chapter
chapter
chapter
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Sea, and the Sandwich Islands in the South Atlantic. The<br />
Lesser Antilles are a product of the subduction of the Atlantic<br />
beneath the Caribbean plate. Located within this<br />
arc is the island of Martinique where Mount Pelé erupted<br />
in 1902, destroying the town of St. Pierre and killing<br />
an estimated 28,000 people, and the island of Montserrat,<br />
where volcanic activity has occurred very recently.<br />
Relatively young island arcs are fairly simple structures<br />
that are underlain by crust that is generally less<br />
than 20 kilometers (12 miles) thick. Examples include<br />
the arcs of Tonga, the Aleutians, and the Lesser Antilles.<br />
By contrast, older island arcs are more complex and are<br />
underlain by crust that ranges in thickness from 20 to 35<br />
kilometers. Examples include the Japanese and Indonesian<br />
arcs, which are built upon material generated<br />
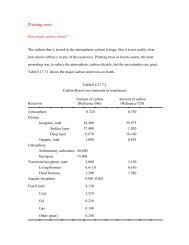
A.<br />
B.<br />
10 million<br />
years ago<br />
India<br />
today<br />
38 million<br />
years ago<br />
55 million<br />
years ago<br />
India Continental<br />
shelf<br />
deposits<br />
71 million<br />
years ago<br />
Continental<br />
crust<br />
C.<br />
Asthenosphere<br />
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics 209<br />
by earlier episodes of subduction. In a few places, volcanic<br />
island arcs are gradually transformed into an<br />
Andean-type volcanic chain. For example, the western<br />
section of the Aleutian arc consists of numerous volcanic<br />
islands built on oceanic crust whereas the volcanoes<br />
at the eastern end of the chain are part of the<br />
Alaskan Peninsula—a piece of continental crust.<br />
Continental–Continental<br />
Convergence<br />
As you saw earlier, when an oceanic plate is subducted<br />
beneath continental lithosphere, an Andean-type volcanic<br />
arc develops along the margin of the continent.<br />
However, if the subducting plate also contains conti-<br />
Ocean basin<br />
Developing<br />
accretionary<br />
wedge<br />
Subducting oceanic lithosphere<br />
India<br />
(Ganges Plain)<br />
Asthenosphere<br />
Himalayas<br />
Continental volcanic arc<br />
Tibet<br />
Suture<br />
Melting<br />
Tibetan<br />
Plateau<br />
Figure 7.14 The ongoing collision of India and Asia, starting about 45 million years ago, produced the majestic Himalayas. A. Converging<br />
plates generated a subduction zone, while partial melting triggered by the subducting oceanic slab produced a continental volcanic arc.<br />
Sediments scraped from the subducting plate were added to the accretionary wedge. B. Position of India in relation to Eurasia at various<br />
times. (Modified after Peter Molnar) C. Eventually the two landmasses collided, deforming and elevating the accetionary wedge and<br />
continental shelf deposits. In addition, slices of the Indian crust were thrust up onto the Indian plate.