nevertheless, more than 40 percent of nearly 250,000 vehiclesinspected between 1982 <strong>and</strong> 1993 had defectivetires.Tire inflation Tires must be inflated properlyto provide maximum traction <strong>and</strong> control. Toolittle tire pressure (underinflation) or too muchtire pressure (overinflation) reduces traction,makes a vehicle harder to h<strong>and</strong>le, <strong>and</strong> lowersfuel efficiency.Most vehicles require different pressures forthe front <strong>and</strong> rear tires. To find the recommendedmaximum air pressures for your vehi-_cle! check your owner's manual or look for a--7------ypsticker that may be affixed to a doorpost or insidethe fuel filler door. Usually two tire pressuresare listed-one for normal <strong>and</strong> a highernumber for long trips or when carrying heavyloads. The lower number may result in a softerride but will likely mean lower tread life. Thehigher number will improve both h<strong>and</strong>ling <strong>and</strong>wear at the cost of some ride quality.UNIT 4Phnning for Your Future
Tire tread The grooved outer surface of a tire is its tread. On wet orslippery surfaces, the amount of tread on your tires determines howmuch traction your vehicle will have. Compared with tires that havegood tread, overly worn tires have double the risk of skidding <strong>and</strong> arealso more likely to go flat or blow out.Tires should be replaced when the depth of the tread is %6 inch. Tohelp you judge tread depth, all tires have tread wear bars that run acrossthe tire.Tire rotation Front tires generally wear faster than rear tires. To equalizetire wear, have your vehicle's tires rotated about every 5,000 to 6,000miles. Rotating tires means switching their position from front to rear<strong>and</strong> sometimes from one side to the other. Check your owner's manualfor the recommended tire-rotation pattern.When tires are rotated, they often need to be balanced. This helps ensurethat weight is evenly distributed as the wheel turns. Balanced tiresprovide better steering control, a smoother ride, <strong>and</strong> longer tire life.What Are Some Warning Signsof <strong>Vehicle</strong> Problems?Sometimes vehicle problems appear unexpectedly. More often,though, advance warnings signal that a part or system needs attention.Suspension <strong>and</strong> Steering ProblemsMost problems affecting the suspension <strong>and</strong> steeringsystem develop gradually as a result of wear. Watchfor the following warning signs.There is too much play (free movement) in the steeringwheel. With rack <strong>and</strong> pinion power steering, thereshould be virtually no play in the wheel. In a manualsystem, there should be no more than 2 inches of play.The steering wheel vibrates or is difficult to turn.The front end of the vehicle wobbles or shimmies.The vehicle bumps as you turn the wheel while drivingon a smooth road.The vehicle pulls to one side as you drive.The vehicle bounces too much after hitting a bump.Tread wear on the front tires is uneven.Have a mechanic check your vehicle if any of thesewarning signs appear. The front end of your vehicle mayneed aligning, the tires may need to be balanced, orsome other problem may need correction.IHave a mechani~checkthe vehicleif any warning signs of suspensionor brake problems appear.I -1CZ -1<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> und Muintenonce
Richard Russell-~.S#istyaf-EngbwncnafonpnyaMtitkd~artarDrhrhrgkrstructg<strong>and</strong>tcmsultnt~IUATires are arguably the most important safety feature on your vehicle.The four small patches of rubber in contact with the road determine howyou stop, steer. <strong>and</strong> go. Don7 think of buying new tires as a "grudgebuy." Tires are the one area where a purchase decision can directly affectthe safety of your vehicle. This is not an area to try to save money.Generally speaking, the more you spend on a tire, the better the grip itwill provide <strong>and</strong> the safer you will be.I WHATWOULD YOUDO?IBrake ProblemsSee Chapter 14 for a description of brake failure. Neglecting a problemwith the brake system can have fatal consequences. Check with amechanic if any warning signs appear.Tire ProblemsInspecting your tires regularly before you dnve will help avoid problemson the road. Watch for the following warning signs of tire troubles:tread wear bars appear, indicatingless than K6 inch treadareas of little or no tread-"bald spotsuneven wearbulgesembedded nails, glass, or metalfrequent pressure loss in oneparticular tire, suggesting a slowleakLesson 4 Review1. How are the steering, suspension,brakes, <strong>and</strong> tires importantto your safety?2. What are some warning signsthat indicate tire problems?)u just test-drove this car. As you stepped on the brake, the car pulledI the right What could cause this problem? Would you buy the car?UNIT 4Planning for Your Future
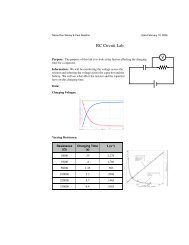
. -.BUILDING SKILLS: SCIENCGraphing Braking DistancesAher you apply the brakes, the distance ittakes to come to a stop depends in part on thespeed at which your vehicle is moving.The formula for figuring out braking distanceisD = S x XoS t 2.4where S = speed <strong>and</strong> D = distance in feet.Here is how you would figure braking distanceat 35 mph.D = 35 x (%o x 35) t 2.4D = 35 X 3.5 + 2.4D = 51.04Thus, braking distance at 35 rnph is 51 -04 feet,or a little more than <strong>17</strong> yards.Make a graph to show how braking distancechanges in relation to speed.Try It Yourself1. First, use the formula to figure the stoppingdistance for these speeds:20 mph 30 mph 40 mph 50 mph 60 mph2- On a sheet of graph PaPec write the speedsalong the bottom of the graph at regular intervals,as shown below.3. On the left side of the graph, write distancesin regular intervals, as shown below.4. For each distance you figure, put a dot atthe appropriate place on your graph.5. Finally, draw a line from the first dot to thesecond, from the second to the third, <strong>and</strong> soon, beginning with the dot at the shortestbraking distance.What conclusion can you draw from yourgraph?Speed (rnph)
Write the letter of the answer that best completeseach sentence.1. A driver interested in fuel efficiency woulda. buy a vehicle with 4 cylinders.b. buy a vehicle with 8 cylinders.c. buy a vehicle with 16 cylinders.2. When buying a vehicle, most peoplea. pay with a credit card.b. pay cash.c. take out a loan.3. Before buying a vehicle, considera. how clean it is.b. how many passengers you will have.c. whether it is a convertible.4. A driving record <strong>and</strong> marital status can affecta. the cost of your insurance.b. the purchase price of a vehicle.c. your concentration at the wheel.5. Expensive vehiclesa. cost more to insure than inexpensivevehicles.b. cost less to insure than inexpensivevehicles.c. use less fuel than inexpensive vehicles.6. The death rate in the smallest vehicles isa. lower than that in the largest vehicles.b. the same as that in the largest vehicles.c. twice as high as that in the largest vehicles.7. The Blue Book is a guide toa. vehicle dealerships in the United States.b. the average price paid to dealers for variousused vehicles.c. different types of vehicle engines.8. Liability insurancea. protects you against claims if you are atfault in a collision.b. is available to drivers over 21 years of age.c. protects you if you are accused of lying.9. The purchase price of a vehicle isa. one of the many expenses associatedwith owning a vehicle.b. the only expense in owning a vehicle.c. generally lower than it was ten years ago.10. Bodily injury insurance coversa. any damages to the body of your vehicle.b. the death or injury of other people whileyou are driving.c. only the driver of a vehicle.Write the word or phrase that best completeseach sentence.fuel consumptionwarrantycomprehensive insurance financinguninsured motorist insurance deductible11. A(n) - is a written guarantee that theseller will repair your vehicle.12. If your vehicle is damaged by anything otherthan a collision, - will pay the bills.13. There can be large differences in -among different vehicle models.14. <strong>Vehicle</strong> dealers can offer you a(n) -arrangement when you buy a new vehicle.15. If you are involved in a collision with a hit<strong>and</strong>-rundriver, - can protect you.DRIVER'S LOGI, ,. .his chapter, you have learned someconsiderations to keep in mind when you areready to buy a vehicle. Write a paragraph inresponse to each of the following questions.Describe the guideposts you use to measurematurity.Which do you need to work on?What will you look for when you buy avehicle? What do you think your choicewill say about your maturity? Why?<strong>CHAPTER</strong> 1 6 Buying a Vehide 313
Write the letter of the answer that best cornpleteseach sentence.1. A catalytic converter is part of a vehicle'sa. transmission.b. exhaust system.c. fuel system.2. You should check your engine oila. while your engine is running.b. before starting your engine.c. every 12,000 miles.3. Springs <strong>and</strong> shock absorbers are parts of avehicle'sa. transmission.b. front-end alignment.c. suspension system.4. Most vehicles' engines area. turbine engines.b. external combustion engines.c. internal combustion engines.5. When you step on your brake pedal, youshould feela. firm resistance.b. no resistance.c. the floor.6. The temperature of a vehicle's engine mayexceeda. 212°F.b. 500°F.c. 4,000°F.7. You should rotate your vehicle's tires toa. equalize tire wear.b. increase fuel efficiency.c. improve suspension.8. Most vehicles today operate ona. lead-free gasoline.b. leaded gasoline.c. diesel fuel.9. Many vehicles are equipped witha. a power clutch.b. drum brakes on the front wheels <strong>and</strong>disc brakes on the back wheels.c. disc brakes on the front wheels <strong>and</strong>drum brakes on the back wheels.10. Your vehicle's alternatora. controls suspension.b. mixes oxygen with gasoline.c. supplies electricity to run the engine.Write the word or phrase that best completeseach sentence.pistons hydraulic pressure power trainmuffler electrical system owner's manual11. The parts of a vehicle that transmit the en-'gine's power to the wheels make up the-.12. The heart of a vehicle's is called thebattery.13. Brakes slow or stop a vehicle by applying- against the four wheels.14. A(n) - contains specific guidelines forservicing <strong>and</strong> maintaining a vehicle.15. The pipes that make up the exhaust manifoldcollect unburned gases from the engine<strong>and</strong> carry them to the -.In this chapter, you have learned how thesystems that operate a vehicle function <strong>and</strong>what the maintenance requirements of thesesystems are. Based on your observations, domost drivers pay attention to these maintenancerequirements? Write a paragraph aboutwhat you would tell those who do not.<strong>CHAPTER</strong> <strong>17</strong><strong>Vehicle</strong> Svstems <strong>and</strong> <strong>Maintenance</strong>